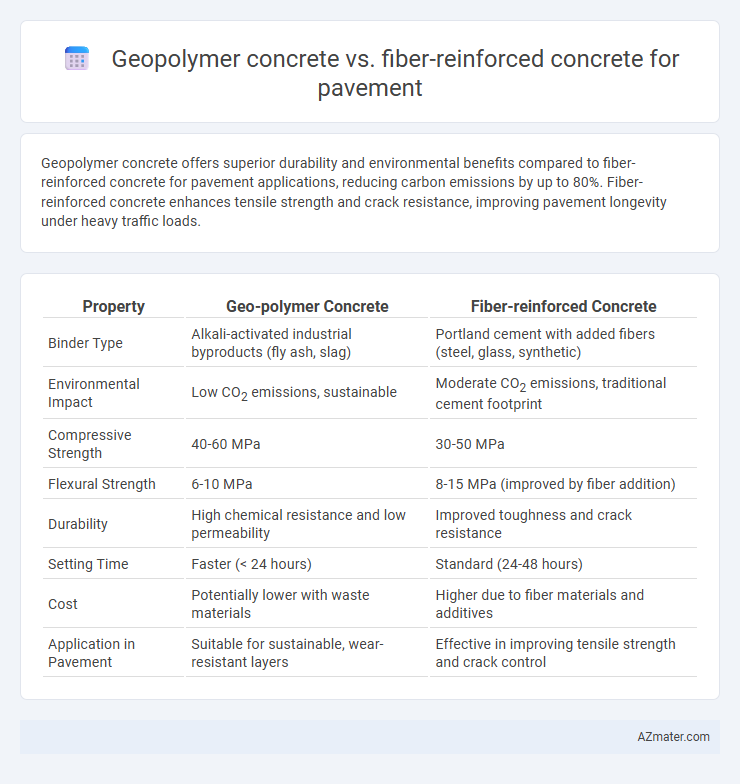
Geopolymer concrete offers superior durability and environmental benefits compared to fiber-reinforced concrete for pavement applications, reducing carbon emissions by up to 80%. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances tensile strength and crack resistance, improving pavement longevity under heavy traffic loads.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Geo-polymer Concrete | Fiber-reinforced Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Binder Type | Alkali-activated industrial byproducts (fly ash, slag) | Portland cement with added fibers (steel, glass, synthetic) |
| Environmental Impact | Low CO2 emissions, sustainable | Moderate CO2 emissions, traditional cement footprint |
| Compressive Strength | 40-60 MPa | 30-50 MPa |
| Flexural Strength | 6-10 MPa | 8-15 MPa (improved by fiber addition) |
| Durability | High chemical resistance and low permeability | Improved toughness and crack resistance |
| Setting Time | Faster (< 24 hours) | Standard (24-48 hours) |
| Cost | Potentially lower with waste materials | Higher due to fiber materials and additives |
| Application in Pavement | Suitable for sustainable, wear-resistant layers | Effective in improving tensile strength and crack control |
Introduction to Geo-Polymer and Fiber-Reinforced Concrete
Geo-polymer concrete utilizes industrial by-products like fly ash or slag activated with alkaline solutions to form durable, eco-friendly binders that reduce carbon emissions compared to traditional Portland cement. Fiber-reinforced concrete incorporates materials such as steel, glass, or synthetic fibers to enhance tensile strength, crack resistance, and toughness, improving pavement longevity under dynamic loads. Both materials offer innovative alternatives for pavement construction, promoting sustainability and structural performance in infrastructure projects.
