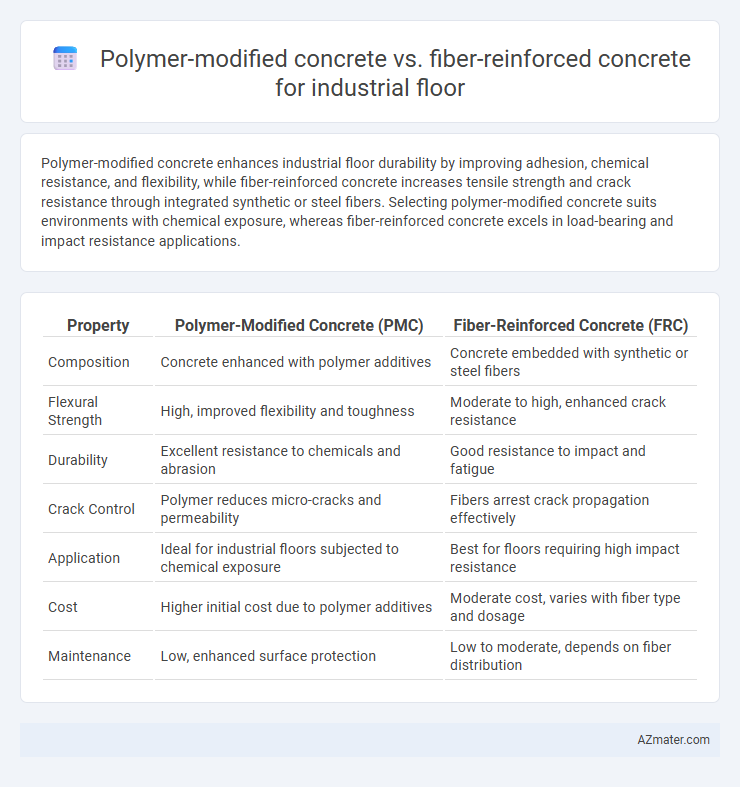
Polymer-modified concrete enhances industrial floor durability by improving adhesion, chemical resistance, and flexibility, while fiber-reinforced concrete increases tensile strength and crack resistance through integrated synthetic or steel fibers. Selecting polymer-modified concrete suits environments with chemical exposure, whereas fiber-reinforced concrete excels in load-bearing and impact resistance applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymer-Modified Concrete (PMC) | Fiber-Reinforced Concrete (FRC) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Concrete enhanced with polymer additives | Concrete embedded with synthetic or steel fibers |
| Flexural Strength | High, improved flexibility and toughness | Moderate to high, enhanced crack resistance |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to chemicals and abrasion | Good resistance to impact and fatigue |
| Crack Control | Polymer reduces micro-cracks and permeability | Fibers arrest crack propagation effectively |
| Application | Ideal for industrial floors subjected to chemical exposure | Best for floors requiring high impact resistance |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to polymer additives | Moderate cost, varies with fiber type and dosage |
| Maintenance | Low, enhanced surface protection | Low to moderate, depends on fiber distribution |
Introduction to Industrial Flooring Solutions
Polymer-modified concrete enhances industrial floors by improving durability, chemical resistance, and adhesion to substrates, making it ideal for heavy machinery and high-traffic environments. Fiber-reinforced concrete incorporates synthetic or steel fibers to increase tensile strength, reduce cracking, and improve impact resistance, ensuring long-term structural integrity. Both materials offer tailored solutions for industrial flooring, optimizing performance based on specific operational demands and environmental conditions.
What is Polymer-Modified Concrete?
Polymer-modified concrete (PMC) incorporates polymers such as latex, acrylics, or styrene-butadiene into the cement mixture to enhance adhesion, flexibility, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for industrial floor applications subjected to heavy loads and chemical exposure. This modification improves durability by reducing permeability and increasing impact resistance compared to conventional concrete. PMC is preferred in environments where increased tensile strength and enhanced bonding to substrates are critical for structural integrity and longevity.
