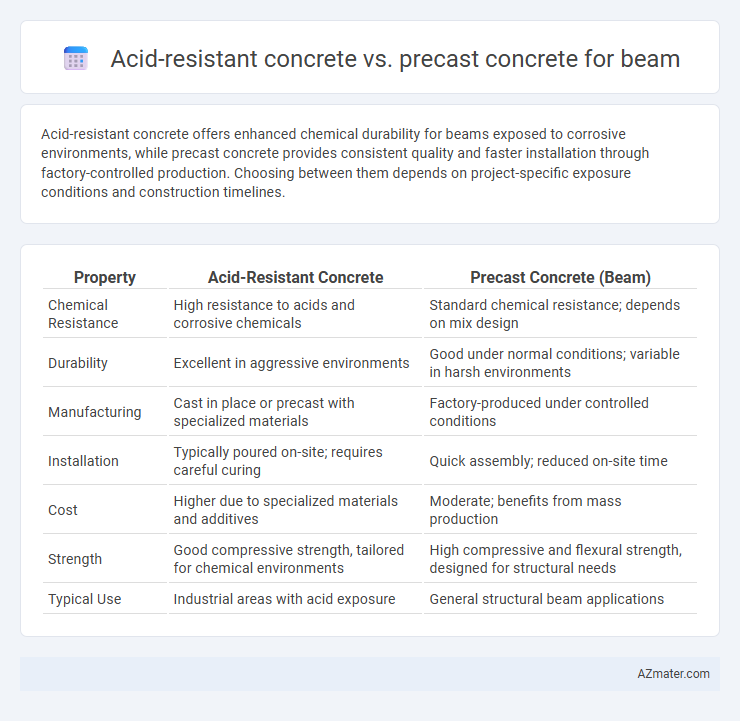
Acid-resistant concrete offers enhanced chemical durability for beams exposed to corrosive environments, while precast concrete provides consistent quality and faster installation through factory-controlled production. Choosing between them depends on project-specific exposure conditions and construction timelines.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acid-Resistant Concrete | Precast Concrete (Beam) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to acids and corrosive chemicals | Standard chemical resistance; depends on mix design |
| Durability | Excellent in aggressive environments | Good under normal conditions; variable in harsh environments |
| Manufacturing | Cast in place or precast with specialized materials | Factory-produced under controlled conditions |
| Installation | Typically poured on-site; requires careful curing | Quick assembly; reduced on-site time |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized materials and additives | Moderate; benefits from mass production |
| Strength | Good compressive strength, tailored for chemical environments | High compressive and flexural strength, designed for structural needs |
| Typical Use | Industrial areas with acid exposure | General structural beam applications |
Introduction to Acid-Resistant Concrete and Precast Concrete
Acid-resistant concrete is specially formulated with corrosion inhibitors and dense aggregates to withstand harsh acidic environments, making it ideal for industrial applications such as chemical plants and wastewater treatment facilities. Precast concrete beams are manufactured in controlled factory settings, ensuring consistent quality, faster installation, and enhanced structural integrity for various construction projects. Comparing these two, acid-resistant concrete prioritizes durability against chemical attack, while precast concrete emphasizes precision and efficiency in construction.
Chemical Composition and Properties
Acid-resistant concrete for beams typically contains a higher proportion of silica fume, quartz aggregates, and specialized acid-resistant cement to enhance chemical durability against acidic environments, maintaining integrity in pH ranges as low as 2-4. Precast concrete beams primarily use standard Portland cement with uniform curing processes, optimized for structural strength and dimensional accuracy but lacking inherent chemical resistance. The acid-resistant mix exhibits lower permeability, increased resistance to chemical attack, and enhanced longevity in corrosive conditions compared to conventional precast concrete, which is vulnerable to acid-induced degradation without additional protective coatings.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Acid-resistant concrete beams are manufactured by incorporating specialized cementitious materials and chemical additives that enhance resistance to harsh acidic environments, requiring precise quality control during mixing and curing to ensure durability. Precast concrete beams are produced in controlled factory settings using standardized molds, allowing for uniform curing, high strength, and reduced on-site construction time. Manufacturing acid-resistant concrete demands careful selection of raw materials and stringent process monitoring, while precast beams emphasize efficiency and consistency through automation and repetitive casting techniques.