Material Composition Differences
Geo-polymer concrete utilizes industrial by-products such as fly ash or slag activated by alkaline solutions, creating a binder with high chemical resistance and low carbon footprint, while fiber-reinforced concrete incorporates synthetic or steel fibers to enhance tensile strength and crack resistance. The alkali-activated materials in geo-polymer concrete provide superior durability and environmental benefits, contrasting with the mechanical reinforcement mechanism provided by fibers in fiber-reinforced concrete. These fundamental material composition differences influence their performance characteristics and suitability for various pavement applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Geo-polymer concrete exhibits higher compressive strength and improved resistance to chemical attack compared to fiber-reinforced concrete, making it ideal for durable pavement applications. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances tensile strength and crack resistance due to the inclusion of materials such as steel or synthetic fibers, which improve flexibility and impact resistance under load. Both materials demonstrate distinct mechanical advantages, with geo-polymer concrete excelling in durability and load-bearing capacity, while fiber-reinforced concrete offers superior toughness and deformability in pavement structures.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Geo-polymer concrete significantly reduces carbon emissions by utilizing industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional cement-based materials in pavement construction. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances durability and crack resistance, extending pavement lifespan and reducing maintenance frequency, which indirectly supports environmental sustainability. Both materials contribute to eco-friendly infrastructure, but geo-polymer concrete presents a more substantial advantage in lowering the overall environmental footprint due to its reduced reliance on Portland cement.
Durability and Longevity in Pavement Applications
Geo-polymer concrete exhibits superior chemical resistance and reduced permeability, significantly enhancing durability in pavement applications exposed to aggressive environments. Fiber-reinforced concrete improves tensile strength and crack resistance, leading to increased longevity by mitigating fatigue and shrinkage-related damages. Both materials offer extended service life compared to traditional concrete, with Geo-polymer concrete excelling in corrosive conditions and fiber-reinforced concrete providing enhanced mechanical resilience.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Geo-polymer concrete offers significant cost savings in pavement applications due to lower raw material expenses and reduced energy consumption during production compared to fiber-reinforced concrete. Fiber-reinforced concrete incurs higher upfront costs driven by the price of synthetic or steel fibers and complex mixing processes, but may provide longer service life and reduced maintenance expenses. Economic considerations must balance initial investment against lifecycle costs, with geo-polymer concrete often favored in regions prioritizing sustainability and cost-efficiency.
Construction Techniques and Workability
Geopolymer concrete offers enhanced workability with lower water demand and faster setting times, making it suitable for rapid pavement construction using conventional batching and mixing techniques. Fiber-reinforced concrete requires careful dispersion of synthetic or steel fibers to avoid clumping, often involving specialized mixing protocols to maintain uniform workability and improve crack resistance in pavement applications. Construction techniques differ as geopolymer concrete benefits from ambient curing without extensive moisture control, while fiber-reinforced concrete may need controlled curing environments to optimize fiber-matrix bonding.
Performance Under Load and Traffic
Geo-polymer concrete offers superior chemical resistance and reduced shrinkage, enhancing pavement durability under heavy traffic loads compared to traditional concretes. Fiber-reinforced concrete improves tensile strength and crack control, providing better flexural performance and fatigue resistance in high-traffic conditions. Both materials enhance pavement lifespan, but geo-polymer concrete excels in load-bearing capacity while fiber reinforcement optimizes toughness and load distribution.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Case studies highlight Geo-polymer concrete's superior durability and reduced carbon footprint in pavement applications, showcasing projects like the Australian road trials with enhanced chemical resistance and faster curing times. Fiber-reinforced concrete demonstrates improved tensile strength and crack resistance in heavy-traffic pavements, evidenced by U.S. highway installations utilizing steel or synthetic fibers to extend lifespan and reduce maintenance. Real-world applications confirm Geo-polymer concrete's sustainability benefits, while fiber-reinforced concrete offers pragmatic resilience in load-bearing scenarios, influencing material selection in modern pavement engineering.
Future Trends and Innovations in Pavement Materials
Geo-polymer concrete offers a sustainable alternative to traditional cement by utilizing industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, significantly reducing carbon emissions in pavement construction. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances pavement durability and crack resistance through the integration of synthetic or steel fibers, improving load-bearing capacity and lifespan. Emerging innovations include hybrid composites combining geo-polymers with nanofibers and self-healing capabilities, aimed at maximizing environmental benefits and structural performance in next-generation pavements.
Infographic: Geo-polymer concrete vs Fiber-reinforced concrete for Pavement
 azmater.com
azmater.com