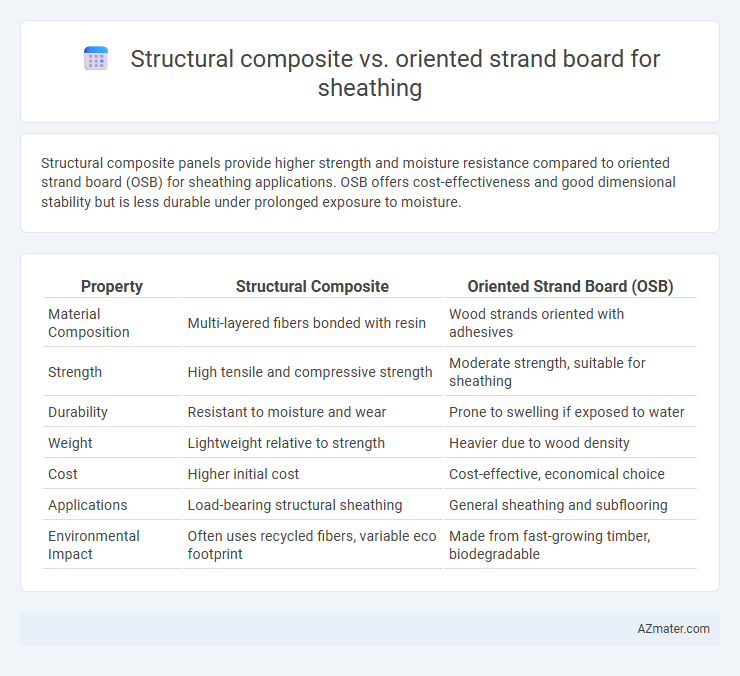
Structural composite panels provide higher strength and moisture resistance compared to oriented strand board (OSB) for sheathing applications. OSB offers cost-effectiveness and good dimensional stability but is less durable under prolonged exposure to moisture.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Structural Composite | Oriented Strand Board (OSB) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Multi-layered fibers bonded with resin | Wood strands oriented with adhesives |
| Strength | High tensile and compressive strength | Moderate strength, suitable for sheathing |
| Durability | Resistant to moisture and wear | Prone to swelling if exposed to water |
| Weight | Lightweight relative to strength | Heavier due to wood density |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Cost-effective, economical choice |
| Applications | Load-bearing structural sheathing | General sheathing and subflooring |
| Environmental Impact | Often uses recycled fibers, variable eco footprint | Made from fast-growing timber, biodegradable |
Introduction to Wall Sheathing Materials
Structural composite panels (SCP) and oriented strand board (OSB) are essential wall sheathing materials used in residential and commercial construction. Structural composite panels offer superior strength, durability, and moisture resistance compared to OSB, making them ideal for high-performance building envelopes. OSB remains a cost-effective option with adequate structural properties and widespread availability, but its susceptibility to water damage requires careful installation and vapor barrier application.
Overview of Structural Composite Panels
Structural composite panels (SCPs) provide enhanced strength, moisture resistance, and dimensional stability compared to oriented strand board (OSB), making SCPs a superior choice for sheathing applications in high-performance buildings. SCPs are engineered from layers of wood veneers or fibers bonded with adhesives under heat and pressure, resulting in a uniform panel with consistent structural properties. This manufacturing process allows SCPs to offer better load distribution, resistance to warping, and improved thermal and acoustic insulation compared to traditional OSB sheathing.
Understanding Oriented Strand Board (OSB)
Oriented Strand Board (OSB) is a structural composite panel made by compressing layers of wood strands arranged in specific orientations, enhancing strength and rigidity for sheathing applications. OSB offers superior shear resistance and moisture durability compared to traditional plywood, making it a cost-effective and reliable choice for wall, roof, and floor sheathing. Its uniform composition and engineered design provide consistent performance, crucial for structural stability and building envelope protection.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Structural composite panels (SCP) and oriented strand board (OSB) differ significantly in strength, stiffness, and durability. SCP typically offers higher shear strength and improved moisture resistance due to its engineered fiber alignment and resin formulation, making it ideal for load-bearing sheathing applications. OSB, composed of layered wood strands, provides cost-effective stiffness and adequate nail-holding capacity but may be more susceptible to swelling and degradation under prolonged moisture exposure.
Strength and Load-Bearing Capabilities
Structural composite panels (SCP) and oriented strand board (OSB) serve as crucial materials in sheathing, with SCP generally offering superior strength and load-bearing capabilities due to engineered fiber alignment and resin bonding techniques. OSB, composed of compressed wood strands arranged in cross-oriented layers, provides adequate structural support but typically features lower modulus of elasticity and bending strength compared to structural composite materials. For applications demanding high load resistance and rigidity, SCP demonstrates enhanced performance in shear strength and dimensional stability, making it preferable in heavy-load-bearing wall and roof systems.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
Structural composites like plywood offer superior moisture resistance and long-term durability compared to oriented strand board (OSB) due to their cross-laminated veneer construction, which limits water absorption. OSB tends to swell and degrade faster when exposed to humidity or direct water contact, making it less ideal for high-moisture environments. Choosing plywood for sheathing can extend the lifespan of the structure by minimizing moisture-related damage and maintaining structural integrity.
Installation and Workability Differences
Structural composite panels offer faster installation due to their uniform thickness and lightweight properties, allowing easier handling and cutting compared to oriented strand board (OSB). OSB requires more effort to cut precisely because of its dense, layered structure, which can slow down the work process on-site. The dimensional stability of structural composites reduces the risk of warping, improving overall workability during sheathing applications.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Oriented Strand Board (OSB) offers a lower cost advantage compared to Structural Composite Panels (SCP) for sheathing applications due to more abundant raw materials and simpler manufacturing processes. OSB is widely available in major markets, benefiting from established supply chains and standardized sizes that reduce overall project expenses. Structural Composite Panels, while typically more expensive, provide enhanced durability but face limited availability which can increase lead times and logistical costs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Structural composite panels (SCPs) typically use recycled wood fibers and formaldehyde-free adhesives, resulting in lower volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and enhanced sustainability compared to oriented strand board (OSB). OSB production, while efficient in utilizing small-diameter trees, involves more energy-intensive processes and synthetic resin adhesives that can release formaldehyde, contributing to greater environmental impact. Choosing SCPs for sheathing promotes reduced deforestation and improved air quality, supporting eco-friendly building practices and LEED certification goals.
Choosing the Right Sheathing Material
Structural composite panels offer superior strength and uniformity, making them ideal for load-bearing sheathing applications where durability and moisture resistance are crucial. Oriented strand board (OSB) provides a cost-effective sheathing solution with good shear strength but may be more susceptible to swelling and degradation in high-moisture environments. Selecting the right sheathing material depends on climate conditions, budget constraints, and specific structural requirements to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Structural composite vs Oriented strand board for Sheathing
 azmater.com
azmater.com