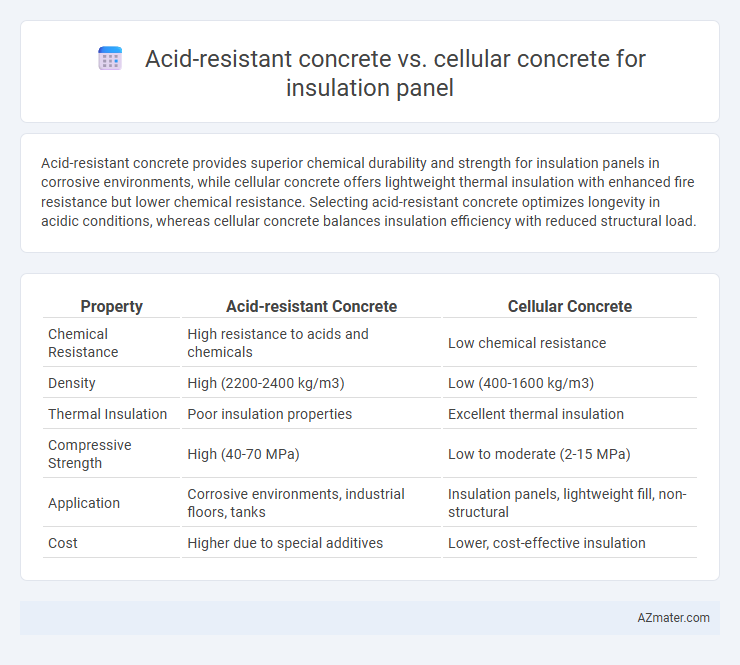
Acid-resistant concrete provides superior chemical durability and strength for insulation panels in corrosive environments, while cellular concrete offers lightweight thermal insulation with enhanced fire resistance but lower chemical resistance. Selecting acid-resistant concrete optimizes longevity in acidic conditions, whereas cellular concrete balances insulation efficiency with reduced structural load.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acid-resistant Concrete | Cellular Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to acids and chemicals | Low chemical resistance |
| Density | High (2200-2400 kg/m3) | Low (400-1600 kg/m3) |
| Thermal Insulation | Poor insulation properties | Excellent thermal insulation |
| Compressive Strength | High (40-70 MPa) | Low to moderate (2-15 MPa) |
| Application | Corrosive environments, industrial floors, tanks | Insulation panels, lightweight fill, non-structural |
| Cost | Higher due to special additives | Lower, cost-effective insulation |
Understanding Acid-Resistant Concrete: Key Properties
Acid-resistant concrete features a dense, non-porous matrix enhanced with chemically stable aggregates like quartz or flint, which provide exceptional resistance to acidic environments. Its high compressive strength and low permeability prevent acid penetration, making it ideal for industrial insulation panels exposed to harsh chemical conditions. In contrast, cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation due to its lightweight, porous structure but lacks the chemical durability necessary for acid resistance applications.
Cellular Concrete: Composition and Basic Characteristics
Cellular concrete is composed of cement, water, fine aggregates, and a foaming agent that introduces air bubbles to create a lightweight, porous structure. Its basic characteristics include high thermal insulation, low density, and excellent fire resistance, making it ideal for insulation panels. Compared to acid-resistant concrete, cellular concrete offers superior thermal performance and ease of installation due to its reduced weight.
Comparative Overview: Acid-Resistant vs Cellular Concrete
Acid-resistant concrete exhibits superior chemical durability and high compressive strength, making it ideal for environments exposed to aggressive acids and industrial chemicals, while cellular concrete offers excellent thermal insulation due to its porous structure and low density, enhancing energy efficiency in building panels. Acid-resistant concrete's dense matrix resists corrosion and extends service life in harsh chemical conditions, whereas cellular concrete provides better sound absorption and fire resistance properties with lower weight. Selection between the two depends on the primary application needs: durability under chemical attack versus insulation performance and structural weight considerations.
Thermal Insulation Performance in Both Concrete Types
Acid-resistant concrete exhibits moderate thermal insulation performance due to its dense matrix and chemical additives designed to enhance durability against corrosive environments. Cellular concrete outperforms acid-resistant concrete in thermal insulation because of its porous structure, which traps air and reduces heat transfer significantly. Thermal conductivity values for cellular concrete typically range between 0.1 to 0.3 W/m*K, substantially lower than the 0.8 to 1.2 W/m*K observed in acid-resistant concrete, making cellular concrete more effective for insulation panel applications.
Durability and Chemical Resistance Analysis
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior durability and chemical resistance due to its dense matrix and specialized cementitious materials that protect against harsh acidic environments, making it ideal for insulation panels exposed to aggressive chemicals. Cellular concrete, while lightweight and providing excellent thermal insulation, has lower chemical resistance and can degrade faster when exposed to acidic substances, limiting its long-term durability in such applications. For insulation panels requiring both structural integrity and robust chemical resistance, acid-resistant concrete remains the more reliable choice.
Weight and Density Considerations for Insulation Panels
Acid-resistant concrete typically exhibits higher density, ranging from 2200 to 2500 kg/m3, resulting in heavier insulation panels that provide superior durability in corrosive environments. Cellular concrete, with a significantly lower density between 300 to 1600 kg/m3, offers lightweight insulation panels that enhance thermal performance and ease of installation. Weight considerations are crucial for structural load limitations, making cellular concrete preferable where minimal dead load and improved insulation efficiency are prioritized.
Installation Methods and Construction Advantages
Acid-resistant concrete installation involves precise batching and mixing to ensure chemical stability, typically poured or cast in molds on-site for durability in harsh environments. Cellular concrete panels are lightweight and self-leveling, allowing easy cutting and fitting during installation, which reduces labor time and improves thermal insulation performance. The construction advantages of acid-resistant concrete include superior chemical resistance and long-term durability, while cellular concrete offers excellent insulation properties, reduced structural load, and faster project completion.
Cost Analysis: Material and Long-term Maintenance
Acid-resistant concrete incurs higher initial material costs due to specialized additives and manufacturing processes compared to cellular concrete, which is more economical and lightweight. Long-term maintenance expenses for acid-resistant concrete are lower because of its enhanced durability and resistance to chemical degradation, reducing repair frequency. Cellular concrete panels may require more frequent inspections and potential replacements over time, increasing overall lifecycle costs despite their affordable upfront price.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Factors
Acid-resistant concrete offers enhanced durability in corrosive environments, reducing maintenance frequency and associated resource consumption, but tends to have a higher carbon footprint due to specialized raw materials and production processes. Cellular concrete, characterized by its lightweight and porous structure, provides superior thermal insulation and lower embodied energy, contributing to reduced operational energy use and improved sustainability. The environmental impact of cellular concrete is generally lower, making it a preferable choice for insulation panels aimed at minimizing resource depletion and promoting eco-friendly construction practices.
Best Applications: Selecting the Right Concrete for Insulation Panels
Acid-resistant concrete is best suited for insulation panels in industrial environments where chemical exposure and corrosion resistance are critical, such as in wastewater treatment plants and chemical processing facilities. Cellular concrete, known for its lightweight and thermal insulation properties, excels in applications requiring energy efficiency and ease of installation, including building envelope insulation and flooring underlays. Choosing the right concrete hinges on evaluating factors like chemical resistance, thermal performance, and structural requirements specific to the insulation panel's end-use environment.
Infographic: Acid-resistant concrete vs Cellular concrete for Insulation panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com