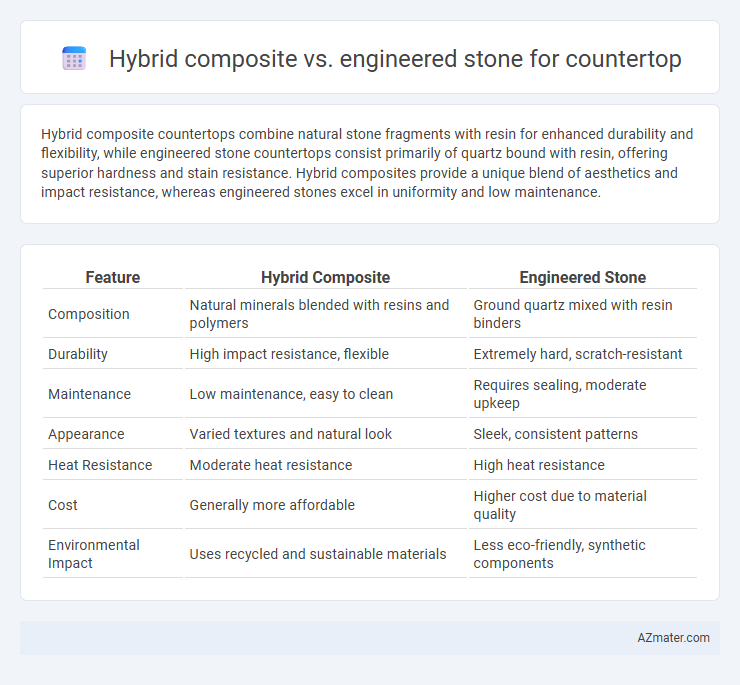
Hybrid composite countertops combine natural stone fragments with resin for enhanced durability and flexibility, while engineered stone countertops consist primarily of quartz bound with resin, offering superior hardness and stain resistance. Hybrid composites provide a unique blend of aesthetics and impact resistance, whereas engineered stones excel in uniformity and low maintenance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hybrid Composite | Engineered Stone |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Natural minerals blended with resins and polymers | Ground quartz mixed with resin binders |
| Durability | High impact resistance, flexible | Extremely hard, scratch-resistant |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, easy to clean | Requires sealing, moderate upkeep |
| Appearance | Varied textures and natural look | Sleek, consistent patterns |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate heat resistance | High heat resistance |
| Cost | Generally more affordable | Higher cost due to material quality |
| Environmental Impact | Uses recycled and sustainable materials | Less eco-friendly, synthetic components |
Introduction to Hybrid Composite and Engineered Stone
Hybrid composite countertops combine natural stone particles with resin binders, creating a durable and non-porous surface resistant to stains and scratches. Engineered stone, also known as quartz countertops, consists of crushed quartz mixed with resins and pigments, offering a consistent appearance and high strength. Both materials provide excellent durability and low maintenance, with engineered stone typically offering a wider range of colors and patterns due to its manufacturing process.
Material Composition and Structure
Hybrid composite countertops combine natural stone particles with resins and polymers, creating a lightweight yet durable surface resistant to impacts and heat. Engineered stone, primarily made from crushed quartz bonded with resin, offers consistent color and pattern with enhanced hardness and scratch resistance. Both materials provide non-porous surfaces, but hybrid composites typically have higher flexibility due to resin content, while engineered stone emphasizes stone density for durability.
Aesthetic Variety and Design Options
Hybrid composites offer a broad palette of colors and textures, combining natural stone and resin to mimic marble, granite, and quartz flawlessly. Engineered stone provides consistent patterns and uniform colors, ideal for modern, sleek designs with minimal variation. Both materials support custom shapes and intricate edge profiles, allowing for tailored aesthetic choices in countertop applications.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Hybrid composite countertops offer superior impact resistance and flexibility due to their combination of natural minerals and resin, making them less prone to cracking under stress compared to engineered stone. Engineered stone, composed primarily of quartz and resin, provides exceptional hardness and scratch resistance but can be more brittle and susceptible to chipping from heavy impacts. When prioritizing durability and strength, hybrid composite surfaces excel in impact absorption, while engineered stone delivers higher surface hardness and longevity against everyday wear.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Hybrid composite countertops offer superior resistance to stains and scratches, requiring minimal maintenance with only regular mild soap and water cleaning, whereas engineered stone surfaces, made primarily of quartz, resist most stains but may need special non-abrasive cleaners to maintain their polish. Engineered stone is less prone to harboring bacteria due to its non-porous nature, making it easier to sanitize, while hybrid composites can sometimes require prompt spill cleanup to avoid surface damage. Both materials benefit from avoiding harsh chemicals or abrasive pads, but hybrid composites typically demand more careful handling to prevent compounded wear over time.
Heat, Stain, and Scratch Resistance
Hybrid composite countertops combine natural stone and resin, offering superior heat resistance up to 300degF, excellent stain resistance due to non-porous surfaces, and high scratch resistance from embedded minerals. Engineered stone, primarily quartz-based with resin binders, boasts exceptional stain resistance and scratch hardness rating around 7 on the Mohs scale but can tolerate lower heat thresholds, typically up to 150degF before damage. Both materials provide durable options, yet hybrid composites excel in heat resistance while engineered stones offer consistent stain and scratch performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hybrid composites for countertops often incorporate recycled materials and bio-based resins, offering a lower environmental footprint compared to engineered stones, which primarily rely on natural quartz extraction. The production of engineered stone typically involves energy-intensive processes and generates significant waste, whereas hybrid composites promote sustainability through resource efficiency and reduced carbon emissions. Selecting hybrid composites can contribute to eco-friendly building practices by minimizing landfill waste and preserving natural quartz reserves.
Cost and Value Considerations
Hybrid composite countertops typically offer a balance between affordability and durability, with prices ranging from $50 to $100 per square foot, making them a cost-effective option for homeowners seeking moderate investment and longevity. Engineered stone, including quartz, commands higher upfront costs, typically between $70 and $150 per square foot, but provides superior resistance to stains, scratches, and heat, which enhances long-term value through reduced maintenance and increased durability. When considering cost and value, hybrid composite suits budget-conscious projects with moderate wear, while engineered stone maximizes ROI through premium aesthetics and lasting performance.
Installation Process and Flexibility
Hybrid composite countertops offer greater installation flexibility due to their lighter weight and easier cutting capabilities compared to engineered stone, which is denser and requires specialized tools for precise installation. The installation process for hybrid composites is typically faster, allowing for on-site adjustments and reduced labor time, while engineered stone demands careful handling and professional expertise to avoid damage. Hybrid composites also accommodate irregular or custom shapes more efficiently, making them ideal for complex kitchen designs.
Choosing the Right Countertop for Your Needs
Hybrid composite countertops blend natural stone and resin to offer enhanced durability, stain resistance, and a wide range of design options, making them ideal for high-traffic kitchens. Engineered stone, such as quartz, provides a non-porous surface that is highly resistant to scratches and bacteria, suitable for homeowners prioritizing low maintenance and hygiene. Choosing between hybrid composite and engineered stone depends on the balance of aesthetic appeal, durability requirements, and budget constraints specific to your kitchen's usage.
Infographic: Hybrid composite vs Engineered stone for Countertop
 azmater.com
azmater.com