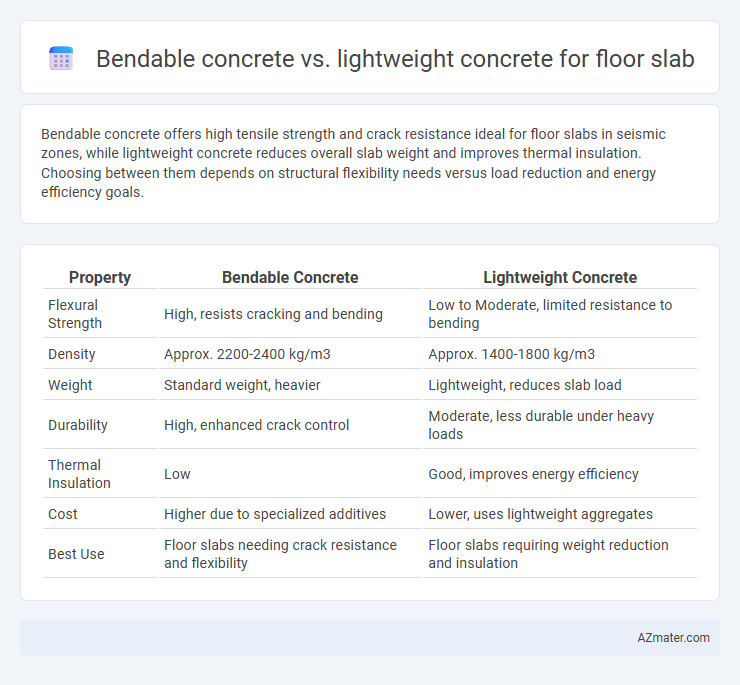
Bendable concrete offers high tensile strength and crack resistance ideal for floor slabs in seismic zones, while lightweight concrete reduces overall slab weight and improves thermal insulation. Choosing between them depends on structural flexibility needs versus load reduction and energy efficiency goals.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bendable Concrete | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Flexural Strength | High, resists cracking and bending | Low to Moderate, limited resistance to bending |
| Density | Approx. 2200-2400 kg/m3 | Approx. 1400-1800 kg/m3 |
| Weight | Standard weight, heavier | Lightweight, reduces slab load |
| Durability | High, enhanced crack control | Moderate, less durable under heavy loads |
| Thermal Insulation | Low | Good, improves energy efficiency |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized additives | Lower, uses lightweight aggregates |
| Best Use | Floor slabs needing crack resistance and flexibility | Floor slabs requiring weight reduction and insulation |
Introduction to Bendable and Lightweight Concrete
Bendable concrete, also known as engineered cementitious composite (ECC), features enhanced tensile strain capacity and flexibility, reducing cracking and improving durability in floor slabs. Lightweight concrete incorporates air-entraining aggregates such as expanded clay or polymer beads, resulting in reduced density and thermal insulation benefits for flooring applications. Both materials offer distinct performance advantages, with bendable concrete excelling in flexibility and crack resistance, while lightweight concrete prioritizes weight reduction and thermal efficiency.
Key Properties of Bendable Concrete
Bendable concrete exhibits enhanced tensile strength and superior crack resistance compared to lightweight concrete, making it ideal for floor slabs subjected to dynamic loads and structural deformations. Its high strain capacity and fiber reinforcement enable improved durability and flexibility without compromising compressive strength. This results in reduced maintenance costs and extended service life for floor slabs in both residential and commercial applications.
Key Properties of Lightweight Concrete
Lightweight concrete for floor slabs offers enhanced thermal insulation, reduced dead load, and improved fire resistance compared to traditional materials, making it ideal for multi-story construction. Its density typically ranges from 800 to 1,800 kg/m3, significantly lower than normal concrete, which enhances seismic performance and reduces foundation costs. While bendable concrete provides superior tensile strength and crack resistance due to fiber reinforcement, lightweight concrete excels in compressive strength variations (15-40 MPa) and workability for large-scale floor slab applications.
Structural Performance Comparison
Bendable concrete offers superior tensile strength and crack resistance compared to lightweight concrete, making it ideal for floor slabs requiring enhanced flexural performance and durability. Lightweight concrete reduces dead load on structures, improving seismic performance but generally exhibits lower compressive strength and modulus of elasticity than bendable concrete. Structural performance analysis indicates that bendable concrete provides better long-term load-bearing capacity and resilience under dynamic loading conditions in floor slab applications.
Flexibility and Crack Resistance
Bendable concrete offers superior flexibility and crack resistance compared to lightweight concrete, making it ideal for floor slabs subject to dynamic loads or ground movements. The engineered fibers in bendable concrete enhance tensile strength and energy absorption, significantly reducing the likelihood of cracking under stress. In contrast, lightweight concrete, while beneficial for reducing dead load, typically exhibits lower tensile strength and limited flexibility, increasing vulnerability to cracking in floor slab applications.
Load-Bearing Capabilities
Bendable concrete exhibits superior load-bearing capabilities for floor slabs due to its enhanced tensile strength and crack resistance, allowing it to withstand dynamic and heavy loads more effectively than traditional materials. Lightweight concrete offers reduced self-weight, which decreases the overall load on structural elements but typically has lower compressive strength and bending capacity compared to bendable concrete. For applications requiring high durability and structural resilience under heavy or fluctuating loads, bendable concrete provides a more reliable solution than lightweight concrete.
Installation and Construction Processes
Bendable concrete offers enhanced flexibility and crack resistance during floor slab installation, reducing the need for extensive jointing and allowing for faster curing times compared to traditional materials. Lightweight concrete simplifies handling and transportation due to its reduced density, facilitating quicker placement and easier reinforcement integration on-site. Both materials improve construction efficiency, but bendable concrete's adaptability minimizes structural damage risks, while lightweight concrete primarily aids in reducing overall slab weight and labor intensity.
Cost and Material Availability
Bendable concrete offers enhanced tensile strength and crack resistance for floor slabs but often comes at a higher cost due to specialized fibers and admixtures, which may also impact material availability depending on the region. Lightweight concrete reduces structural load and insulation needs, generally providing cost savings through lower material weight and easier handling, with widespread availability of aggregates like expanded clay or shale. Choosing between the two depends on project budget constraints and local supply chains, balancing initial cost against long-term performance benefits.
Durability and Lifespan Considerations
Bendable concrete offers superior durability and crack resistance for floor slabs due to its enhanced tensile strength and flexibility, significantly extending lifespan under dynamic loads. Lightweight concrete provides improved thermal insulation and reduced dead load but may exhibit lower durability and higher susceptibility to surface wear and maintenance requirements. For long-term performance, bendable concrete ensures better structural resilience, whereas lightweight concrete demands additional protective measures to maintain durability.
Best Applications for Floor Slab Use
Bendable concrete offers superior crack resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for floor slabs subjected to heavy loads and high stress variations, such as industrial warehouses and parking decks. Lightweight concrete provides excellent thermal insulation and reduces structural load, which is beneficial for residential buildings and multi-story constructions requiring improved energy efficiency. Selecting between these materials depends on performance needs, with bendable concrete preferred for durability under dynamic conditions and lightweight concrete favored for reducing dead loads and enhancing thermal properties.
Infographic: Bendable concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Floor slab
 azmater.com
azmater.com