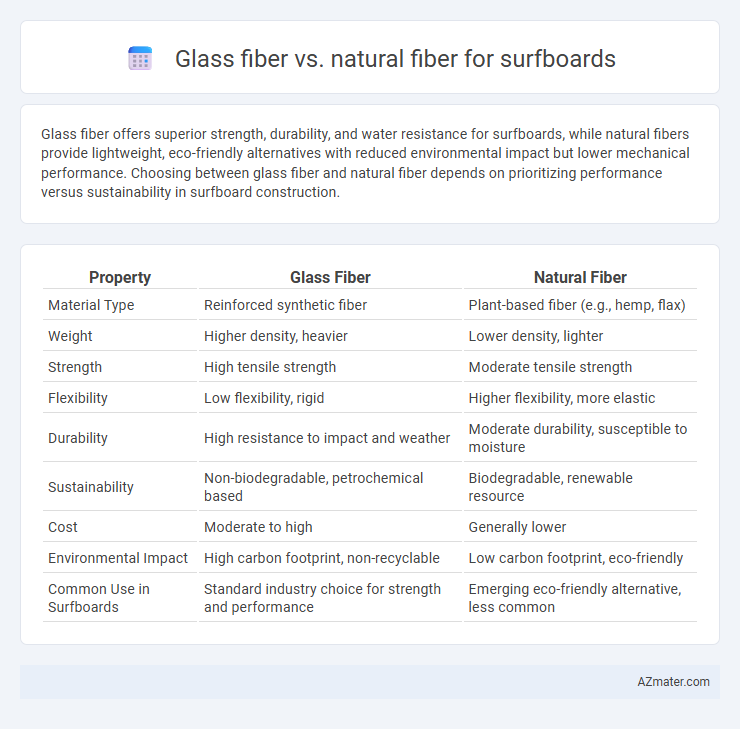
Glass fiber offers superior strength, durability, and water resistance for surfboards, while natural fibers provide lightweight, eco-friendly alternatives with reduced environmental impact but lower mechanical performance. Choosing between glass fiber and natural fiber depends on prioritizing performance versus sustainability in surfboard construction.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Fiber | Natural Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Reinforced synthetic fiber | Plant-based fiber (e.g., hemp, flax) |
| Weight | Higher density, heavier | Lower density, lighter |
| Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Flexibility | Low flexibility, rigid | Higher flexibility, more elastic |
| Durability | High resistance to impact and weather | Moderate durability, susceptible to moisture |
| Sustainability | Non-biodegradable, petrochemical based | Biodegradable, renewable resource |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally lower |
| Environmental Impact | High carbon footprint, non-recyclable | Low carbon footprint, eco-friendly |
| Common Use in Surfboards | Standard industry choice for strength and performance | Emerging eco-friendly alternative, less common |
Introduction to Surfboard Materials
Surfboard construction primarily utilizes glass fiber and natural fiber materials, each offering unique performance benefits and environmental impacts. Glass fiber, known for its durability, lightweight properties, and resistance to water, remains the industry standard in epoxy and polyester resin lamination. Natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or bamboo provide sustainable alternatives with reduced carbon footprints, enhancing eco-friendly surfboard designs while maintaining strength and flex characteristics suitable for various surfing conditions.
What is Glass Fiber?
Glass fiber, also known as fiberglass, is a synthetic material made from fine strands of glass woven into fabric or matting used in surfboard construction. It offers high strength, durability, and resistance to water damage, making it ideal for reinforcing the foam core of surfboards. Its lightweight nature combined with rigidity enhances board performance and longevity compared to natural fiber alternatives.
What are Natural Fibers?
Natural fibers used in surfboard construction primarily include flax, hemp, jute, and cork, which are derived from plant sources and known for their sustainability and biodegradability. These fibers offer advantages such as lower environmental impact, improved flexibility, and enhanced vibration damping compared to traditional glass fiber. Natural fiber composites contribute to lighter, eco-friendly surfboards while maintaining sufficient strength and stiffness for performance on water.
Performance Comparison: Glass Fiber vs Natural Fiber
Glass fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced durability compared to natural fibers, making it the preferred choice for high-performance surfboards that demand rigidity and impact resistance. Natural fibers such as hemp or flax provide increased flexibility and eco-friendliness but tend to absorb more water, reducing overall board longevity and stiffness. Performance-wise, glass fiber surfboards deliver better responsiveness and sustained speed, while natural fiber boards excel in sustainable design with moderate performance trade-offs.
Durability and Longevity
Glass fiber reinforced surfboards exhibit superior durability and longevity due to their resistance to water absorption, impact, and UV damage, maintaining structural integrity over extended periods. Natural fiber surfboards, while eco-friendly and lightweight, typically show reduced durability, as materials like hemp or flax degrade faster when exposed to saltwater and environmental stressors. Choosing glass fiber ensures longer-lasting performance, especially for surfers prioritizing durability in challenging ocean conditions.
Environmental Impact
Glass fiber surfboards generate significant environmental impact due to non-biodegradable resin use and energy-intensive manufacturing processes, releasing toxic pollutants and contributing to landfill waste. Natural fiber surfboards, made from renewable sources like hemp, flax, or jute, offer reduced carbon footprints, improved biodegradability, and lower toxicity, aligning with eco-friendly production standards. The sustainable harvesting and waste management of natural fibers further minimize ecosystem disruption compared to synthetic glass fibers.
Cost Analysis
Glass fiber remains the most cost-effective material for surfboard production due to its lower raw material prices and widespread availability, making it a preferred choice for mass manufacturing. Natural fibers like hemp and flax generally incur higher costs because of limited supply chains and more labor-intensive processing requirements. However, the increasing demand for sustainable surfboards is gradually driving advancements that may reduce natural fiber costs in the near future.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Glass fiber surfboards are typically heavier due to the density of fiberglass materials, offering increased durability but reduced portability compared to natural fiber alternatives like hemp or flax. Natural fibers provide superior flexibility, allowing surfboards to absorb wave energy more effectively and deliver a smoother ride, which enhances performance in varying water conditions. The weight difference impacts board responsiveness, with glass fiber boards favoring stability and control, while natural fiber boards prioritize lightweight agility and dynamic flex patterns.
Manufacturing and Repair Considerations
Glass fiber surfboards offer superior durability and ease of repair due to their consistent resin absorption and well-established manufacturing processes, allowing for precise lamination and quick curing times. Natural fiber boards, such as those made from flax or hemp, require more careful resin selection and handling to ensure proper adhesion, often resulting in longer curing periods and more complex repairs due to variability in fiber density and moisture content. Manufacturing with glass fiber typically involves automated techniques for scalability, whereas natural fiber surfboards emphasize eco-friendly methods but demand skilled craftsmanship to maintain structural integrity and repair efficiency.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Surfboard
Glass fiber offers superior strength, durability, and water resistance, making it ideal for high-performance surfboards that require maximum flexibility and resilience. Natural fibers, such as hemp or flax, provide a more eco-friendly and lightweight alternative, enhancing board sustainability while maintaining adequate strength for casual surfing. Choosing the right material depends on balancing performance needs with environmental impact, where glass fiber suits advanced surfers and natural fibers appeal to those prioritizing sustainability.
Infographic: Glass fiber vs Natural fiber for Surfboard
 azmater.com
azmater.com