Geopolymer concrete offers superior durability, chemical resistance, and lower carbon emissions compared to traditional Portland cement concrete, making it an eco-friendly choice for pavement applications. Its rapid setting time and high compressive strength enhance pavement longevity and reduce maintenance costs.
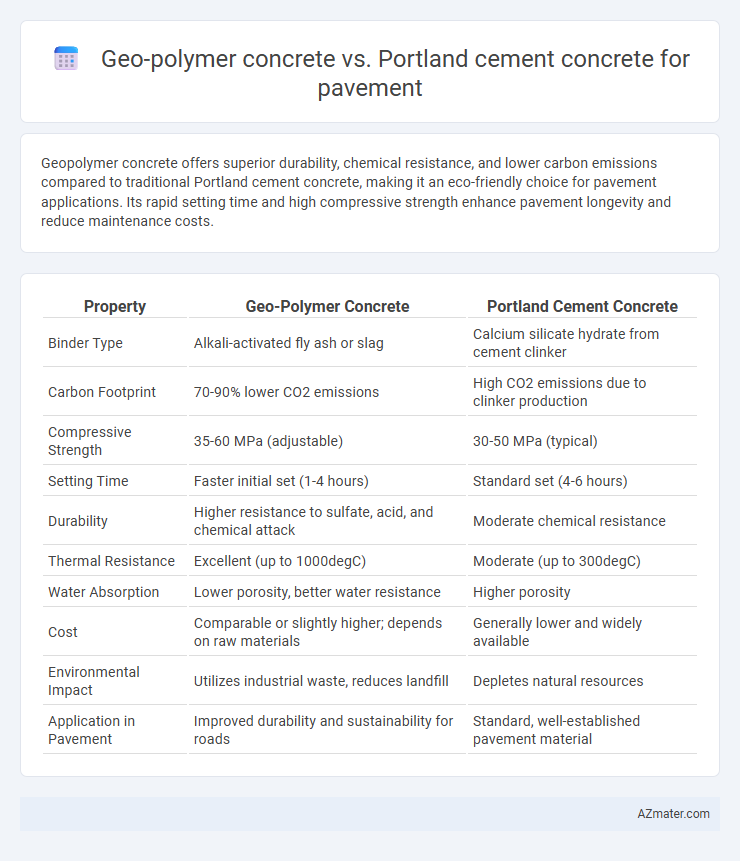
Table of Comparison
| Property | Geo-Polymer Concrete | Portland Cement Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Binder Type | Alkali-activated fly ash or slag | Calcium silicate hydrate from cement clinker |
| Carbon Footprint | 70-90% lower CO2 emissions | High CO2 emissions due to clinker production |
| Compressive Strength | 35-60 MPa (adjustable) | 30-50 MPa (typical) |
| Setting Time | Faster initial set (1-4 hours) | Standard set (4-6 hours) |
| Durability | Higher resistance to sulfate, acid, and chemical attack | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Thermal Resistance | Excellent (up to 1000degC) | Moderate (up to 300degC) |
| Water Absorption | Lower porosity, better water resistance | Higher porosity |
| Cost | Comparable or slightly higher; depends on raw materials | Generally lower and widely available |
| Environmental Impact | Utilizes industrial waste, reduces landfill | Depletes natural resources |
| Application in Pavement | Improved durability and sustainability for roads | Standard, well-established pavement material |
Introduction to Geo-polymer and Portland Cement Concrete
Geopolymer concrete is an innovative, eco-friendly alternative to traditional Portland cement concrete, utilizing industrial by-products like fly ash or slag as binders instead of clinker-based cement. Portland cement concrete, the most widely used construction material globally, relies on the hydration of calcium silicates to gain strength and durability, but it contributes significantly to CO2 emissions. Geopolymer concrete offers superior resistance to chemical attack, high temperature tolerance, and reduced carbon footprint, making it suitable for sustainable pavement applications compared to conventional Portland cement concrete.
