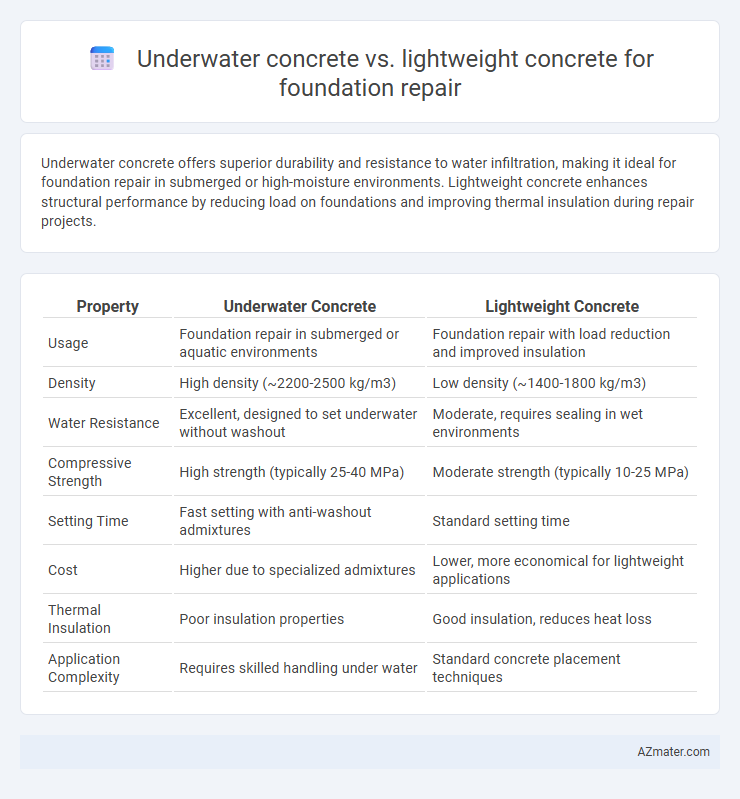
Underwater concrete offers superior durability and resistance to water infiltration, making it ideal for foundation repair in submerged or high-moisture environments. Lightweight concrete enhances structural performance by reducing load on foundations and improving thermal insulation during repair projects.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Underwater Concrete | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Foundation repair in submerged or aquatic environments | Foundation repair with load reduction and improved insulation |
| Density | High density (~2200-2500 kg/m3) | Low density (~1400-1800 kg/m3) |
| Water Resistance | Excellent, designed to set underwater without washout | Moderate, requires sealing in wet environments |
| Compressive Strength | High strength (typically 25-40 MPa) | Moderate strength (typically 10-25 MPa) |
| Setting Time | Fast setting with anti-washout admixtures | Standard setting time |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized admixtures | Lower, more economical for lightweight applications |
| Thermal Insulation | Poor insulation properties | Good insulation, reduces heat loss |
| Application Complexity | Requires skilled handling under water | Standard concrete placement techniques |
Introduction to Foundation Repair: Underwater vs. Lightweight Concrete
Foundation repair requires selecting materials that provide durability and structural integrity under specific environmental conditions. Underwater concrete is specially formulated for subaqueous environments, offering excellent cohesion and rapid setting properties to prevent washout, making it ideal for submerged foundation repairs. Lightweight concrete, characterized by its reduced density and enhanced thermal insulation, is preferred for foundation repairs where load reduction and improved workability are critical factors.
Key Differences Between Underwater and Lightweight Concrete
Underwater concrete is specifically designed to set and harden in submerged conditions, using anti-washout admixtures to prevent cement dispersion, making it ideal for foundation repairs in aquatic environments. Lightweight concrete, while possessing lower density due to materials like expanded clay or shale, offers improved thermal insulation and reduced structural load but is not suitable for underwater applications. The key differences lie in their composition, setting environment, and performance characteristics, with underwater concrete emphasizing durability in wet conditions and lightweight concrete focusing on weight reduction and insulating properties.
Composition and Properties of Underwater Concrete
Underwater concrete is specifically formulated with additives such as anti-washout agents, polymers, and higher cement content to maintain cohesiveness and prevent dispersion when placed underwater, ensuring effective bonding and durability in submerged conditions. Its density and impermeability are higher compared to lightweight concrete, which is designed with porous aggregates like expanded clay or shale to reduce weight but lacks the necessary robustness for underwater applications. The composition of underwater concrete balances workability and rapid setting properties, enabling foundation repairs in aquatic environments without compromising structural integrity.
Features and Advantages of Lightweight Concrete
Lightweight concrete offers superior workability and reduced structural load compared to underwater concrete, making it ideal for foundation repair in areas with limited load-bearing capacity. Its excellent thermal insulation and higher fire resistance enhance the durability and safety of repaired foundations. The material's lower density improves ease of handling and placement, reducing labor costs and accelerating construction timelines.
Applications of Underwater Concrete in Foundation Repair
Underwater concrete is specifically designed for use in foundation repairs where structures are submerged or in contact with water, such as bridge piers, harbor structures, and submerged retaining walls. Its composition includes anti-washout admixtures that prevent cement from dispersing in water, ensuring effective setting and strength development in wet environments. This makes underwater concrete ideal for stabilizing and restoring foundations exposed to continuous water flow or pressure, unlike lightweight concrete, which is primarily used for reducing load rather than underwater durability.
Uses of Lightweight Concrete for Foundation Strengthening
Lightweight concrete offers excellent thermal insulation and reduces overall structural load, making it ideal for foundation repair in residential and low-rise buildings. Its high strength-to-weight ratio improves foundation stability while minimizing settlement issues in weak soil conditions. Used in underpinning and void filling, lightweight concrete enhances load distribution and durability in foundation strengthening projects.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Underwater concrete offers superior durability due to its improved resistance to water penetration and chemical attacks, making it ideal for submerged foundation repairs. Lightweight concrete provides enhanced thermal insulation and reduced load on existing structures while maintaining adequate strength for non-submerged repairs. Performance comparisons reveal that underwater concrete excels in high-moisture environments, whereas lightweight concrete is preferred for projects requiring ease of handling and faster curing times.
Cost Analysis: Underwater Concrete vs. Lightweight Concrete
Underwater concrete typically incurs higher costs due to specialized materials and installation techniques required for submerged conditions, increasing labor and equipment expenses. Lightweight concrete tends to be more economical for foundation repair, offering reduced transportation costs and easier handling while maintaining sufficient strength and durability. Evaluating total project expenses, lightweight concrete often proves cost-efficient, though the specific site conditions and repair complexity may influence the final cost comparison.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Underwater concrete used for foundation repair is designed to set and harden underwater, minimizing water contamination and reducing environmental disruption in aquatic ecosystems. Lightweight concrete offers advantages of reduced material usage and lower carbon footprint due to its incorporation of industrial waste like fly ash or expanded polystyrene aggregates. Both materials contribute to sustainable construction practices, but lightweight concrete provides greater energy efficiency in transportation and installation, enhancing overall environmental benefits.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Your Foundation Repair
Underwater concrete offers superior durability and rapid setting properties essential for foundation repairs in submerged or high-moisture environments, effectively preventing washout and ensuring structural stability. Lightweight concrete, with its lower density and enhanced insulation capabilities, is ideal for reducing load on weakened foundations while providing improved thermal performance. Selecting the right concrete depends on site conditions, load requirements, and moisture exposure, with underwater concrete favored for damp or underwater repairs and lightweight concrete suited for load-sensitive or insulation-needing foundation projects.
Infographic: Underwater concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Foundation repair
 azmater.com
azmater.com