Green concrete incorporates recycled materials and reduces carbon emissions, making it eco-friendly and sustainable for sidewalks. Pervious concrete enhances stormwater management by allowing water to permeate through, reducing runoff and improving groundwater recharge in sidewalk applications.
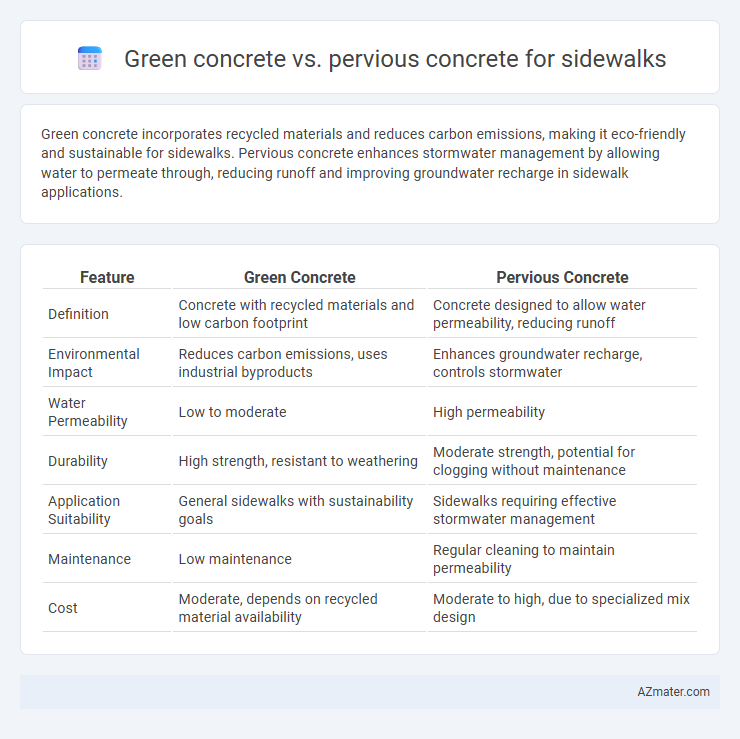
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Green Concrete | Pervious Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete with recycled materials and low carbon footprint | Concrete designed to allow water permeability, reducing runoff |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces carbon emissions, uses industrial byproducts | Enhances groundwater recharge, controls stormwater |
| Water Permeability | Low to moderate | High permeability |
| Durability | High strength, resistant to weathering | Moderate strength, potential for clogging without maintenance |
| Application Suitability | General sidewalks with sustainability goals | Sidewalks requiring effective stormwater management |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Regular cleaning to maintain permeability |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on recycled material availability | Moderate to high, due to specialized mix design |
Introduction to Sustainable Sidewalk Solutions
Green concrete incorporates recycled materials and industrial byproducts, reducing carbon footprint and enhancing sustainability. Pervious concrete improves stormwater management by allowing water to infiltrate through the sidewalk, minimizing runoff and preventing flooding. Both materials offer environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional concrete, promoting sustainable urban infrastructure.
Defining Green Concrete: Composition and Benefits
Green concrete consists of recycled industrial waste materials such as fly ash, slag, and recycled aggregates, reducing the consumption of natural resources and lowering carbon emissions. It offers enhanced sustainability by utilizing eco-friendly components that improve durability and thermal insulation, making it an ideal choice for sidewalks. Green concrete also contributes to waste reduction while maintaining structural integrity and promoting environmental conservation in urban infrastructure.
Understanding Pervious Concrete: Structure and Functionality
Pervious concrete consists of a highly porous structure that allows water to infiltrate through the pavement, reducing runoff and promoting groundwater recharge, making it an eco-friendly solution for sidewalks. Unlike green concrete, which incorporates recycled materials to reduce carbon footprint, pervious concrete focuses on permeability with void spaces typically ranging from 15% to 25%. Its functionality in stormwater management makes it ideal for sidewalks in urban areas where minimizing surface water accumulation is critical.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Green concrete incorporates recycled materials and industrial by-products, significantly reducing carbon emissions and conserving natural resources compared to traditional concrete. Pervious concrete enhances stormwater management by allowing water infiltration, reducing runoff and improving groundwater recharge, thereby mitigating urban flooding and decreasing pollutant transport. Both materials promote sustainability in sidewalk construction, with green concrete focusing on carbon footprint reduction and pervious concrete optimizing water management and ecosystem health.
Durability and Longevity for Urban Walkways
Green concrete enhances durability and longevity in urban walkways by incorporating recycled materials and reducing permeability, which minimizes cracking and surface wear. Pervious concrete improves water drainage, reducing hydrostatic pressure and freeze-thaw damage, but generally has lower compressive strength, impacting its long-term resilience under heavy foot traffic. Selecting green concrete provides stronger structural integrity, while pervious concrete supports sustainable stormwater management at the potential cost of reduced lifespan.
Water Management and Permeability Differences
Green concrete incorporates recycled materials and supplementary cementitious substances, enhancing sustainability but typically exhibiting lower permeability compared to pervious concrete. Pervious concrete is specifically designed with high porosity to facilitate rapid water infiltration, effectively managing stormwater runoff and reducing surface water accumulation on sidewalks. The distinct permeability of pervious concrete makes it more suitable for water management applications, while green concrete excels in environmental impact reduction through resource conservation.
Installation Process and Maintenance Requirements
Green concrete for sidewalks typically involves mixing eco-friendly materials like fly ash or slag cement, requiring standard pouring and curing processes similar to traditional concrete, with minimal specialized equipment. Pervious concrete installation demands careful proportioning of coarse aggregates and controlled water content to maintain porosity, along with precise compaction to prevent clogging. Maintenance for green concrete sidewalks mainly includes routine cleaning and occasional surface repairs, while pervious concrete requires regular vacuuming or pressure washing to preserve permeability and prevent sediment buildup.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-Term Expenses
Green concrete typically incurs higher initial costs due to the use of recycled materials and sustainable additives, but offers long-term savings through durability and reduced maintenance. Pervious concrete features moderate upfront expenses and excels in stormwater management, potentially lowering municipal drainage costs over time. Evaluating both materials requires balancing initial investments with lifecycle benefits, including environmental impact and infrastructure resilience.
Suitability for Different Sidewalk Environments
Green concrete, infused with recycled materials and low-carbon cement, excels in urban sidewalks by reducing environmental impact and enhancing durability against heavy pedestrian traffic. Pervious concrete is ideal for sidewalks in areas prone to heavy rainfall or stormwater runoff, as its porous structure allows efficient water drainage, reducing puddling and improving safety. Selecting between green and pervious concrete depends on factors such as local climate, soil drainage, and sustainability goals for the sidewalk environment.
Future Trends in Eco-Friendly Concrete Technologies
Green concrete innovations focus on reducing carbon emissions through the use of recycled materials and alternative cementitious binders, enhancing sustainability in sidewalk construction. Pervious concrete advances emphasize improving water permeability and stormwater management, supporting urban heat island mitigation and groundwater recharge. Future trends highlight the integration of nanomaterials and bio-based additives to enhance durability, strength, and environmental performance of eco-friendly concrete solutions.
Infographic: Green concrete vs Pervious concrete for Sidewalk
 azmater.com
azmater.com