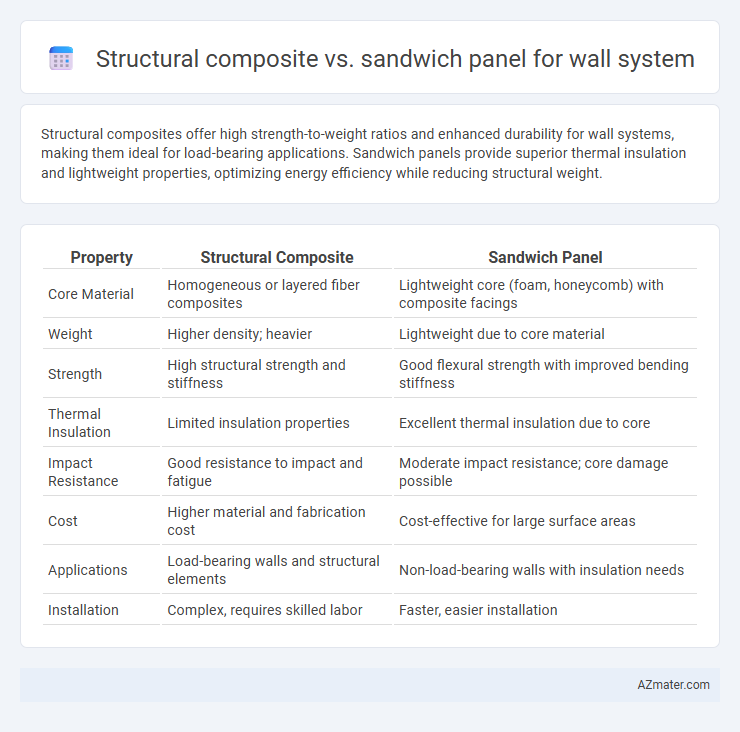
Structural composites offer high strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced durability for wall systems, making them ideal for load-bearing applications. Sandwich panels provide superior thermal insulation and lightweight properties, optimizing energy efficiency while reducing structural weight.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Structural Composite | Sandwich Panel |
|---|---|---|
| Core Material | Homogeneous or layered fiber composites | Lightweight core (foam, honeycomb) with composite facings |
| Weight | Higher density; heavier | Lightweight due to core material |
| Strength | High structural strength and stiffness | Good flexural strength with improved bending stiffness |
| Thermal Insulation | Limited insulation properties | Excellent thermal insulation due to core |
| Impact Resistance | Good resistance to impact and fatigue | Moderate impact resistance; core damage possible |
| Cost | Higher material and fabrication cost | Cost-effective for large surface areas |
| Applications | Load-bearing walls and structural elements | Non-load-bearing walls with insulation needs |
| Installation | Complex, requires skilled labor | Faster, easier installation |
Introduction to Wall System Technologies
Structural composite wall systems integrate materials like fiber-reinforced polymers with traditional building components to enhance strength and durability while reducing weight. Sandwich panels consist of two rigid face sheets bonded to a lightweight core, offering superior thermal insulation and high stiffness-to-weight ratios ideal for energy-efficient buildings. Both technologies improve wall performance, but sandwich panels provide enhanced thermal resistance and rapid installation compared to conventional structural composites.
What are Structural Composites?
Structural composites are engineered materials composed of two or more distinct constituents, such as fibers and resin, combined to achieve superior mechanical properties like high strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced durability. In wall systems, these composites offer improved load-bearing capacity and resistance to environmental conditions compared to traditional materials. Their versatility and structural efficiency make them a preferred choice over sandwich panels, which typically feature a core material between two face sheets for thermal insulation rather than load-bearing performance.
Defining Sandwich Panels in Construction
Sandwich panels in construction consist of two outer facings bonded to a lightweight core, typically made of materials like polyurethane foam, polystyrene, or mineral wool, providing exceptional thermal insulation and structural rigidity. Unlike structural composites, which integrate reinforcing fibers within a matrix for strength, sandwich panels offer a balanced combination of strength, lightweight properties, and thermal efficiency ideal for wall systems. These panels enhance energy performance and reduce installation time due to their prefabricated nature and high strength-to-weight ratio.
Comparative Material Composition
Structural composites typically consist of fiber reinforcements such as glass, carbon, or aramid fibers embedded in a resin matrix, providing high strength-to-weight ratios and durability. Sandwich panels feature a core material like foam, honeycomb, or balsa wood, bonded between two thin, rigid face sheets made from metals, composites, or plywood, optimizing stiffness and thermal insulation. Comparing material composition, structural composites prioritize load-bearing efficiency through fiber-matrix integration, while sandwich panels emphasize a combination of lightweight cores and strong facings to achieve enhanced bending resistance and energy absorption.
Key Performance Characteristics
Structural composites offer high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent load-bearing capacity, making them ideal for demanding wall systems requiring durability and resistance to environmental stresses. Sandwich panels enhance thermal insulation and energy efficiency due to their core material, commonly foam or honeycomb, providing superior thermal resistance and sound attenuation. Both systems vary in fire resistance, with structural composites often requiring additional treatment, while sandwich panels can integrate fire-retardant cores to meet stringent safety standards.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
Structural composite panels and sandwich panels offer distinct advantages for wall systems in thermal and acoustic insulation. Structural composite panels typically incorporate dense core materials like wood or resin-infused fibers, providing moderate thermal resistance and sound absorption suitable for residential applications. Sandwich panels, consisting of insulating foam cores such as polyurethane or polystyrene between two rigid facings, deliver superior thermal insulation with higher R-values and enhanced acoustic dampening due to their layered construction, making them ideal for energy-efficient buildings and noise-sensitive environments.
Structural Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity
Structural composites exhibit superior load-bearing capacity due to their homogeneous fiber-reinforced matrix, providing enhanced tensile strength and rigidity ideal for demanding wall systems. Sandwich panels combine lightweight cores, such as foam or honeycomb, with strong outer facings, optimizing structural strength while significantly reducing weight. In applications requiring high structural performance and impact resistance, structural composites outperform sandwich panels, whereas sandwich panels excel in thermal insulation and weight-sensitive designs.
Installation Process and Construction Speed
Structural composite panels offer a streamlined installation process due to their integrated load-bearing and insulating properties, reducing the need for additional framing or insulation materials. Sandwich panels, consisting of two outer layers with a core material, require precise handling and alignment but enable faster construction speed by providing pre-insulated wall systems ready for quick assembly. Both systems enhance onsite efficiency, though sandwich panels tend to accelerate project timelines by minimizing sequential construction steps.
Cost Analysis and Lifecycle Assessment
Structural composite wall systems typically incur higher initial costs due to advanced materials like fiberglass or carbon fiber combined with resin matrices, while sandwich panels offer cost advantages with lightweight cores such as foam or honeycomb structures that reduce material usage. Lifecycle assessment reveals sandwich panels provide superior thermal insulation and reduced energy consumption, lowering operational costs and environmental impact over time, whereas structural composites often require less maintenance but may involve higher embodied energy during production. Choosing between these systems depends on balancing upfront investment against long-term performance, energy efficiency, and sustainability goals.
Applications and Suitability for Different Projects
Structural composite panels offer high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent durability, making them suitable for commercial and industrial wall systems requiring load-bearing capabilities. Sandwich panels, consisting of insulating cores bonded between two rigid facings, excel in thermal performance and quick installation, ideal for residential and modular construction. Both systems provide versatile solutions, with structural composites favored for heavy-duty applications and sandwich panels preferred where insulation and rapid assembly are priorities.
Infographic: Structural composite vs Sandwich panel for Wall system
 azmater.com
azmater.com