Sandwich structure doors offer superior thermal insulation and lightweight strength compared to traditional plywood doors, which provide durability and natural aesthetics. Sandwich panels feature core materials like foam or honeycomb, enhancing energy efficiency, while plywood relies on layered wood veneers for structural integrity.
Table of Comparison
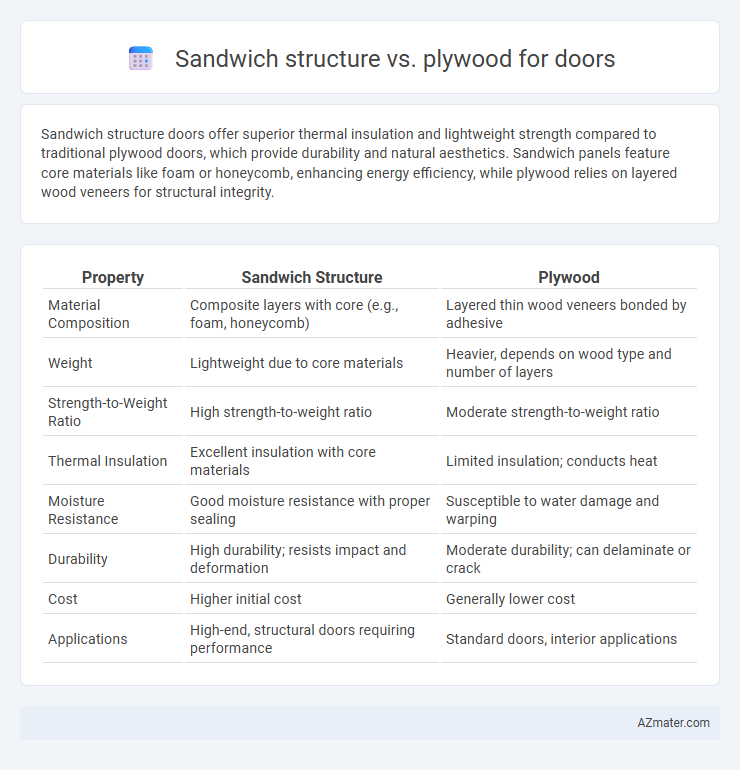
| Property | Sandwich Structure | Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Composite layers with core (e.g., foam, honeycomb) | Layered thin wood veneers bonded by adhesive |
| Weight | Lightweight due to core materials | Heavier, depends on wood type and number of layers |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | High strength-to-weight ratio | Moderate strength-to-weight ratio |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent insulation with core materials | Limited insulation; conducts heat |
| Moisture Resistance | Good moisture resistance with proper sealing | Susceptible to water damage and warping |
| Durability | High durability; resists impact and deformation | Moderate durability; can delaminate or crack |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Generally lower cost |
| Applications | High-end, structural doors requiring performance | Standard doors, interior applications |
Introduction to Door Material Choices
Sandwich structure doors offer superior insulation and lightweight properties due to their core materials like foam or honeycomb, making them ideal for energy efficiency and ease of installation. Plywood doors provide durability and strength through layered wood veneers, ensuring resistance to warping and enhanced structural integrity. Both materials serve distinct functional and aesthetic purposes, guiding homeowners in selecting doors based on environmental conditions and design preferences.
What is Sandwich Structure?
Sandwich structure doors consist of a lightweight core material, such as foam or honeycomb, enclosed between two outer layers, typically made of plywood or MDF, providing enhanced strength and insulation compared to traditional plywood doors. This structure offers superior thermal and acoustic insulation properties, making it ideal for energy-efficient and noise-reducing applications. Sandwich structure doors also exhibit improved durability and resistance to warping, often outperforming standard plywood doors in longevity and maintenance.
Understanding Plywood Door Construction
Plywood doors consist of multiple thin layers of wood veneer glued together with grains alternating direction, providing enhanced strength, durability, and resistance to warping compared to sandwich structures. Sandwich door cores typically involve a lightweight material such as foam or honeycomb between two veneer layers, which prioritizes weight reduction and insulation but often sacrifices structural integrity found in solid plywood construction. Understanding plywood door construction is vital for applications requiring robust, impact-resistant doors with superior load-bearing capacity and long-term dimensional stability.
Comparative Strength and Durability
Sandwich structures, featuring a lightweight core between two face sheets, offer superior strength-to-weight ratios compared to plywood, which consists of multiple thin wood veneers glued together. The composite design of sandwich panels enhances resistance to bending and impact, providing increased durability under varying environmental conditions. Plywood, while durable and cost-effective, tends to be more susceptible to moisture damage and delamination over time, making sandwich structures a preferable choice for applications demanding long-term structural integrity.
Insulation Properties: Sandwich Structure vs Plywood
Sandwich structures provide superior thermal and acoustic insulation compared to plywood due to their multi-layered composition with insulating core materials like foam or honeycomb. Plywood, made from layers of wood veneer, offers lower insulation efficiency because wood's density and grain promote heat transfer and sound transmission. The enhanced insulation properties of sandwich doors make them ideal for energy-efficient buildings and noise reduction applications.
Weight and Handling Differences
Sandwich structure doors typically weigh less than plywood doors due to their core materials such as foam or honeycomb, allowing easier handling and installation. Plywood doors, composed of multiple wood veneers, are denser and heavier, which can make them more cumbersome to maneuver and require more support during installation. The reduced weight of sandwich structure doors contributes to improved energy efficiency and less strain on hinges and frames compared to traditional plywood doors.
Cost Comparison: Sandwich Structure vs Plywood
Sandwich structure doors typically incur higher initial costs than plywood doors due to advanced materials like foam cores and composite layers, which enhance insulation and durability. Plywood doors offer a more budget-friendly option, leveraging readily available wood veneers bonded to a core, resulting in lower manufacturing expenses. Long-term cost efficiency may favor sandwich structures, as their superior thermal performance and resistance to warping reduce maintenance and replacement needs compared to traditional plywood doors.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Sandwich structure doors provide superior design flexibility with customizable core materials and veneers, allowing for a wide range of textures, finishes, and colors to suit modern aesthetics. Plywood doors, while durable and cost-effective, offer limited surface customization due to their fixed veneer layers, restricting intricate design options. The lightweight nature of sandwich doors supports sleek, contemporary styles, whereas plywood tends to favor traditional, robust appearances.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sandwich structure doors typically use foam cores and composite skins that offer superior insulation and durability but may involve synthetic materials with higher environmental footprints. Plywood doors utilize layers of natural wood veneers bonded with adhesives, making them more biodegradable and often sourced from renewable forestry, contributing to lower carbon emissions. Choosing plywood supports sustainable forestry practices, while sandwich structures can enhance energy efficiency, requiring a balanced assessment of material origin and lifecycle impact.
Which Option is Best for Your Door?
Sandwich structure doors offer superior insulation and lightweight durability due to their core materials like polystyrene or polyurethane, making them ideal for energy efficiency and soundproofing. Plywood doors provide excellent strength and resistance to warping, with a natural wood grain finish that enhances aesthetic appeal and durability in varied humidity conditions. Choosing the best option depends on your priorities: opt for sandwich structure doors for thermal performance and noise reduction or plywood doors for structural robustness and classic wood appearance.
Infographic: Sandwich structure vs Plywood for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com