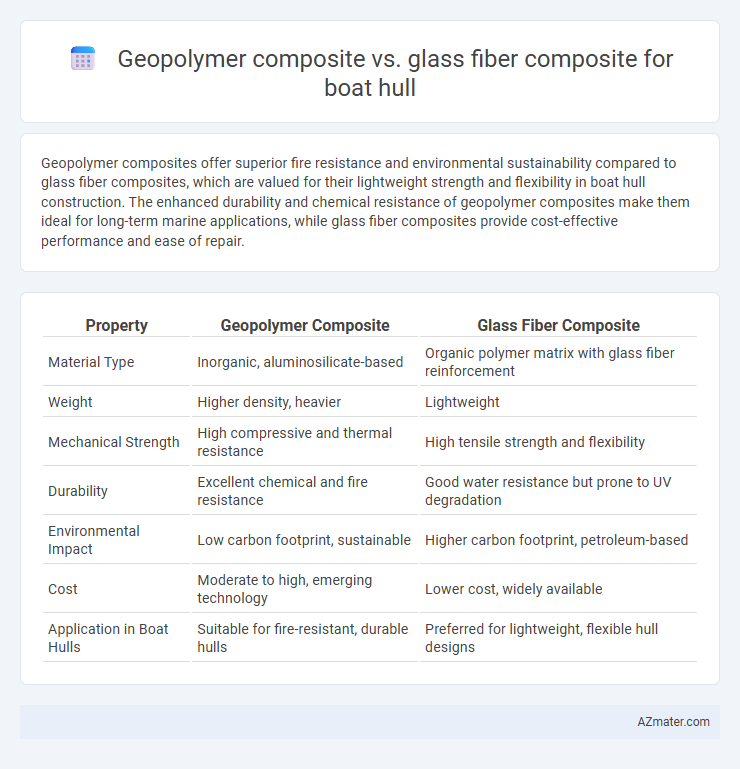
Geopolymer composites offer superior fire resistance and environmental sustainability compared to glass fiber composites, which are valued for their lightweight strength and flexibility in boat hull construction. The enhanced durability and chemical resistance of geopolymer composites make them ideal for long-term marine applications, while glass fiber composites provide cost-effective performance and ease of repair.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Geopolymer Composite | Glass Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Inorganic, aluminosilicate-based | Organic polymer matrix with glass fiber reinforcement |
| Weight | Higher density, heavier | Lightweight |
| Mechanical Strength | High compressive and thermal resistance | High tensile strength and flexibility |
| Durability | Excellent chemical and fire resistance | Good water resistance but prone to UV degradation |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, sustainable | Higher carbon footprint, petroleum-based |
| Cost | Moderate to high, emerging technology | Lower cost, widely available |
| Application in Boat Hulls | Suitable for fire-resistant, durable hulls | Preferred for lightweight, flexible hull designs |
Introduction to Composite Materials in Boat Hulls
Geopolymer composites and glass fiber composites are prominent materials used in boat hull construction, each offering unique advantages in strength and durability. Geopolymer composites provide enhanced fire resistance, chemical stability, and environmental sustainability due to their inorganic polymer matrix. Glass fiber composites, widely adopted in marine applications, deliver excellent tensile strength, impact resistance, and lightweight properties essential for performance and fuel efficiency in boat hulls.
Overview of Geopolymer Composites
Geopolymer composites for boat hulls consist of inorganic aluminosilicate polymers that offer superior fire resistance, chemical stability, and environmental sustainability compared to conventional materials. These composites provide high compressive strength and excellent durability in marine environments while reducing carbon footprint due to their low-temperature synthesis process. Geopolymer matrices combined with natural or synthetic reinforcements create lightweight, corrosion-resistant hulls suitable for long-term marine applications.
Overview of Glass Fiber Composites
Glass fiber composites consist of glass fibers embedded in a polymer matrix, offering high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent corrosion resistance ideal for marine environments. Their widespread use in boat hulls is driven by durability, impact resistance, and ease of fabrication compared to traditional materials. Advances in resin technology and fiber orientation optimize mechanical properties, making glass fiber composites a popular choice for lightweight, high-performance boat construction.
