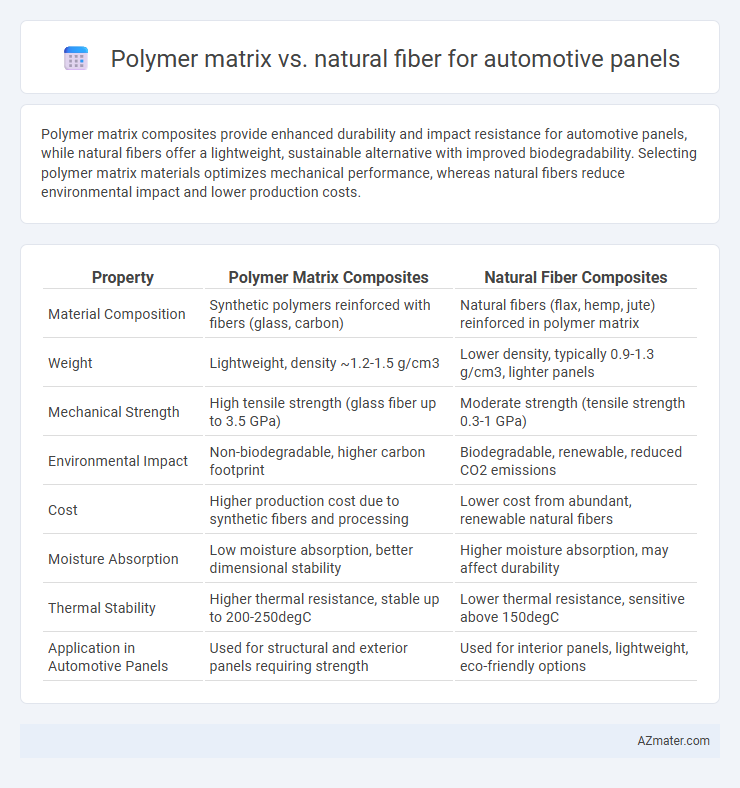
Polymer matrix composites provide enhanced durability and impact resistance for automotive panels, while natural fibers offer a lightweight, sustainable alternative with improved biodegradability. Selecting polymer matrix materials optimizes mechanical performance, whereas natural fibers reduce environmental impact and lower production costs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymer Matrix Composites | Natural Fiber Composites |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Synthetic polymers reinforced with fibers (glass, carbon) | Natural fibers (flax, hemp, jute) reinforced in polymer matrix |
| Weight | Lightweight, density ~1.2-1.5 g/cm3 | Lower density, typically 0.9-1.3 g/cm3, lighter panels |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength (glass fiber up to 3.5 GPa) | Moderate strength (tensile strength 0.3-1 GPa) |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint | Biodegradable, renewable, reduced CO2 emissions |
| Cost | Higher production cost due to synthetic fibers and processing | Lower cost from abundant, renewable natural fibers |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption, better dimensional stability | Higher moisture absorption, may affect durability |
| Thermal Stability | Higher thermal resistance, stable up to 200-250degC | Lower thermal resistance, sensitive above 150degC |
| Application in Automotive Panels | Used for structural and exterior panels requiring strength | Used for interior panels, lightweight, eco-friendly options |
Introduction to Automotive Panel Materials
Automotive panels commonly utilize polymer matrices due to their lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio, and excellent durability. Natural fibers are increasingly integrated as sustainable reinforcements, offering benefits such as biodegradability, reduced environmental impact, and cost-effectiveness. The choice between polymer matrix and natural fiber composites depends on performance requirements, weight reduction goals, and eco-friendly material considerations in automotive panel manufacturing.
Overview of Polymer Matrix Composites
Polymer matrix composites (PMCs) are widely used in automotive panels due to their excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and design flexibility. These composites typically consist of a polymer resin matrix such as epoxy, polyester, or polypropylene reinforced with fibers, enhancing mechanical properties and impact resistance. Compared to natural fiber composites, PMCs offer superior durability, thermal stability, and easier integration into mass production processes.
