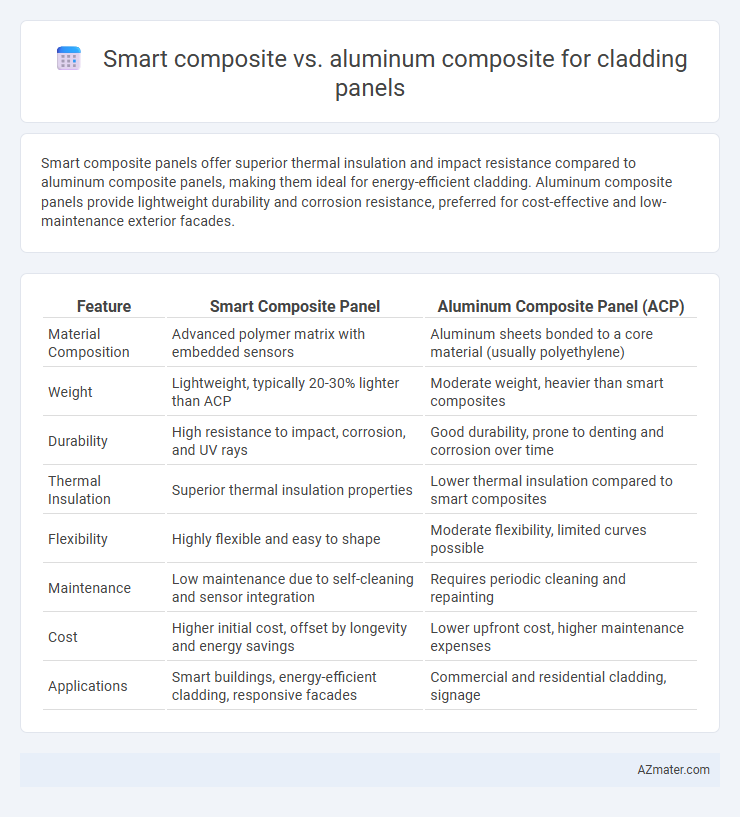
Smart composite panels offer superior thermal insulation and impact resistance compared to aluminum composite panels, making them ideal for energy-efficient cladding. Aluminum composite panels provide lightweight durability and corrosion resistance, preferred for cost-effective and low-maintenance exterior facades.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Smart Composite Panel | Aluminum Composite Panel (ACP) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Advanced polymer matrix with embedded sensors | Aluminum sheets bonded to a core material (usually polyethylene) |
| Weight | Lightweight, typically 20-30% lighter than ACP | Moderate weight, heavier than smart composites |
| Durability | High resistance to impact, corrosion, and UV rays | Good durability, prone to denting and corrosion over time |
| Thermal Insulation | Superior thermal insulation properties | Lower thermal insulation compared to smart composites |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and easy to shape | Moderate flexibility, limited curves possible |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to self-cleaning and sensor integration | Requires periodic cleaning and repainting |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, offset by longevity and energy savings | Lower upfront cost, higher maintenance expenses |
| Applications | Smart buildings, energy-efficient cladding, responsive facades | Commercial and residential cladding, signage |
Introduction to Cladding Panels
Cladding panels serve as protective and decorative facades for buildings, enhancing durability and aesthetics. Smart composite panels integrate advanced materials offering improved thermal insulation and lightweight properties compared to traditional aluminum composite panels. Aluminum composite panels remain popular for their strength, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness in exterior cladding applications.
Overview of Smart Composite Materials
Smart composite materials for cladding panels consist of advanced fiber-reinforced polymers with integrated sensing capabilities, offering superior strength-to-weight ratios and environmental resistance compared to traditional aluminum composites. These materials enhance building envelope performance by providing thermal insulation, impact resistance, and real-time structural health monitoring through embedded sensors. Their adaptability in design, durability, and energy efficiency makes smart composites a cutting-edge alternative in modern architectural cladding applications.
Overview of Aluminum Composite Panels
Aluminum composite panels (ACP) consist of two aluminum sheets bonded to a non-aluminum core, offering durability, lightweight properties, and resistance to corrosion and weathering for cladding applications. ACPs provide high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent flatness, making them ideal for architectural facades and exterior cladding systems. These panels also offer fire-resistant options and various finishes, contributing to versatile aesthetic and safety features in modern building designs.
Key Differences Between Smart and Aluminum Composites
Smart composites feature advanced polymers and nanomaterials that offer superior impact resistance and thermal insulation compared to traditional aluminum composite panels, making them ideal for energy-efficient building facades. Aluminum composites, made from aluminum sheets bonded to a non-aluminum core, provide excellent durability, lightweight properties, and fire resistance but lack the enhanced adaptability and eco-friendly traits of smart composites. The key differences lie in smart composites' enhanced performance in sustainability, flexibility, and insulation versus aluminum composites' emphasis on structural strength and cost-effectiveness.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Smart composite panels exhibit superior impact resistance and tensile strength compared to aluminum composite panels, making them ideal for high-stress cladding applications. Aluminum composite panels provide excellent rigidity and weather resistance but generally lack the enhanced flexibility and energy absorption characteristics found in smart composites. The advanced mechanical properties of smart composites contribute to improved durability and longer service life in architectural cladding systems.
Durability and Lifespan Analysis
Smart composite cladding panels exhibit superior durability due to enhanced resistance to corrosion, UV radiation, and impact compared to traditional aluminum composite panels. Aluminum composite panels typically offer a lifespan of 20-30 years, whereas smart composites can extend durability up to 40 years through advanced protective coatings and material innovation. This extended lifespan reduces maintenance costs and improves long-term structural integrity in harsh environmental conditions.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Performance
Smart composite panels offer superior thermal insulation due to their multi-layered construction incorporating advanced insulating cores, reducing heat transfer more effectively than aluminum composite panels. Acoustic performance is enhanced in smart composites by integrating sound-dampening materials that minimize noise penetration, whereas aluminum composites typically provide moderate sound insulation primarily through their metal layers. These attributes make smart composite panels a preferred choice in building cladding applications where energy efficiency and noise reduction are critical.
Fire Resistance and Safety Features
Smart composite panels demonstrate superior fire resistance compared to aluminum composite panels, often incorporating fire-retardant cores like mineral-filled or non-combustible materials that significantly reduce flame spread and smoke emission. Aluminum composite panels, particularly those with polyethylene cores, are more susceptible to ignition and rapid flame propagation, posing higher fire hazards in building applications. Enhanced safety features in smart composites include compliance with stringent fire safety standards such as ASTM E84 Class A ratings and EN 13501-1 classifications, ensuring better protection in cladding systems.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Smart composite panels typically offer better environmental performance than aluminum composite panels due to their use of recycled and eco-friendly raw materials, reducing carbon footprint significantly. Aluminum composite panels, while durable and recyclable, require intensive energy for aluminum extraction and manufacturing, contributing to higher greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable cladding choices favor smart composites for their lower embodied energy and potential for improved thermal insulation, enhancing overall building energy efficiency.
Cost-Effectiveness and Application Suitability
Smart composite panels offer enhanced durability and weather resistance, making them highly suitable for exterior cladding in harsh environments while typically costing 10-15% more than aluminum composite panels. Aluminum composite panels provide a cost-effective solution with excellent lightweight properties and ease of installation, preferred for commercial buildings requiring budget-friendly options. Both materials excel in facade applications, but smart composites deliver better longevity and maintenance savings, balancing initial expenditure with long-term value.
Infographic: Smart composite vs Aluminum composite for Cladding panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com