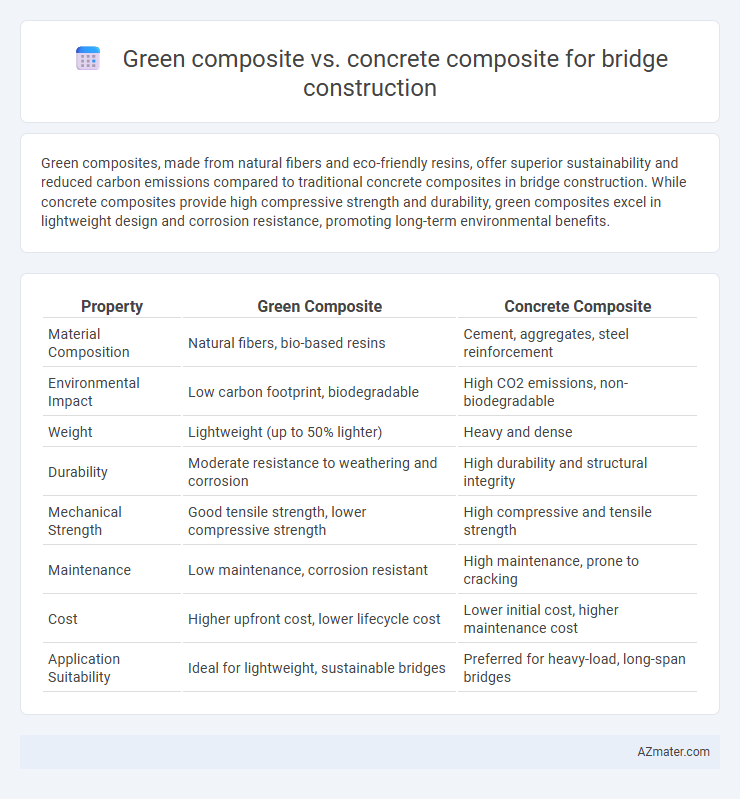
Green composites, made from natural fibers and eco-friendly resins, offer superior sustainability and reduced carbon emissions compared to traditional concrete composites in bridge construction. While concrete composites provide high compressive strength and durability, green composites excel in lightweight design and corrosion resistance, promoting long-term environmental benefits.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Green Composite | Concrete Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural fibers, bio-based resins | Cement, aggregates, steel reinforcement |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable | High CO2 emissions, non-biodegradable |
| Weight | Lightweight (up to 50% lighter) | Heavy and dense |
| Durability | Moderate resistance to weathering and corrosion | High durability and structural integrity |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength, lower compressive strength | High compressive and tensile strength |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, corrosion resistant | High maintenance, prone to cracking |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost, lower lifecycle cost | Lower initial cost, higher maintenance cost |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for lightweight, sustainable bridges | Preferred for heavy-load, long-span bridges |
Introduction to Bridge Construction Materials
Green composites, composed of natural fibers and biodegradable polymers, offer lightweight, corrosion-resistant alternatives to traditional materials in bridge construction. Concrete composites, reinforced with steel or fiber additives, provide high compressive strength and durability essential for load-bearing structures. Selecting between green and concrete composites depends on factors like environmental impact, structural performance, and lifecycle costs in bridge engineering.
What Are Green Composites?
Green composites are eco-friendly materials made from natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or jute combined with biodegradable or recyclable polymers, offering sustainable alternatives to traditional composites in bridge construction. These composites reduce carbon footprint and enhance environmental compatibility by using renewable resources and lowering energy consumption during production. Compared to concrete composites, green composites provide lightweight solutions with improved corrosion resistance and potential for enhanced durability in specific structural applications.
Overview of Concrete Composites
Concrete composites combine concrete with reinforcing materials such as steel fibers, polymers, or natural fibers to enhance durability, tensile strength, and crack resistance in bridge construction. These composites offer improved load-bearing capacity and resistance to environmental factors, making them suitable for long-span bridges and heavy traffic loads. Advances in concrete composite technology focus on reducing weight while maintaining structural integrity and sustainability through recycled or industrial by-products.
Material Properties: Strength and Durability
Green composites for bridge construction offer high tensile strength and excellent corrosion resistance due to natural fiber reinforcements, resulting in lightweight structures with enhanced durability in humid environments. Concrete composites exhibit superior compressive strength and longevity under heavy loads but are prone to cracking and chemical degradation over time unless properly treated. Material selection depends on balancing strength requirements with environmental exposure, where green composites provide sustainable alternatives with lower maintenance demands compared to traditional concrete composites.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Green composites for bridge construction significantly reduce carbon emissions due to their bio-based fibers and recycled polymers, unlike traditional concrete composites that rely heavily on carbon-intensive cement production. The production of concrete composites generates substantial greenhouse gases and involves resource-intensive processes, contributing to environmental degradation and waste accumulation. Green composites also offer enhanced recyclability and lower energy consumption throughout their lifecycle, making them a more sustainable option for eco-conscious infrastructure projects.
Cost Analysis: Green vs Concrete Composites
Green composites in bridge construction offer significant cost savings due to their lightweight nature, reducing transportation and installation expenses compared to concrete composites. While concrete composites have higher initial material costs and longer curing times, they provide durability and low maintenance, potentially offsetting upfront expenses over the bridge lifespan. Life cycle cost analysis often favors green composites for projects prioritizing sustainability and rapid deployment, whereas concrete composites remain cost-effective for long-term structural resilience.
Structural Performance in Bridges
Green composites in bridge construction offer enhanced structural performance through high strength-to-weight ratios and superior fatigue resistance compared to traditional concrete composites, enabling longer spans and reduced support requirements. Concrete composites provide exceptional compressive strength and durability, but their higher density results in increased dead loads, impacting overall structural efficiency. Advances in fiber-reinforced polymers within green composites contribute to improved tensile strength and corrosion resistance, promoting longevity and reduced maintenance for bridge structures.
Maintenance and Longevity
Green composites for bridge construction offer superior corrosion resistance and reduced maintenance needs compared to concrete composites, which are prone to cracking and spalling over time. The longevity of green composites is enhanced by their lightweight nature and durability against environmental stressors such as moisture and temperature fluctuations. Concrete composites require more frequent inspections and repair cycles due to susceptibility to freeze-thaw damage and chemical degradation.
Case Studies: Successful Bridge Applications
Green composites in bridge construction, exemplified by projects like the Pedestrian Bridge in Malaysia using hemp fiber-reinforced polymer, demonstrate enhanced sustainability and corrosion resistance compared to traditional concrete composites. Case studies from the Netherlands showcase Green composite bridges with reduced carbon footprints and increased lifespan under harsh environmental conditions. Concrete composites remain prevalent in large infrastructure projects, such as the Millau Viaduct in France, but Green composite innovations increasingly provide lightweight, durable alternatives for pedestrian and small vehicular bridges.
Future Trends in Bridge Material Innovation
Green composites in bridge construction offer enhanced sustainability through biodegradable fibers and recycled resins, reducing carbon footprint compared to traditional concrete composites. Advances in nanotechnology and smart materials integration are driving the development of self-healing and corrosion-resistant green composites, promising longer service life and reduced maintenance costs. Future trends emphasize hybrid composites combining bio-based polymers with additives for improved strength and durability, positioning green composites as a viable replacement for concrete in load-bearing bridge structures.
Infographic: Green composite vs Concrete composite for Bridge construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com