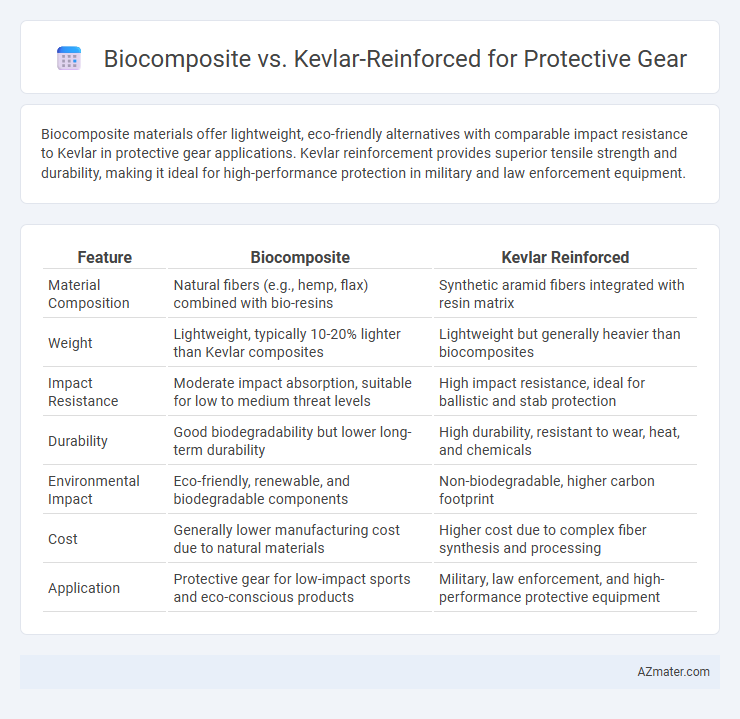
Biocomposite materials offer lightweight, eco-friendly alternatives with comparable impact resistance to Kevlar in protective gear applications. Kevlar reinforcement provides superior tensile strength and durability, making it ideal for high-performance protection in military and law enforcement equipment.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biocomposite | Kevlar Reinforced |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural fibers (e.g., hemp, flax) combined with bio-resins | Synthetic aramid fibers integrated with resin matrix |
| Weight | Lightweight, typically 10-20% lighter than Kevlar composites | Lightweight but generally heavier than biocomposites |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate impact absorption, suitable for low to medium threat levels | High impact resistance, ideal for ballistic and stab protection |
| Durability | Good biodegradability but lower long-term durability | High durability, resistant to wear, heat, and chemicals |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, renewable, and biodegradable components | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint |
| Cost | Generally lower manufacturing cost due to natural materials | Higher cost due to complex fiber synthesis and processing |
| Application | Protective gear for low-impact sports and eco-conscious products | Military, law enforcement, and high-performance protective equipment |
Introduction to Protective Gear Materials
Protective gear materials are critical for ensuring safety and durability in high-impact environments, with biocomposites and Kevlar reinforcement being prominent options. Biocomposites combine natural fibers and polymers to offer lightweight, eco-friendly alternatives with good mechanical strength, suitable for sustainable protective applications. Kevlar, a para-aramid synthetic fiber, boasts exceptional tensile strength and heat resistance, making it ideal for high-performance protective gear like bulletproof vests and helmets.
Overview of Biocomposites
Biocomposites for protective gear are engineered from natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or jute combined with polymer matrices to provide a sustainable alternative to synthetic materials like Kevlar. These composites offer benefits in terms of biodegradability, lower environmental impact, and lightweight properties while maintaining adequate mechanical strength and impact resistance for various protective applications. Innovations in fiber treatment and resin technology continue to enhance the durability and performance of biocomposites, positioning them as a promising material in eco-friendly protective gear development.
Understanding Kevlar Reinforced Fibers
Kevlar reinforced fibers are synthetic aramid fibers known for exceptional tensile strength, heat resistance, and durability, making them ideal for high-performance protective gear such as body armor and helmets. Their molecular structure provides superior energy absorption and impact resistance compared to many biocomposites, which primarily rely on natural fibers combined with polymer matrices. Understanding Kevlar's fiber alignment and resin impregnation is crucial for optimizing protection levels in ballistic and cut-resistant applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Biocomposite materials offer a high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent impact resistance due to their natural fiber reinforcements, making them eco-friendly alternatives in protective gear applications. Kevlar reinforced composites exhibit superior tensile strength and exceptional abrasion resistance, providing enhanced durability and protection against penetration. Mechanical strength comparison highlights Kevlar's advantage in high-stress environments, while biocomposites excel in lightweight and sustainable performance scenarios.
Weight and Flexibility Analysis
Biocomposite materials used in protective gear typically offer significant weight reduction compared to Kevlar reinforcements, enhancing wearer comfort and mobility. Kevlar, known for its exceptional tensile strength, tends to be heavier and less flexible, potentially limiting prolonged use in dynamic environments. Flexibility analysis reveals biocomposites provide superior conformability without compromising impact resistance, making them ideal for applications where lightweight protection and maneuverability are critical.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Biocomposite materials offer a significantly lower environmental impact compared to Kevlar, as they are derived from renewable resources and are biodegradable, reducing long-term waste. Kevlar, while highly durable and effective in protective gear, relies on petrochemical-based production processes that contribute to carbon emissions and non-biodegradable waste accumulation. Choosing biocomposite reinforcements promotes sustainability by minimizing ecological footprints and enhancing recyclability in protective equipment manufacturing.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Biocomposite materials offer significant cost efficiency due to lower raw material expenses and simpler manufacturing processes compared to Kevlar, which involves complex synthesis and higher production costs. Biocomposites are increasingly available as sustainable options derived from natural fibers and resins, promoting eco-friendly supply chains, while Kevlar, produced by specialized chemical companies, has limited availability and higher procurement costs. The combination of affordability and growing accessibility makes biocomposites a competitive alternative in protective gear markets prioritizing budget and supply reliability.
Performance in Real-World Scenarios
Biocomposite protective gear demonstrates superior environmental sustainability and lightweight properties, enhancing wearer comfort and mobility during prolonged use in real-world scenarios. Kevlar reinforced gear offers exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance, making it highly effective in high-risk environments requiring maximum protection against ballistic threats and abrasions. Performance evaluations reveal that while Kevlar excels in durability and protection, biocomposites provide balanced benefits in flexibility and eco-friendliness, influencing choice based on specific operational demands.
Advances in Material Technology
Biocomposite materials have emerged as a sustainable alternative to traditional Kevlar reinforcements in protective gear, offering enhanced biodegradability and reduced environmental impact while maintaining high tensile strength and impact resistance. Advances in nanocellulose fibers and bio-based resin matrices have significantly improved the mechanical properties and durability of biocomposites, matching or exceeding the performance metrics of conventional Kevlar. Innovations in hybrid composites integrating natural fibers with synthetic reinforcements provide optimized weight-to-strength ratios and increased comfort, driving the next generation of eco-friendly protective equipment.
Future Prospects for Protective Gear Materials
Biocomposite materials offer promising future prospects for protective gear with their lightweight, sustainable, and biodegradable properties, potentially reducing environmental impact compared to synthetic fibers. Kevlar reinforced composites provide exceptional durability, high tensile strength, and superior ballistic resistance, making them a benchmark for high-performance protective equipment. Advances in nanotechnology and hybrid material development are driving enhanced performance by combining biocomposites' eco-friendly traits with Kevlar's robustness, fostering innovative, next-generation protective gear solutions.
Infographic: Biocomposite vs Kevlar Reinforced for Protective Gear
 azmater.com
azmater.com