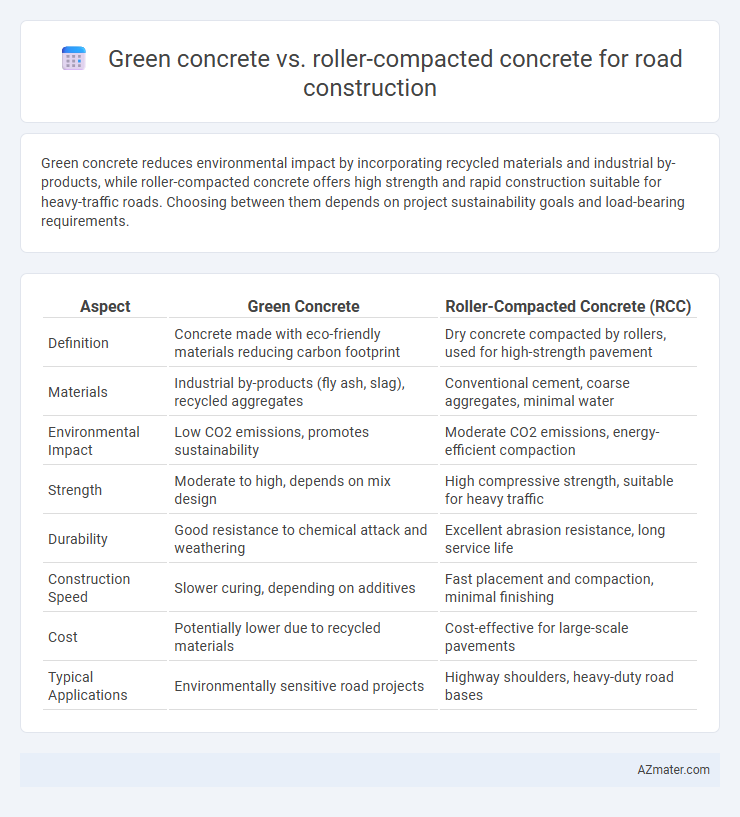
Green concrete reduces environmental impact by incorporating recycled materials and industrial by-products, while roller-compacted concrete offers high strength and rapid construction suitable for heavy-traffic roads. Choosing between them depends on project sustainability goals and load-bearing requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Green Concrete | Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete made with eco-friendly materials reducing carbon footprint | Dry concrete compacted by rollers, used for high-strength pavement |
| Materials | Industrial by-products (fly ash, slag), recycled aggregates | Conventional cement, coarse aggregates, minimal water |
| Environmental Impact | Low CO2 emissions, promotes sustainability | Moderate CO2 emissions, energy-efficient compaction |
| Strength | Moderate to high, depends on mix design | High compressive strength, suitable for heavy traffic |
| Durability | Good resistance to chemical attack and weathering | Excellent abrasion resistance, long service life |
| Construction Speed | Slower curing, depending on additives | Fast placement and compaction, minimal finishing |
| Cost | Potentially lower due to recycled materials | Cost-effective for large-scale pavements |
| Typical Applications | Environmentally sensitive road projects | Highway shoulders, heavy-duty road bases |
Introduction to Green Concrete and Roller-Compacted Concrete
Green concrete utilizes industrial byproducts such as fly ash or slag to reduce carbon emissions while maintaining structural integrity in road construction. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) is a zero-slump concrete mixture compacted with rollers, offering rapid construction and high durability for pavements. Both materials aim to enhance sustainability and performance, with green concrete emphasizing eco-friendly composition and RCC focusing on efficient placement and load-bearing capacity.
Composition and Key Materials Used
Green concrete incorporates industrial by-products such as fly ash, slag cement, and recycled aggregates, reducing cement content to lower carbon emissions while maintaining strength. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) relies on a drier mix with minimal water, primarily using ordinary Portland cement, coarse aggregates, and fine aggregates to facilitate compaction by rollers. The distinct compositions influence their environmental impact and structural performance in road construction projects.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Green concrete significantly reduces carbon emissions by incorporating industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, enhancing sustainability in road construction. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers environmental benefits through reduced cement content and faster construction, lowering overall energy consumption. Both materials contribute to eco-friendly infrastructure, but green concrete demonstrates a stronger emphasis on minimizing carbon footprint and promoting circular economy principles.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Green concrete, incorporating recycled materials and industrial by-products, offers enhanced durability through reduced permeability and improved resistance to chemical attacks, making it suitable for sustainable road construction. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) provides superior strength due to its dense, low-slump mixture and compaction method, enabling high load-bearing capacity and fast construction. While RCC delivers higher compressive strength and rapid curing, green concrete excels in long-term durability and environmental benefits, balancing performance with sustainability in road infrastructure projects.
Application Methods in Road Construction
Green concrete employs low-carbon materials like fly ash and recycled aggregates, using standard wet mixing and pouring techniques ideal for structural sections requiring environmental sustainability. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) utilizes a zero-slump mixture spread by bulldozers or pavers and compacted with heavy rollers, providing rapid strength gain and durability suited for high-traffic road surfaces. The application method of RCC allows faster construction with reduced curing time, making it advantageous for large-scale highway and airport pavements compared to traditional green concrete methods.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Green concrete reduces environmental impact by incorporating recycled materials and industrial by-products, often resulting in lower raw material costs compared to traditional mixes. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers rapid construction and reduced labor expenses due to its dry mix and efficient placement, making it cost-effective for large-scale road projects. Evaluating life-cycle costs reveals green concrete provides long-term savings through durability and reduced maintenance, while RCC excels in upfront cost efficiency and faster project completion.
Curing Process and Setting Time
Green concrete utilizes supplementary cementitious materials and requires a controlled curing process, often involving moist curing for 7 to 14 days to enhance durability and strength development, with a typical setting time of 4 to 6 hours. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) features a low-slump mix compacted by heavy rollers, curing rapidly with initial set times around 2 to 3 hours, enabling early load application and faster construction cycles. Proper curing in RCC involves minimizing moisture loss through methods like fogging or covering to prevent shrinkage cracks, while green concrete's extended curing process significantly reduces carbon footprint and improves long-term performance.
Performance in Different Climates
Green concrete demonstrates superior thermal insulation and reduced heat absorption, making it highly effective in hot climates by minimizing pavement temperature fluctuations. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers enhanced durability and faster curing times, excelling in regions with high traffic loads and variable moisture conditions. Both materials provide sustainable solutions, but green concrete's eco-friendly additives improve resistance to freeze-thaw cycles, while RCC's dense compaction optimizes performance in cold and wet environments.
Maintenance and Longevity
Green concrete offers enhanced durability through reduced permeability and improved resistance to chemical attacks, leading to lower maintenance costs over time compared to conventional materials. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) provides high load-bearing capacity and rapid construction, yet may require more frequent surface maintenance to address wear and potential cracking under heavy traffic. Both materials contribute to road longevity, with green concrete excelling in sustainability and corrosion resistance, while RCC benefits from strength and quick curing for long-lasting pavement structures.
Future Trends and Innovations in Road Construction Materials
Green concrete incorporates sustainable materials such as industrial by-products and recycled aggregates, significantly reducing carbon emissions compared to traditional concrete used in road construction. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC), known for its rapid construction and high durability, is evolving with improved mix designs that enhance workability and compressive strength, making it ideal for heavy-traffic roads. Future trends emphasize integrating nanomaterials and self-healing technologies in both green concrete and RCC to increase lifespan, reduce maintenance costs, and promote eco-friendly infrastructure development.
Infographic: Green concrete vs Roller-compacted concrete for Road construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com