Key Differences in Chemical Composition
Geo-polymer concrete utilizes aluminosilicate materials activated by alkaline solutions, primarily composed of silicon, aluminum, oxygen, and sodium or potassium ions, differing fundamentally from Portland cement concrete which relies on calcium silicates such as tricalcium silicate and dicalcium silicate. The chemical composition of geo-polymer concrete results in a polymeric Si-O-Al framework, offering enhanced resistance to chemical attacks and high temperatures compared to the calcium-silicate-hydrate (C-S-H) gel matrix in Portland cement concrete. This key compositional difference drives variations in hydration mechanisms, durability, and environmental impact between the two pavement materials.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Geopolymer concrete significantly reduces carbon emissions by utilizing industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, unlike Portland cement concrete, which relies on energy-intensive clinker production emitting large amounts of CO2. The enhanced durability and chemical resistance of geopolymer concrete extend pavement lifespan, decreasing maintenance frequency and resource consumption. Sustainable pavement solutions favor geopolymer concrete due to lower environmental footprints and improved long-term performance compared to traditional Portland cement concrete.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Geopolymer concrete demonstrates higher compressive strength and superior resistance to chemical attacks compared to Portland cement concrete, making it more durable for pavement applications. Its enhanced tensile strength and lower shrinkage rates contribute to improved crack resistance and load-bearing capacity on road surfaces. Portland cement concrete typically exhibits faster curing times but is more prone to carbonation and sulfate attack, impacting long-term mechanical performance in pavements.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Geo-polymer concrete exhibits superior durability and weather resistance compared to Portland cement concrete, due to its dense microstructure and high resistance to chemical attacks, freeze-thaw cycles, and sulfate exposure. Its aluminosilicate-based composition significantly reduces permeability, enhancing resilience against water ingress and thermal cracking commonly faced in pavement applications. Portland cement concrete, although widely used, is more susceptible to carbonation, chloride penetration, and spalling, leading to reduced lifespan under aggressive environmental conditions.
Construction Methods and Workability
Geopolymer concrete for pavement utilizes alkaline activators and industrial byproducts like fly ash or slag, enabling faster setting times and reduced curing requirements compared to Portland cement concrete. Construction methods for geopolymer concrete often involve standard mixing and placing techniques but require careful temperature control and curing conditions to optimize strength development and workability. In contrast, Portland cement concrete typically demands longer curing periods and is more sensitive to temperature fluctuations, impacting both the workability and timeline of pavement construction.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Geo-polymer concrete offers significant cost savings over Portland cement concrete in pavement construction due to lower raw material costs and reduced energy consumption during production. The use of industrial by-products like fly ash or slag in geo-polymer concrete not only diminishes disposal costs but also enhances long-term durability, reducing maintenance expenses. Economic considerations highlight geo-polymer concrete's potential for lifecycle cost reduction, making it a sustainable and financially viable alternative in large-scale pavement projects.
Case Studies: Performance in Pavement Applications
Geo-polymer concrete exhibits superior durability and chemical resistance compared to Portland cement concrete in pavement applications, as demonstrated by multiple case studies in high-traffic and corrosive environments. Field performance data from Australian highways indicate significantly reduced cracking and maintenance costs over a 10-year period when using geo-polymer concrete. In contrast, Portland cement concrete pavements commonly experience early deterioration due to freeze-thaw cycles and sulfate attack, underscoring geo-polymer concrete's potential for long-term sustainability in infrastructure projects.
Regulatory Standards and Industry Adoption
Geo-polymer concrete is gaining traction in pavement applications due to its lower carbon footprint and compliance with emerging environmental regulations, such as ASTM C1157 for sustainable materials. Portland cement concrete remains widely adopted under established standards like ASTM C94 and AASHTO M 85, ensuring consistency and proven durability in pavement infrastructure. Industry adoption of geo-polymer concrete is accelerating in regions with stringent environmental policies, while Portland cement continues to dominate markets prioritizing traditional performance benchmarks and regulatory familiarity.
Future Trends and Innovations in Pavement Materials
Geo-polymer concrete is gaining traction as a sustainable alternative to Portland cement concrete in pavement construction due to its lower carbon footprint and enhanced chemical resistance. Innovations in nano-additives and fiber-reinforced geo-polymer composites are improving mechanical strength and durability, making them viable for high-traffic roads. Future trends include integrating smart sensor technologies within geo-polymer pavements to enable real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, advancing infrastructure longevity and performance.
Infographic: Geo-polymer concrete vs Portland cement concrete for Pavement
 azmater.com
azmater.com