Material Properties Comparison: Strength and Durability
Geopolymer composites exhibit excellent compressive strength and superior chemical resistance, making them highly durable against marine environmental factors such as saltwater corrosion and UV exposure. Glass fiber composites provide high tensile strength and flexibility, allowing better impact resistance and fatigue performance essential for dynamic loading on boat hulls. While glass fiber composites are widely used due to their lightweight properties and toughness, geopolymer composites offer enhanced fire resistance and long-term durability in harsh conditions, suggesting a potential for hybrid applications in marine hull construction.
Water Resistance and Corrosion Performance
Geopolymer composites exhibit superior water resistance due to their dense, inorganic matrix that minimizes water absorption and prevents micro-cracking, enhancing durability in marine environments. Glass fiber composites, while lightweight and strong, are prone to hydrolytic degradation and resin matrix swelling, which can compromise water resistance over prolonged exposure. Corrosion performance of geopolymer composites outperforms glass fiber composites as their chemically stable mineral structure resists saltwater-induced deterioration, whereas glass fiber composites may suffer from fiber-matrix interface degradation leading to reduced mechanical integrity.
Weight and Buoyancy Analysis
Geopolymer composites exhibit higher density compared to glass fiber composites, resulting in increased hull weight but enhanced structural rigidity, which can affect overall vessel performance. Glass fiber composites offer lighter weight and superior buoyancy due to lower material density, contributing to better fuel efficiency and ease of handling in marine applications. Weight and buoyancy analysis indicate that while glass fiber composites optimize payload capacity and speed, geopolymer composites may provide improved durability but require compensations in hull design to maintain buoyancy.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Geopolymer composites offer a significantly lower carbon footprint than glass fiber composites due to their utilization of industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, reducing reliance on virgin materials. These composites exhibit enhanced durability and resistance to marine degradation, which extends the lifespan of boat hulls and minimizes waste generation over time. Glass fiber composites, while widely used, involve energy-intensive production and pose challenges in recyclability, contributing to greater environmental burdens compared to the more sustainable, eco-friendly geopolymer alternatives.
Cost Effectiveness and Production Considerations
Geopolymer composites offer significant cost advantages over glass fiber composites for boat hulls due to lower raw material expenses and reduced environmental impact from sustainable sourcing. The production process of geopolymer composites requires less energy and can utilize locally available industrial by-products, resulting in shorter manufacturing cycles and decreased labor costs. Glass fiber composites, while offering excellent strength-to-weight ratios, involve higher material costs and longer curing times, which increase overall production expenses and affect scalability.
Real-World Performance: Case Studies
Geopolymer composites have demonstrated exceptional fire resistance and chemical durability in boat hull applications, outperforming traditional glass fiber composites in harsh marine environments, as evidenced by the case study of the EcoMarine 2022 project. Glass fiber composites maintain superior flexibility and impact resistance, making them favorable for smaller, high-performance vessels, highlighted by the Atlantic Marine 2021 trial where hull integrity was preserved under extreme wave impact. Real-world testing confirms geopolymer composites reduce maintenance costs over time due to resistance to saltwater corrosion, while glass fiber composites offer easier repairability and widespread industry familiarity.
Future Trends and Innovations in Marine Composites
Geopolymer composites are gaining traction in marine applications due to their excellent fire resistance, corrosion tolerance, and lower environmental impact compared to traditional glass fiber composites, which remain favored for their high strength-to-weight ratio and cost-effectiveness. Innovations in geopolymer matrix formulations and hybrid composites integrating nanomaterials aim to enhance mechanical properties and durability, positioning them as sustainable alternatives for future boat hulls. Research into self-healing geopolymer composites and advanced resin infusion techniques for glass fibers is driving the evolution of marine composites toward higher performance and ecological sustainability.
Infographic: Geopolymer composite vs Glass fiber composite for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com