Understanding Natural Fiber Composites
Natural fiber composites in automotive panels offer enhanced sustainability, combining renewable fibers like flax, hemp, or jute with polymer matrices to achieve lightweight structures and improved impact resistance. These composites provide superior damping properties and reduced carbon footprint compared to traditional polymer matrix composites reinforced with synthetic fibers. Performance optimization depends on fiber treatment, matrix compatibility, and manufacturing techniques such as compression molding or injection molding to maximize strength and durability in automotive applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polymer matrices reinforced with natural fibers exhibit a balance of mechanical properties suitable for automotive panels, offering improved tensile strength, impact resistance, and flexibility compared to pure polymers. Natural fiber composites typically provide higher specific stiffness and lower density, contributing to lightweight vehicle components without compromising durability. However, polymer matrices often outperform natural fibers in moisture resistance and long-term mechanical stability under varying environmental conditions.
Weight and Density Considerations
Polymer matrix composites typically offer lower weight and density compared to traditional materials, enhancing fuel efficiency and performance in automotive panels. Natural fibers, such as flax or hemp, provide biodegradable, lightweight alternatives with densities around 1.2 g/cm3, reducing overall vehicle mass while maintaining adequate strength. The combination of low-density natural fibers with polymer matrices results in panels optimized for weight savings and sustainability without compromising structural integrity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polymer matrix composites, while offering high durability and lightweight properties for automotive panels, often rely on non-renewable petroleum resources and contribute to microplastic pollution during disposal. Natural fiber composites, made from renewable materials such as flax, hemp, and kenaf, provide a biodegradable and lower carbon footprint alternative that reduces greenhouse gas emissions throughout the lifecycle of vehicle components. Sustainable automotive design increasingly favors natural fiber reinforcements due to their ability to improve recyclability and reduce the environmental impact of manufacturing and end-of-life processing.
Manufacturing Processes and Scalability
Polymer matrix composites used in automotive panels benefit from established manufacturing processes like injection molding and compression molding, offering high scalability and consistent quality for mass production. Natural fiber composites, while eco-friendly and lightweight, often require specialized processing techniques such as resin transfer molding and may face challenges in scalability due to variability in fiber properties and higher moisture sensitivity. Advances in hybrid composite technology and automated fabrication methods are gradually improving the manufacturability and scalability of natural fiber automotive panels.
Cost Analysis and Economic Viability
Polymer matrix composites generally exhibit higher initial material costs compared to natural fiber composites but offer enhanced durability and lower maintenance expenses, impacting total lifecycle costs for automotive panels. Natural fiber composites, derived from renewable sources such as flax, hemp, or jute, present significant cost advantages due to lower raw material prices and reduced energy consumption during processing, making them economically viable for mass production. Economic viability analysis highlights that while polymer matrix composites ensure long-term performance benefits, natural fiber composites deliver substantial savings in production and disposal phases, aligning well with sustainability-driven market demands.
Performance in Real-World Automotive Applications
Polymer matrix composites combined with natural fibers provide a lightweight, durable solution for automotive panels, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. Natural fibers like flax and hemp offer excellent impact resistance and vibration damping, enhancing passenger comfort and crashworthiness. Performance in real-world applications demonstrates superior mechanical strength, thermal stability, and environmental sustainability compared to traditional materials.
Future Trends and Innovations in Automotive Panels
Polymer matrix composites and natural fiber reinforcements are driving future innovations in automotive panels by enhancing lightweight structures and sustainability. Advancements in bio-based resins and hybrid composite technologies are improving impact resistance and thermal stability, enabling greater design flexibility and reduced vehicle emissions. Integration of nanomaterials and smart sensors within these composites is also emerging, paving the way for intelligent, durable, and eco-friendly automotive panels.
Infographic: Polymer matrix vs Natural fiber for Automotive panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com