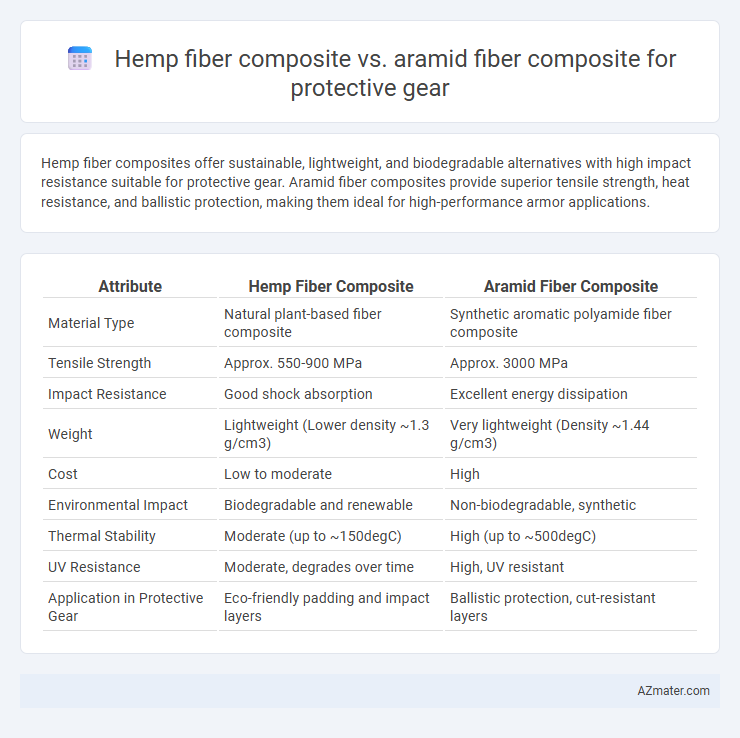
Hemp fiber composites offer sustainable, lightweight, and biodegradable alternatives with high impact resistance suitable for protective gear. Aramid fiber composites provide superior tensile strength, heat resistance, and ballistic protection, making them ideal for high-performance armor applications.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Hemp Fiber Composite | Aramid Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Natural plant-based fiber composite | Synthetic aromatic polyamide fiber composite |
| Tensile Strength | Approx. 550-900 MPa | Approx. 3000 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | Good shock absorption | Excellent energy dissipation |
| Weight | Lightweight (Lower density ~1.3 g/cm3) | Very lightweight (Density ~1.44 g/cm3) |
| Cost | Low to moderate | High |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and renewable | Non-biodegradable, synthetic |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate (up to ~150degC) | High (up to ~500degC) |
| UV Resistance | Moderate, degrades over time | High, UV resistant |
| Application in Protective Gear | Eco-friendly padding and impact layers | Ballistic protection, cut-resistant layers |
Introduction to Hemp and Aramid Fiber Composites
Hemp fiber composites offer a sustainable and biodegradable alternative with high tensile strength and excellent vibration damping, making them suitable for lightweight protective gear. Aramid fiber composites, such as Kevlar, provide exceptional impact resistance, heat stability, and ballistic protection, widely used in body armor and helmets. Both materials excel in different protective applications, with hemp fibers emphasizing eco-friendliness and aramid fibers delivering superior durability and safety.
Material Properties Comparison
Hemp fiber composites exhibit high tensile strength, excellent biodegradability, and lower density, making them lightweight and environmentally sustainable options for protective gear. Aramid fiber composites, such as Kevlar, provide superior impact resistance, exceptional thermal stability, and higher tensile strength, crucial for ballistic protection and durability. The trade-off between hemp's eco-friendliness and aramid's advanced mechanical properties influences material selection based on performance requirements and sustainability goals.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Hemp fiber composites offer significantly lower environmental impact compared to aramid fiber composites due to their biodegradability, renewable sourcing, and lower energy-intensive production processes. Aramid fibers, while providing superior strength and durability, rely on petrochemical inputs and result in higher carbon emissions and non-biodegradable waste. Choosing hemp fiber composites enhances sustainability in protective gear by reducing ecological footprints and supporting circular economy principles without compromising essential protective performance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Hemp fiber composites exhibit high tensile strength and excellent impact resistance, making them a sustainable alternative for protective gear with enhanced mechanical performance. Aramid fiber composites, such as Kevlar, provide superior tensile strength, exceptional abrasion resistance, and outstanding durability under extreme conditions. While aramid composites dominate in performance-critical applications due to their proven long-term durability and fatigue resistance, hemp fiber composites offer a cost-effective, eco-friendly option with competitive mechanical strength for intermediate protection levels.
Weight and Comfort in Protective Gear
Hemp fiber composites offer lightweight properties and superior breathability, enhancing comfort in protective gear compared to heavier, denser aramid fiber composites such as Kevlar. While aramid fibers provide exceptional strength and impact resistance, their increased weight and reduced flexibility can compromise prolonged wearability. The natural fibers in hemp composites contribute to moisture-wicking and thermal regulation, making them favorable for applications that require both protective performance and user comfort.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Hemp fiber composites offer a cost-effective alternative to aramid fiber composites due to the lower production expenses and renewable nature of hemp, making them more accessible for large-scale manufacturing. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, have higher raw material and processing costs, limiting their widespread availability primarily to specialized applications in protective gear. The abundant cultivation of hemp contributes to its steady supply chain, whereas aramid fiber relies on complex chemical synthesis, impacting both cost and consistent availability for protective equipment production.
Performance in Impact Resistance
Hemp fiber composites show promising impact resistance due to their high tensile strength and natural energy absorption capabilities, making them suitable for lightweight protective gear. Aramid fiber composites, such as Kevlar, offer superior impact resistance with exceptional toughness and resistance to penetration, widely used in ballistic and high-impact protection applications. While aramid composites deliver unmatched durability in extreme conditions, hemp composites provide an eco-friendly alternative with competitive performance in moderate impact resistance scenarios.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Hemp fiber composites exhibit excellent thermal stability with decomposition temperatures around 230-280degC, offering eco-friendly alternatives in protective gear without compromising heat resistance. Aramid fiber composites, such as Kevlar, provide superior chemical resistance to acids and solvents, maintaining structural integrity under harsh environments. The combination of hemp fibers' biodegradability and adequate thermal resistance contrasts with aramid's high-performance chemical durability, making them suitable for different protective applications based on environmental exposure.
Applications in Protective Equipment
Hemp fiber composites offer lightweight, biodegradable, and impact-resistant properties ideal for eco-friendly protective gear such as helmets and body armor. Aramid fiber composites, including Kevlar, provide superior tensile strength, thermal resistance, and ballistic protection, making them the preferred choice for military and law enforcement body armor and high-performance helmets. Both materials are utilized in protective equipment, with hemp composites favored for sustainable applications and aramid fibers for scenarios demanding maximum durability and threat resistance.
Future Trends in Protective Gear Materials
Future trends in protective gear materials emphasize sustainability and enhanced performance, highlighting hemp fiber composites for their biodegradability and cost-effectiveness compared to aramid fiber composites. Aramid fibers continue to dominate due to superior impact resistance and higher tensile strength, crucial for ballistic protection and durability in extreme conditions. Innovations in hybrid composites combining hemp and aramid fibers aim to optimize weight, environmental impact, and mechanical properties, driving advancements in eco-friendly, high-performance protective equipment.
Infographic: Hemp fiber composite vs Aramid fiber composite for Protective gear
 azmater.com
azmater.com