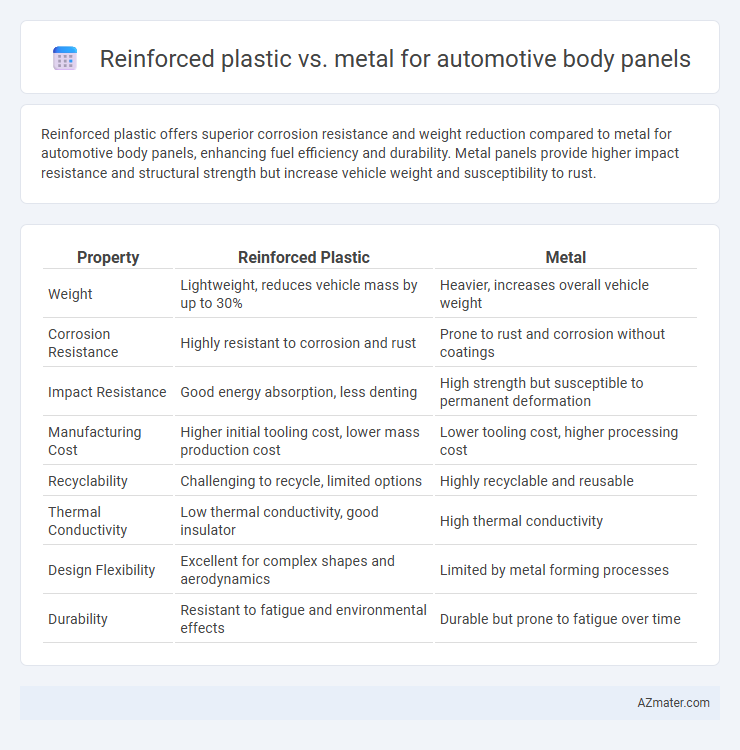
Reinforced plastic offers superior corrosion resistance and weight reduction compared to metal for automotive body panels, enhancing fuel efficiency and durability. Metal panels provide higher impact resistance and structural strength but increase vehicle weight and susceptibility to rust.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Reinforced Plastic | Metal |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces vehicle mass by up to 30% | Heavier, increases overall vehicle weight |
| Corrosion Resistance | Highly resistant to corrosion and rust | Prone to rust and corrosion without coatings |
| Impact Resistance | Good energy absorption, less denting | High strength but susceptible to permanent deformation |
| Manufacturing Cost | Higher initial tooling cost, lower mass production cost | Lower tooling cost, higher processing cost |
| Recyclability | Challenging to recycle, limited options | Highly recyclable and reusable |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low thermal conductivity, good insulator | High thermal conductivity |
| Design Flexibility | Excellent for complex shapes and aerodynamics | Limited by metal forming processes |
| Durability | Resistant to fatigue and environmental effects | Durable but prone to fatigue over time |
Introduction to Automotive Body Panel Materials
Automotive body panels primarily utilize reinforced plastics and metals, each offering distinct advantages in weight, durability, and cost. Reinforced plastics, such as fiberglass and carbon fiber composites, provide high strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and design flexibility. Metals like steel and aluminum remain popular for their superior impact resistance and ease of manufacturing, balancing performance with traditional manufacturing processes.
Overview of Reinforced Plastics in Automotive Applications
Reinforced plastics in automotive body panels offer a significant reduction in weight compared to traditional metals, enhancing fuel efficiency and vehicle performance. These composites, often made from fiberglass or carbon fiber combined with resin, provide exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance. Their ability to be molded into complex shapes enables automotive manufacturers to achieve innovative designs and improved impact resistance.
Traditional Role of Metals in Vehicle Body Panels
Metals such as steel and aluminum have traditionally dominated automotive body panels due to their high strength, durability, and excellent impact resistance. These materials provide structural integrity and enhanced safety in collision scenarios, while allowing for efficient manufacturing processes like stamping and welding. Despite the rise of reinforced plastics, metals remain preferred for their recyclability and ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions without significant degradation.
Weight Comparison: Reinforced Plastic vs Metal
Reinforced plastic automotive body panels typically weigh 30-50% less than traditional metal panels, significantly enhancing fuel efficiency and vehicle performance. These composite materials offer high strength-to-weight ratios by combining fibers such as carbon or glass with polymer resins, reducing overall mass without compromising structural integrity. In contrast, metal panels, often made from steel or aluminum, provide durability but contribute to higher vehicle weight, impacting acceleration and emissions negatively.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Reinforced plastic automotive body panels offer high strength-to-weight ratios, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and corrosion resistance compared to traditional metal panels. Metal panels, typically made from steel or aluminum, provide superior impact resistance and long-term durability under extreme environmental stress and mechanical loading. Evaluations show that while reinforced plastics excel in resistance to fatigue and chemical degradation, metals maintain advantages in structural rigidity and repairability in collision scenarios.
Corrosion and Weather Resistance
Reinforced plastic offers superior corrosion resistance compared to metal body panels, as it does not oxidize or rust when exposed to moisture and road salts. Weather resistance in reinforced plastics ensures long-term durability against UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, and harsh environmental conditions without degradation. Metal panels require protective coatings and regular maintenance to prevent corrosion and weathering, increasing lifecycle costs and potential for structural damage over time.
Manufacturing and Processing Considerations
Reinforced plastic offers advantages in lightweight construction and corrosion resistance, reducing vehicle weight and improving fuel efficiency compared to metal. Manufacturing processes for reinforced plastic, such as injection molding and compression molding, enable complex shapes with fewer assembly steps, while metal panels typically require stamping and welding operations. Processing reinforced plastic often results in lower tooling costs and faster production cycles, but metal remains preferred for high-strength applications due to its durability and impact resistance.
Cost Implications in Production
Reinforced plastic automotive body panels offer significant cost advantages in production due to lower material weight, reduced tooling expenses, and faster molding cycles compared to metal panels. Metal panels, while often more expensive in raw material and processing costs, require energy-intensive stamping and finishing techniques that increase overall manufacturing expenses. The choice impacts not only upfront production costs but also influences long-term assembly and transportation expenses linked to vehicle weight and durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Reinforced plastic automotive body panels offer significant weight reduction compared to metal, leading to improved fuel efficiency and lower carbon emissions throughout the vehicle's lifecycle. Although metal panels are highly recyclable, reinforced plastics increasingly incorporate bio-based resins and recyclable fibers, enhancing their sustainability profile. The environmental impact of reinforced plastics is mitigated by advances in recycling technologies and reduced energy consumption during production, positioning them as a viable alternative to traditional metal panels in sustainable automotive design.
Future Trends in Automotive Body Panel Materials
Future trends in automotive body panel materials emphasize lightweight reinforced plastics to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, driven by stringent environmental regulations. Advanced composites incorporating carbon fiber and thermoplastic polymers offer superior strength-to-weight ratios compared to traditional metal panels, enabling improved vehicle performance and crash safety. Innovations in recyclable reinforced plastics and hybrid metal-composite structures are set to revolutionize automotive manufacturing by combining durability with sustainability.
Infographic: Reinforced plastic vs Metal for Automotive Body Panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com