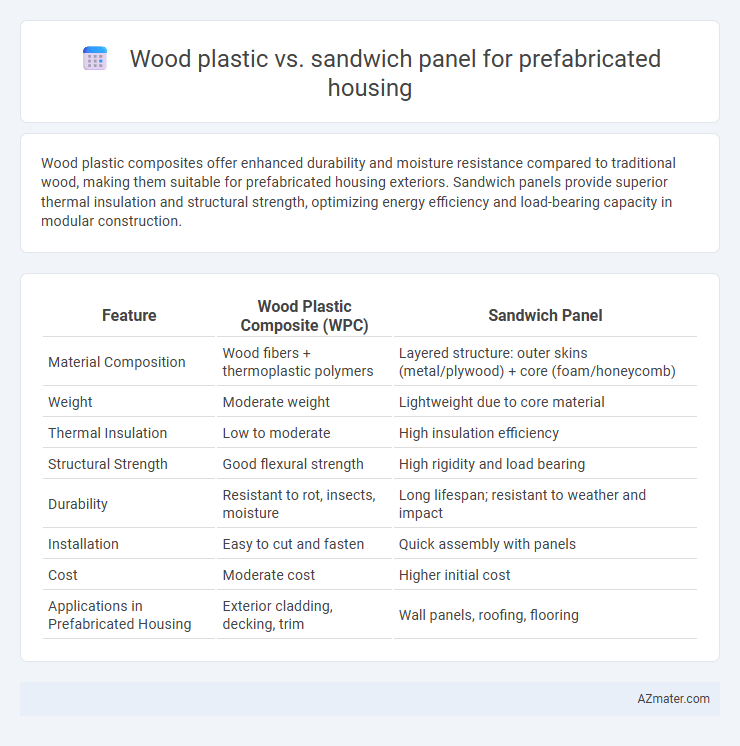
Wood plastic composites offer enhanced durability and moisture resistance compared to traditional wood, making them suitable for prefabricated housing exteriors. Sandwich panels provide superior thermal insulation and structural strength, optimizing energy efficiency and load-bearing capacity in modular construction.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wood Plastic Composite (WPC) | Sandwich Panel |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Wood fibers + thermoplastic polymers | Layered structure: outer skins (metal/plywood) + core (foam/honeycomb) |
| Weight | Moderate weight | Lightweight due to core material |
| Thermal Insulation | Low to moderate | High insulation efficiency |
| Structural Strength | Good flexural strength | High rigidity and load bearing |
| Durability | Resistant to rot, insects, moisture | Long lifespan; resistant to weather and impact |
| Installation | Easy to cut and fasten | Quick assembly with panels |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher initial cost |
| Applications in Prefabricated Housing | Exterior cladding, decking, trim | Wall panels, roofing, flooring |
Introduction to Prefabricated Housing Materials
Wood plastic composites and sandwich panels serve as advanced materials in prefabricated housing, combining structural strength with lightweight properties. Wood plastic composites offer enhanced durability, moisture resistance, and eco-friendliness by integrating recycled wood fibers with plastic polymers. Sandwich panels, composed of insulating cores such as foam or mineral wool between rigid outer layers, provide superior thermal insulation and load-bearing capabilities, making them ideal for energy-efficient and rapid assembly in modular construction.
Overview of Wood Plastic Composites
Wood Plastic Composites (WPC) combine wood fibers and thermoplastics, offering enhanced durability, resistance to moisture, and low maintenance for prefabricated housing applications. WPC panels provide excellent thermal insulation and soundproofing properties, making them suitable for energy-efficient and comfortable living spaces. Compared to sandwich panels, WPC materials are more resistant to rot and insects but may have lower structural strength and fire resistance, requiring careful consideration in design choices.
Key Features of Sandwich Panels
Sandwich panels for prefabricated housing consist of two outer metal sheets with an insulating core, offering superior thermal insulation, lightweight structure, and high structural strength compared to wood plastic composites. Their fire resistance, moisture resistance, and ease of installation make them ideal for rapid construction in diverse climates. These panels also provide excellent soundproofing and durability, ensuring long-term performance and minimal maintenance.
Thermal Insulation Performance: Wood Plastic vs Sandwich Panels
Wood plastic composites exhibit moderate thermal insulation due to the natural insulating properties of wood fibers combined with plastic's thermal resistance, making them suitable for energy-efficient prefabricated housing. Sandwich panels, especially those with polyurethane or polystyrene cores, outperform wood plastic in thermal insulation by offering higher R-values and enhanced energy savings. Choosing sandwich panels ensures superior thermal performance in prefabricated housing, optimizing temperature regulation and reducing HVAC energy consumption.
Structural Strength and Durability Comparison
Wood plastic composites offer enhanced resistance to moisture, insects, and rot, providing consistent structural integrity over time, making them suitable for humid or variable climates in prefabricated housing. Sandwich panels, composed of rigid foam cores between metal or fiber-reinforced facings, deliver superior load-bearing capacity and thermal insulation, ensuring robust structural strength and energy efficiency. While wood plastic composites excel in flexibility and weather resistance, sandwich panels outperform in rigidity and long-term durability under heavy structural demands.
Moisture and Weather Resistance
Wood plastic composites offer enhanced moisture resistance due to their synthetic polymer matrix, preventing water absorption and reducing the risk of warping or mold growth in prefabricated housing. Sandwich panels, typically composed of insulating foam core bonded between two metal or composite facings, provide superior weather resistance with excellent thermal insulation and protection against moisture infiltration. Both materials improve durability in varying climates, but sandwich panels excel in maintaining structural integrity under extreme weather conditions.
Installation and Construction Efficiency
Wood plastic composite panels enable faster installation in prefabricated housing due to lightweight properties and ease of handling, reducing labor costs and construction time. Sandwich panels offer superior insulation and structural strength but often require more precise alignment and specialized equipment, which can extend installation duration. Choosing wood plastic panels enhances construction efficiency for projects prioritizing speed, while sandwich panels suit builds emphasizing durability and thermal performance.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Wood plastic composites for prefabricated housing offer enhanced durability and recyclability due to their blend of natural fibers and recycled plastics, reducing reliance on virgin materials. Sandwich panels, often composed of insulating foam cores between metal or plywood facings, provide superior thermal efficiency but may involve non-biodegradable components that challenge end-of-life disposal. Evaluating sustainability, wood plastic composites typically present lower embodied energy and better circularity, while sandwich panels excel in insulation performance that contributes to long-term energy savings in prefabricated structures.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-term Investment
Wood plastic composites generally offer a lower initial cost compared to sandwich panels due to cheaper raw materials and simpler manufacturing processes. Sandwich panels, while more expensive upfront, provide superior insulation and structural strength, resulting in significant long-term energy savings and reduced maintenance expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals sandwich panels as a more cost-effective solution for prefabricated housing over time due to durability and efficiency benefits.
Best Applications for Wood Plastic and Sandwich Panels in Prefab Homes
Wood plastic composites (WPC) are best suited for exterior elements in prefabricated housing due to their high durability, weather resistance, and low maintenance requirements, making them ideal for cladding, decking, and window frames. Sandwich panels, composed of insulating core material such as polyurethane or polystyrene between metal or composite facings, excel in wall and roof systems where thermal insulation, structural strength, and quick installation are critical for energy-efficient prefab homes. Both materials contribute to sustainable construction, but WPC emphasizes aesthetic durability in external applications, while sandwich panels prioritize insulation performance and structural integrity in building envelopes.
Infographic: Wood plastic vs Sandwich panel for Prefabricated housing
 azmater.com
azmater.com