Recycled composite park benches offer superior durability and environmental benefits compared to traditional asphalt benches, resisting weathering and reducing waste. Asphalt benches tend to deteriorate faster and require more maintenance, making recycled composites a sustainable, long-lasting choice for outdoor seating.
Table of Comparison
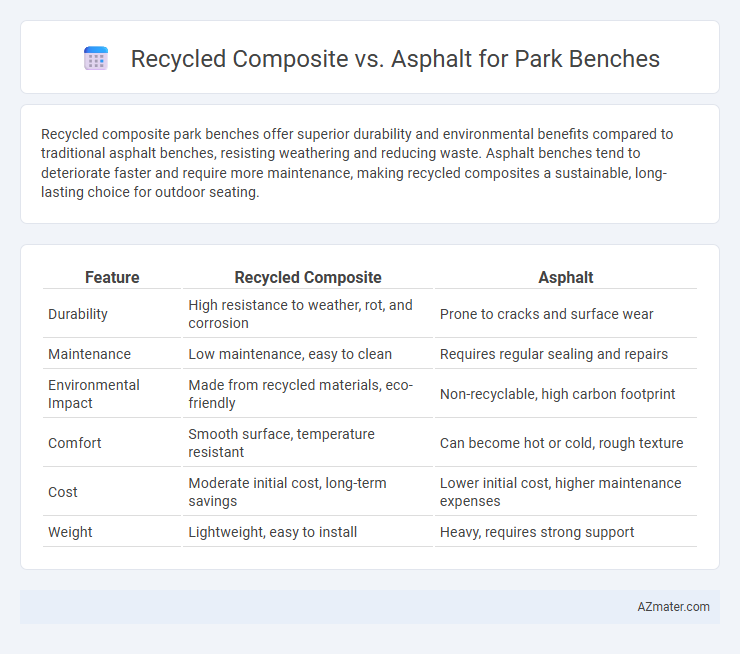
| Feature | Recycled Composite | Asphalt |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to weather, rot, and corrosion | Prone to cracks and surface wear |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, easy to clean | Requires regular sealing and repairs |
| Environmental Impact | Made from recycled materials, eco-friendly | Non-recyclable, high carbon footprint |
| Comfort | Smooth surface, temperature resistant | Can become hot or cold, rough texture |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost, long-term savings | Lower initial cost, higher maintenance expenses |
| Weight | Lightweight, easy to install | Heavy, requires strong support |
Introduction to Park Bench Materials
Recycled composite park benches combine wood fibers and plastic, offering durability, weather resistance, and eco-friendliness by repurposing waste materials. Asphalt benches, less common, provide a solid, heat-resistant surface but lack the aesthetic appeal and comfort of composite materials. Choosing between recycled composite and asphalt hinges on factors like environmental impact, maintenance, and design versatility.
What Are Recycled Composite Benches?
Recycled composite benches are crafted from a blend of recycled plastics and wood fibers, offering a sustainable and durable alternative to traditional wood or metal benches. These benches resist weather, decay, and insects far better than asphalt, making them ideal for outdoor park settings. Their eco-friendly composition helps reduce landfill waste while providing a low-maintenance seating solution with enhanced longevity compared to asphalt surfaces.
Understanding Asphalt Benches
Asphalt benches offer durability and resistance to weather conditions, making them a common choice for park seating. Their solid, non-porous surface requires minimal maintenance and can withstand heavy usage without significant wear. Understanding the advantages of asphalt benches helps in comparing them effectively against recycled composite alternatives, which provide environmental benefits but may differ in longevity and texture.
Durability Comparison: Composite vs Asphalt
Recycled composite park benches offer superior durability compared to asphalt, resisting weathering, moisture, and UV damage without cracking or crumbling over time. Asphalt surfaces tend to degrade through repeated freeze-thaw cycles and heavy use, leading to brittleness and surface deterioration. The longevity of recycled composite materials reduces maintenance costs and extends the lifespan of park benches in outdoor environments.
Environmental Impact: Sustainable Choices
Recycled composite park benches significantly reduce environmental impact by utilizing post-consumer plastics and wood fibers, diverting waste from landfills and lowering resource consumption compared to traditional asphalt. Asphalt production relies heavily on non-renewable petroleum resources and emits higher levels of greenhouse gases during manufacturing and installation. Choosing recycled composite materials supports sustainable waste management practices and contributes to a lower carbon footprint in urban outdoor furniture applications.
Maintenance and Longevity
Recycled composite park benches offer superior durability and require significantly less maintenance compared to traditional asphalt benches, resisting weathering, rot, and insect damage. Asphalt benches often crack and erode over time due to UV exposure and temperature fluctuations, leading to frequent repairs and higher upkeep costs. The longevity of recycled composite materials extends well beyond asphalt, making them a cost-effective and sustainable choice for public park seating.
Aesthetic Appeal: Design Flexibility
Recycled composite park benches offer superior design flexibility, allowing for a variety of shapes, colors, and textures that can mimic natural wood or feature modern finishes, enhancing aesthetic appeal in diverse park settings. Asphalt benches tend to have a more utilitarian and uniform appearance, limiting customization options and visual interest. The ability to tailor recycled composite materials to specific design themes makes them ideal for creating visually engaging and cohesive park environments.
Cost Analysis: Short-term and Long-term
Recycled composite park benches typically involve higher upfront costs due to material processing and manufacturing but offer significant savings in long-term maintenance and replacement expenses compared to asphalt benches, which may require frequent repairs and resurfacing. Asphalt benches have lower initial costs, but their susceptibility to cracking, weather damage, and fading escalates expenses over time. Factoring in durability and lifecycle, recycled composite benches present a cost-effective investment with enhanced resilience and reduced environmental impact.
User Comfort and Safety Considerations
Recycled composite park benches offer enhanced user comfort with their smooth, splinter-free surfaces and resistance to temperature extremes, reducing the risk of burns or cold discomfort. Asphalt benches, while durable, can become uncomfortably hot in direct sunlight and may develop cracks or rough edges that pose safety hazards. The non-toxic, slip-resistant properties of recycled composites further contribute to a safer, more comfortable seating experience in public parks.
Conclusion: Selecting the Best Material for Park Benches
Recycled composite offers superior durability, resistance to weather, and eco-friendly benefits compared to traditional asphalt for park benches. Asphalt may provide a lower initial cost but lacks long-term resilience, often requiring more frequent maintenance and replacement. Choosing recycled composite ensures sustainability and cost-effectiveness in public outdoor furniture.
Infographic: Recycled composite vs Asphalt for Park bench
 azmater.com
azmater.com