Durability in Aggressive Environments
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior durability in aggressive environments by incorporating chemical-resistant additives and dense microstructures that prevent acid penetration and degradation. Precast concrete beams provide consistent quality and controlled curing, but may require additional protective coatings to withstand acidic conditions effectively. Selecting acid-resistant concrete ensures enhanced longevity and reduced maintenance costs for beams exposed to harsh chemical exposures.
Structural Performance for Beams
Acid-resistant concrete offers enhanced durability and chemical resistance for beams exposed to aggressive environments, maintaining structural integrity by preventing corrosion of reinforcement and matrix degradation. Precast concrete beams provide high-quality control, uniformity, and faster installation, resulting in consistent structural performance with reduced curing time and minimal on-site errors. Structural performance in acid-exposed conditions favors acid-resistant concrete, while precast concrete excels in controlled fabrication and efficient construction timelines.
Installation and Construction Methods
Acid-resistant concrete beams require specialized mixing and curing processes to ensure chemical durability, often involving acid-resistant aggregates and coatings applied during casting. Precast concrete beams are manufactured off-site in controlled environments, enabling faster installation through modular assembly and minimizing on-site labor and curing time. Installation of acid-resistant beams demands careful handling and protective measures against chemical exposure, whereas precast beams rely on precise lifting and alignment techniques for efficient erection.
Cost Considerations and Budget Impact
Acid-resistant concrete typically incurs higher upfront costs due to specialized materials like acid-resistant aggregates and additives, impacting the budget significantly in projects requiring chemical durability. Precast concrete beams offer cost savings through standardized production, reduced labor, and faster installation, lowering overall project expenses. Budget impact analysis should weigh the long-term maintenance savings of acid-resistant concrete against the immediate cost efficiency of precast concrete solutions.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Expectations
Acid-resistant concrete beams exhibit superior durability in corrosive environments, significantly reducing maintenance frequency and extending lifecycle expectancy compared to standard precast concrete. Precast concrete beams, while cost-effective and quicker to install, may require more frequent inspections and repairs when exposed to acidic conditions, leading to higher long-term maintenance costs. Selecting acid-resistant concrete enhances structural longevity and minimizes lifecycle expenses in industrial or chemically aggressive settings.
Applications in Industrial and Infrastructure Projects
Acid-resistant concrete is essential in industrial projects where structures are exposed to harsh chemical environments, such as wastewater treatment plants and chemical processing facilities, ensuring durability and longevity by resisting corrosion from acidic substances. Precast concrete beams are favored in infrastructure projects like bridges, highways, and parking structures due to their high quality, uniformity, and rapid installation, significantly reducing construction time and improving structural performance. Choosing acid-resistant concrete enhances safety and maintenance efficiency in chemically aggressive settings, while precast concrete beams provide cost-effective solutions for large-scale infrastructure demands.
Choosing the Right Concrete Type for Beam Solutions
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior chemical durability, making it ideal for beams exposed to aggressive environments such as chemical plants or wastewater treatment facilities, where resistance to corrosion from acids and chemicals is critical. Precast concrete beams provide enhanced quality control, faster installation, and greater uniformity, suitable for projects with tight timelines and standardized structural requirements. Selecting the right beam solution depends on environmental exposure, project schedule, and long-term durability needs, with acid-resistant concrete favored for harsh chemical conditions and precast concrete preferred for efficiency and consistency.
Infographic: Acid-resistant concrete vs Precast concrete for Beam
 azmater.com
azmater.com