What is Fiber-Reinforced Concrete?
Fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) incorporates fibrous materials such as steel, glass, synthetic, or natural fibers into the concrete mix to enhance its tensile strength, durability, and crack resistance, making it ideal for industrial floor applications. Unlike polymer-modified concrete, which relies on polymer additives to improve bonding and flexibility, FRC provides multidirectional reinforcement that controls shrinkage cracking and improves impact resistance under heavy loads. This structural enhancement reduces maintenance frequency and extends the service life of industrial floors exposed to high mechanical stress and chemical exposure.
Key Material Properties Compared
Polymer-modified concrete demonstrates superior adhesion, chemical resistance, and flexibility compared to fiber-reinforced concrete, making it ideal for industrial floors exposed to harsh chemicals and dynamic loads. Fiber-reinforced concrete offers enhanced tensile strength, crack resistance, and impact durability due to dispersed synthetic or steel fibers, improving structural integrity under heavy mechanical stress. Both materials increase durability but differ in key mechanical properties tailored to specific industrial floor requirements.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Polymer-modified concrete enhances industrial floor durability by improving adhesion and chemical resistance, making it highly effective against abrasion and corrosive environments. Fiber-reinforced concrete offers superior wear resistance through crack control and impact absorption, reducing surface degradation under heavy mechanical stress. Choosing polymer-modified concrete or fiber-reinforced concrete depends on specific durability needs, such as chemical exposure or mechanical load intensity in industrial settings.
Installation and Workability Differences
Polymer-modified concrete offers enhanced adhesion and flexibility during installation, allowing for quicker setting times and easier finishing on industrial floors. Fiber-reinforced concrete improves workability by reducing segregation and shrinkage, providing uniform mixing and enhanced tensile strength without compromising flowability. Installation of fiber-reinforced concrete may require less surface preparation compared to polymer-modified variants, which often need priming for optimal bonding.
Performance Under Heavy Loads
Polymer-modified concrete enhances industrial floor performance under heavy loads by improving adhesion, reducing permeability, and increasing tensile strength, resulting in better resistance to cracking and chemical attacks. Fiber-reinforced concrete incorporates synthetic or steel fibers that distribute stress and increase toughness, significantly improving impact resistance and load-bearing capacity. For industrial floors subjected to dynamic heavy loads and repetitive stress, fiber-reinforced concrete offers superior durability and tensile strength compared to polymer-modified options.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Costs
Polymer-modified concrete offers enhanced chemical resistance and reduced permeability, leading to lower maintenance demands in industrial floors subjected to harsh environments. Fiber-reinforced concrete improves crack control and impact resistance, which extends lifespan by mitigating structural damage and reducing repair frequency. Lifecycle cost analysis typically favors fiber-reinforced concrete for high-traffic areas due to its durability, while polymer-modified variants excel where chemical exposure drives maintenance expenses.
Suitability for Industrial Floor Applications
Polymer-modified concrete offers enhanced adhesion, chemical resistance, and flexibility, making it suitable for industrial floors exposed to heavy machinery and chemical spills. Fiber-reinforced concrete improves tensile strength and crack control, ideal for floors subjected to high impact and dynamic loads in industrial environments. Choosing between the two depends on specific industrial floor requirements such as load-bearing capacity, exposure conditions, and durability expectations.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Solution
Polymer-modified concrete offers superior chemical resistance and adhesion properties, making it ideal for industrial floors exposed to harsh chemicals and heavy mechanical stress. Fiber-reinforced concrete provides enhanced tensile strength and crack resistance, improving durability under dynamic loads typical in industrial environments. Selecting the best solution depends on specific site conditions, load requirements, and exposure factors, with polymer modifications favored for chemical resilience and fibers preferred for structural robustness.
Infographic: Polymer-modified concrete vs Fiber-reinforced concrete for Industrial floor
 azmater.com
azmater.com