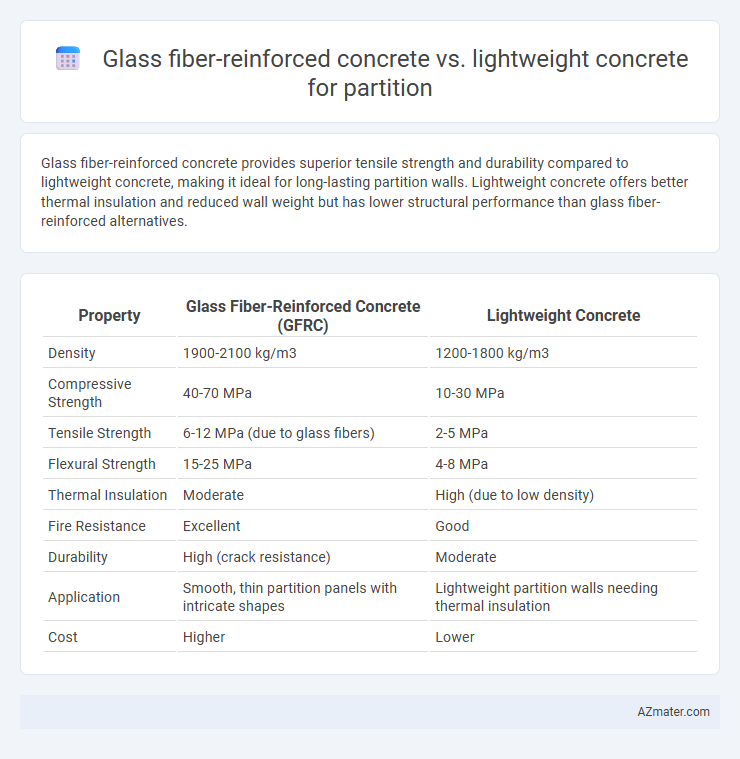
Glass fiber-reinforced concrete provides superior tensile strength and durability compared to lightweight concrete, making it ideal for long-lasting partition walls. Lightweight concrete offers better thermal insulation and reduced wall weight but has lower structural performance than glass fiber-reinforced alternatives.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Fiber-Reinforced Concrete (GFRC) | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1900-2100 kg/m3 | 1200-1800 kg/m3 |
| Compressive Strength | 40-70 MPa | 10-30 MPa |
| Tensile Strength | 6-12 MPa (due to glass fibers) | 2-5 MPa |
| Flexural Strength | 15-25 MPa | 4-8 MPa |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate | High (due to low density) |
| Fire Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Durability | High (crack resistance) | Moderate |
| Application | Smooth, thin partition panels with intricate shapes | Lightweight partition walls needing thermal insulation |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Concrete Partition Materials
Glass fiber-reinforced concrete (GFRC) offers superior tensile strength and durability compared to traditional lightweight concrete, making it ideal for partition applications requiring enhanced structural integrity. Lightweight concrete, often composed of expanded clay or shale aggregates, provides excellent thermal insulation and reduced load, beneficial for non-load-bearing partitions. Selecting between GFRC and lightweight concrete depends on specific performance requirements, such as impact resistance, weight constraints, and fire rating for partition walls.
What is Glass Fiber-Reinforced Concrete?
Glass fiber-reinforced concrete (GFRC) is a composite material consisting of a cement-based matrix embedded with alkali-resistant glass fibers, enhancing its tensile strength and durability compared to traditional lightweight concrete. GFRC offers superior resistance to cracking, impact, and weather conditions, making it an ideal choice for partition walls requiring high structural integrity and thin sections. Its lightweight properties combined with increased flexural strength enable easier installation and design flexibility that outperforms standard lightweight concrete partitions.
What is Lightweight Concrete?
Lightweight concrete is a type of concrete that incorporates lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or pumice to reduce density and improve thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for partition walls where weight reduction is essential. Glass fiber-reinforced concrete (GFRC) offers higher tensile strength and durability but is typically denser and more rigid compared to lightweight concrete. Lightweight concrete provides better sound absorption and fire resistance, contributing to energy efficiency and comfort in building partitions.
Strength Comparison: GFRC vs Lightweight Concrete
Glass fiber-reinforced concrete (GFRC) offers significantly higher tensile strength and impact resistance compared to lightweight concrete, making it ideal for partition walls requiring enhanced structural durability. GFRC's dense matrix combined with alkali-resistant glass fibers results in superior flexural strength and reduced cracking, whereas lightweight concrete, though beneficial for reducing load, typically exhibits lower compressive and tensile strength. For partitions where strength and longevity are critical, GFRC provides a more robust solution than conventional lightweight concrete options.
Weight and Structural Implications
Glass fiber-reinforced concrete (GFRC) offers a significantly lower weight compared to traditional concrete while maintaining superior tensile strength and crack resistance, which enhances the durability and stability of partitions. Lightweight concrete reduces overall structural load, allowing for easier handling and faster installation but generally exhibits lower strength and increased susceptibility to shrinkage and cracking. Choosing GFRC over lightweight concrete for partitions provides a strategic advantage in balancing reduced weight with improved structural performance, especially in load-sensitive applications.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
Glass fiber-reinforced concrete (GFRC) offers superior tensile strength and durability but provides moderate thermal and acoustic insulation compared to lightweight concrete, which excels in reducing heat transfer and sound transmission due to its porous structure. Lightweight concrete's lower density and high air content enhance its ability to absorb sound and resist heat conduction, making it ideal for partition walls requiring thermal and acoustic efficiency. GFRC partitions are better suited for structural integrity where insulation is secondary, whereas lightweight concrete optimizes energy efficiency and noise reduction in interior partition applications.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Glass fiber-reinforced concrete (GFRC) offers superior durability compared to lightweight concrete due to its enhanced tensile strength and crack resistance, making it ideal for partitions exposed to impact or environmental stress. GFRC requires minimal maintenance as its surface resists moisture penetration, chemical attack, and efflorescence, reducing long-term repair costs. In contrast, lightweight concrete partitions, while easier to install and thermally efficient, may experience higher susceptibility to surface wear and require regular sealing or patching to maintain structural integrity and appearance.
Installation Process and Flexibility
Glass fiber-reinforced concrete (GFRC) offers superior flexibility in design and installation compared to lightweight concrete, allowing for thinner panels that reduce overall structure weight and simplify handling. The GFRC installation process is faster and less labor-intensive due to its precast nature and ability to be molded into complex shapes, whereas lightweight concrete often requires longer curing times and more on-site adjustments. These attributes make GFRC particularly advantageous for partition walls where versatility and expedited construction are critical.
Cost Analysis: GFRC vs Lightweight Concrete
Glass fiber-reinforced concrete (GFRC) typically presents a higher initial material cost compared to lightweight concrete due to its specialized fibers and manufacturing process. Lightweight concrete offers cost advantages in bulk material pricing and reduced structural support requirements, leading to savings in labor and foundation expenses. Evaluating total project expenses, including installation and long-term maintenance, often favors lightweight concrete for budget-sensitive partition applications.
Choosing the Right Partition Material
Glass fiber-reinforced concrete (GFRC) offers superior tensile strength, durability, and fire resistance, making it ideal for partitions requiring high structural performance and longevity, especially in commercial and industrial buildings. Lightweight concrete provides excellent thermal insulation and sound absorption, reducing overall wall weight and enhancing energy efficiency, which is beneficial for residential and low-rise constructions. Selecting the right partition material depends on balancing structural demands, insulation properties, and installation feasibility to meet specific project requirements.
Infographic: Glass fiber-reinforced concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Partition
 azmater.com
azmater.com