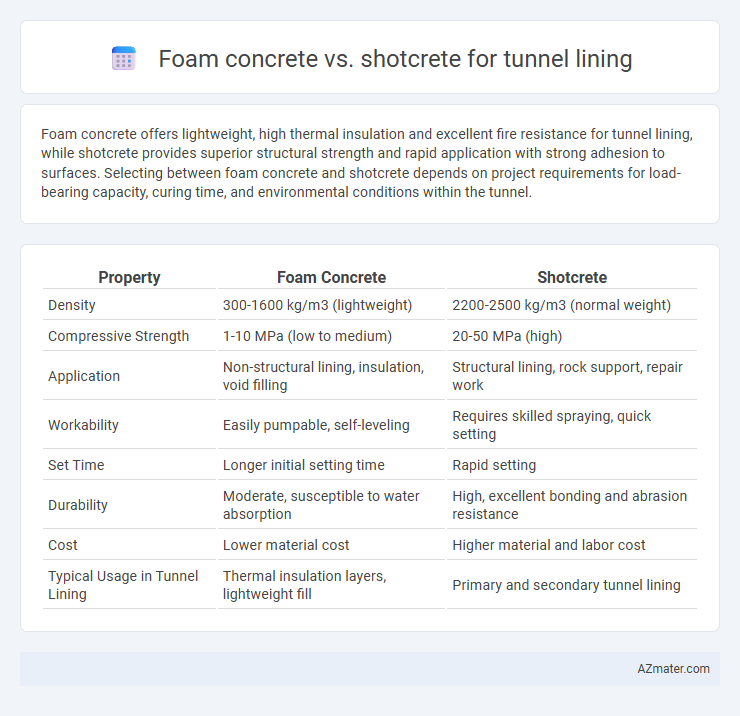
Foam concrete offers lightweight, high thermal insulation and excellent fire resistance for tunnel lining, while shotcrete provides superior structural strength and rapid application with strong adhesion to surfaces. Selecting between foam concrete and shotcrete depends on project requirements for load-bearing capacity, curing time, and environmental conditions within the tunnel.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Foam Concrete | Shotcrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 300-1600 kg/m3 (lightweight) | 2200-2500 kg/m3 (normal weight) |
| Compressive Strength | 1-10 MPa (low to medium) | 20-50 MPa (high) |
| Application | Non-structural lining, insulation, void filling | Structural lining, rock support, repair work |
| Workability | Easily pumpable, self-leveling | Requires skilled spraying, quick setting |
| Set Time | Longer initial setting time | Rapid setting |
| Durability | Moderate, susceptible to water absorption | High, excellent bonding and abrasion resistance |
| Cost | Lower material cost | Higher material and labor cost |
| Typical Usage in Tunnel Lining | Thermal insulation layers, lightweight fill | Primary and secondary tunnel lining |
Introduction to Tunnel Lining Methods
Foam concrete and shotcrete are widely used tunnel lining methods with distinct properties suited for various geological conditions. Foam concrete offers lightweight, excellent thermal insulation, and easy application for initial support and permanent lining in tunnels. Shotcrete provides superior compressive strength, rapid curing, and strong bond to rock surfaces, making it ideal for immediate ground stabilization and reinforcement.
Overview of Foam Concrete
Foam concrete is a lightweight, cellular material composed of cement, water, and pre-formed foam that offers excellent thermal insulation and reduced self-weight for tunnel lining applications. Its low density and flowable consistency enable easy placement and rapid setting, which can enhance construction speed and reduce formwork requirements. This material provides improved crack resistance and durability, making it a cost-effective alternative to traditional concrete and shotcrete methods in underground projects.
Overview of Shotcrete
Shotcrete is a pneumatically applied concrete mixture renowned for its excellent adhesion, rapid setting time, and high compressive strength, making it ideal for tunnel lining reinforcement. It provides superior structural support through its dense, durable layers, effectively sealing surfaces against water ingress and reducing the need for extensive formwork. Its versatility in application allows for precise layering on complex geometries, enhancing tunnel stability and safety during excavation.
Material Properties Comparison
Foam concrete exhibits lower density and higher thermal insulation compared to shotcrete, making it advantageous for reducing overall tunnel weight and improving energy efficiency. Shotcrete offers superior compressive strength and adhesion, essential for immediate structural support and stability in tunnel lining applications. The choice between foam concrete and shotcrete depends on balancing factors like load-bearing requirements, thermal performance, and application speed in tunnel construction projects.
Installation Techniques and Equipment
Foam concrete installation for tunnel lining typically involves lightweight mixer units and specialized foam generators to create a stable, aerated mix applied using pump systems, emphasizing ease of handling and rapid placement in large, continuous layers. Shotcrete requires robotic or handheld spraying equipment with compressors and pumps to apply a high-velocity, wet or dry mix directly onto the tunnel surface, ensuring dense compaction and strong adhesion. Both methods demand precise equipment calibration and material control, but shotcrete offers superior support in irregular geometries, whereas foam concrete excels in thermal insulation and volume fill efficiency.
Structural Performance in Tunnels
Foam concrete offers lightweight properties and high thermal insulation, reducing the load on tunnel linings while providing sufficient compressive strength ranging from 2 to 15 MPa for non-structural applications. Shotcrete delivers superior structural performance with high early strength, excellent adhesion to rock surfaces, and enhanced durability, making it ideal for primary tunnel support where load-bearing capacity and crack resistance are critical. The choice between foam concrete and shotcrete depends on tunnel design requirements, with shotcrete favored for structural integrity and foam concrete suited for void filling and insulation in tunnels.
Durability and Longevity
Foam concrete offers excellent durability for tunnel lining due to its lightweight, low permeability, and resistance to chemical attacks, which significantly reduces maintenance needs over time. Shotcrete provides superior structural strength and adhesion, making it highly durable under mechanical stress and ideal for immediate rock support in tunnel construction. Both materials ensure longevity; however, foam concrete excels in thermal insulation and shrinkage control, while shotcrete is preferred for rapid application and high load-bearing capacity.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Foam concrete offers lower material and pumping costs compared to shotcrete, primarily due to its lightweight properties and reduced cement consumption, making it a cost-effective solution for tunnel lining projects. Shotcrete involves higher labor and equipment expenses because of its specialized application process, but it provides faster setting times and superior structural strength, potentially reducing long-term maintenance costs. Evaluating project-specific parameters such as tunnel length, diameter, and load requirements is essential to balance initial investment against lifecycle economic benefits effectively.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Foam concrete offers superior environmental benefits for tunnel lining due to its lightweight nature, lower cement content, and reduced carbon footprint compared to shotcrete, which typically involves higher energy consumption for spray equipment and additional additives. The use of foam concrete enhances sustainability by improving thermal insulation and reducing material waste, while shotcrete's dense application can lead to increased resource use and higher embodied energy. Choosing foam concrete aligns with green construction practices aiming to minimize ecological damage and promote energy efficiency in underground infrastructure.
Best Practices and Application Scenarios
Foam concrete is optimal for tunnel lining when lightweight, thermal insulation, and easy placement are priorities, offering superior flowability and reduced ground pressure compared to shotcrete. Shotcrete excels in scenarios requiring rapid strength gain, structural support, and adaptability to complex tunnel geometries due to its pneumatically applied, high-density material properties. Best practices recommend foam concrete for non-structural lining and void filling, while shotcrete suits primary support and rehabilitation phases, ensuring robust reinforcement and durability under high stress conditions.
Infographic: Foam concrete vs Shotcrete for Tunnel lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com