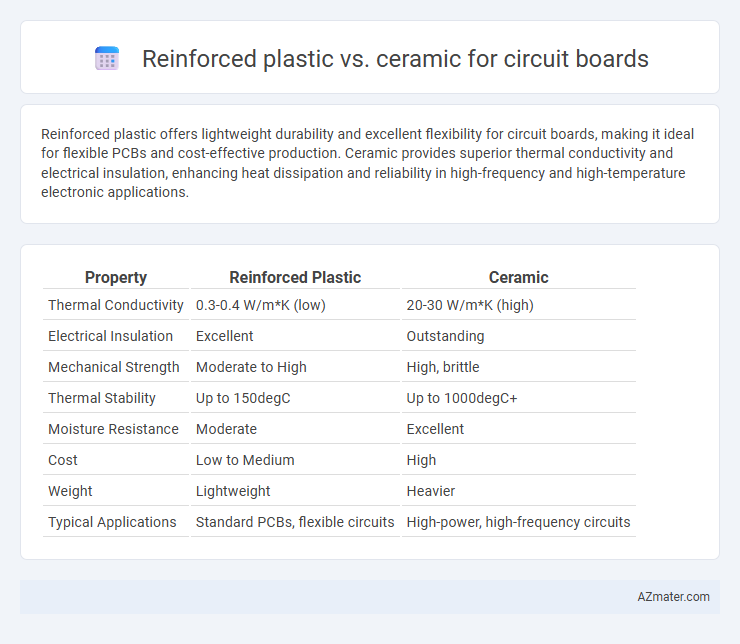
Reinforced plastic offers lightweight durability and excellent flexibility for circuit boards, making it ideal for flexible PCBs and cost-effective production. Ceramic provides superior thermal conductivity and electrical insulation, enhancing heat dissipation and reliability in high-frequency and high-temperature electronic applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Reinforced Plastic | Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.3-0.4 W/m*K (low) | 20-30 W/m*K (high) |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent | Outstanding |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate to High | High, brittle |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 150degC | Up to 1000degC+ |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Cost | Low to Medium | High |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Typical Applications | Standard PCBs, flexible circuits | High-power, high-frequency circuits |
Introduction to Circuit Board Materials
Circuit board materials primarily consist of reinforced plastics and ceramics, each offering unique properties for electronic applications. Reinforced plastics like FR-4 provide excellent electrical insulation, mechanical strength, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for most standard circuit boards. Ceramics, while more expensive, deliver superior thermal conductivity, high-temperature resistance, and enhanced durability for high-performance or specialized electronic devices.
Key Properties of Reinforced Plastic
Reinforced plastic circuit boards offer superior mechanical strength, high impact resistance, and excellent thermal stability, making them ideal for demanding electronic applications. Their lightweight nature and resistance to moisture and chemicals enhance durability and performance in harsh environments. Compared to ceramics, reinforced plastics provide better flexibility and cost-effectiveness while maintaining adequate electrical insulation properties.
Key Properties of Ceramic
Ceramic circuit boards offer exceptional thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, and high-temperature resistance, making them ideal for high-power and high-frequency applications. Their low dielectric loss and mechanical stability under heat stress surpass reinforced plastic alternatives, which generally possess lower thermal stability and higher dielectric constants. The superior chemical inertness and hardness of ceramics contribute to their durability in harsh environments compared to reinforced plastic circuit boards.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Reinforced plastic offers high impact resistance and flexibility, making it suitable for applications requiring durability under mechanical stress. Ceramic materials provide superior hardness and excellent compressive strength, resulting in better resistance to deformation and wear. While reinforced plastic is more resistant to cracking under bending, ceramics excel in high-temperature environments due to their rigid and brittle nature.
Thermal Conductivity and Heat Resistance
Ceramic materials for circuit boards exhibit superior thermal conductivity, often exceeding 20 W/m*K, compared to reinforced plastics, which typically range below 1 W/m*K, enabling more efficient heat dissipation. Ceramics also demonstrate higher heat resistance withstanding temperatures above 1000degC, whereas reinforced plastics generally degrade beyond 150-200degC. These thermal properties make ceramics preferable in high-power or high-temperature electronic applications requiring reliable thermal management.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Reinforced plastic offers excellent electrical insulation due to its high dielectric strength and resistance to moisture, making it suitable for standard circuit board applications. Ceramic materials provide superior electrical insulation with higher thermal conductivity and stability, allowing operation under extreme temperatures and high-frequency signals without degradation. Choosing between reinforced plastic and ceramic depends on the required dielectric constant, thermal management needs, and environmental conditions of the circuit board application.
Durability and Longevity
Reinforced plastic circuit boards offer excellent impact resistance and flexibility, making them highly durable in dynamic environments prone to mechanical stress. Ceramic circuit boards provide superior thermal stability and corrosion resistance, significantly enhancing longevity in high-temperature or chemically aggressive conditions. The choice between reinforced plastic and ceramic depends on the balance required between mechanical durability and long-term performance under extreme thermal or environmental stress.
Cost Analysis: Reinforced Plastic vs Ceramic
Reinforced plastic circuit boards typically offer lower manufacturing costs due to cheaper raw materials and simpler production processes compared to ceramic boards. Ceramic boards incur higher expenses driven by advanced fabrication techniques and superior thermal management properties, which can justify the investment in high-performance applications. Cost analysis favors reinforced plastic for budget-sensitive projects, while ceramic boards provide value in scenarios demanding enhanced durability and heat resistance despite higher costs.
Application Suitability in Electronics
Reinforced plastic circuit boards offer superior flexibility and lightweight properties, making them ideal for wearable devices and consumer electronics with complex shapes. Ceramic circuit boards excel in high-temperature environments and provide exceptional thermal conductivity and electrical insulation, suited for aerospace and high-frequency RF applications. Choosing between reinforced plastic and ceramic depends on specific application requirements such as mechanical stress tolerance, thermal management, and electrical performance.
Choosing the Right Material for Circuit Boards
Reinforced plastic offers excellent flexibility, lightweight properties, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for standard circuit boards with moderate thermal and mechanical demands. Ceramic materials provide superior thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, and high-temperature resistance, essential for high-performance or harsh environment applications. Selecting the right material depends on balancing factors such as operating temperature, mechanical stress, thermal management, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Reinforced plastic vs Ceramic for Circuit board
 azmater.com
azmater.com