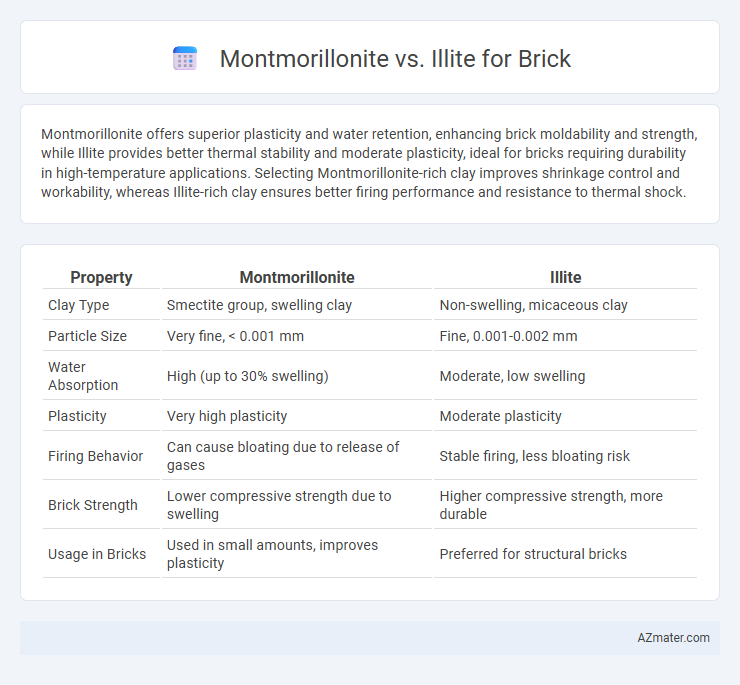
Montmorillonite offers superior plasticity and water retention, enhancing brick moldability and strength, while Illite provides better thermal stability and moderate plasticity, ideal for bricks requiring durability in high-temperature applications. Selecting Montmorillonite-rich clay improves shrinkage control and workability, whereas Illite-rich clay ensures better firing performance and resistance to thermal shock.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Montmorillonite | Illite |
|---|---|---|
| Clay Type | Smectite group, swelling clay | Non-swelling, micaceous clay |
| Particle Size | Very fine, < 0.001 mm | Fine, 0.001-0.002 mm |
| Water Absorption | High (up to 30% swelling) | Moderate, low swelling |
| Plasticity | Very high plasticity | Moderate plasticity |
| Firing Behavior | Can cause bloating due to release of gases | Stable firing, less bloating risk |
| Brick Strength | Lower compressive strength due to swelling | Higher compressive strength, more durable |
| Usage in Bricks | Used in small amounts, improves plasticity | Preferred for structural bricks |
Introduction to Montmorillonite and Illite in Brick Production
Montmorillonite and illite are key clay minerals influencing brick production, with montmorillonite known for its high swelling capacity and plasticity, which enhances workability and water retention in clay mixtures. Illite, characterized by its moderate cation exchange capacity and lower swelling behavior, contributes to improved brick strength and durability after firing. Understanding the distinct mineralogical properties of montmorillonite and illite helps optimize the raw clay selection for producing bricks with desirable mechanical and thermal performance.
Chemical Composition: Montmorillonite vs Illite
Montmorillonite primarily consists of a 2:1 layer silicate structure with high amounts of aluminum, silicon, magnesium, and calcium, contributing to its expansive properties useful in brick manufacturing. Illite, a non-expanding 2:1 clay mineral, contains potassium, aluminum, silicon, and iron, providing greater structural stability but less plasticity compared to montmorillonite. The chemical composition differences impact brick durability, shrinkage, and porosity, with montmorillonite offering better plasticity and illite enhancing mechanical strength.
Physical Properties Comparison
Montmorillonite exhibits high plasticity and significant swelling capacity due to its expansive clay mineral structure, which can lead to increased water absorption and dimensional changes in bricks. Illite, with its non-expanding, layered silicate structure, offers moderate plasticity and better dimensional stability, resulting in bricks with less shrinkage and enhanced durability. The lower swelling potential and improved strength profile of illite make it preferable for brick manufacturing where mechanical integrity and resistance to moisture are critical.
Impact on Brick Strength and Durability
Montmorillonite, a swelling clay mineral, significantly reduces brick strength and durability due to its high water absorption and expansion properties, causing cracking and structural instability during drying and firing. Illite, with a more stable lattice and lower swelling capacity, enhances brick strength by providing better particle bonding and less deformation under moisture variations. The predominance of illite over montmorillonite in clay compositions results in bricks with superior mechanical integrity and long-term durability.
Water Absorption and Shrinkage Rates
Montmorillonite clay exhibits higher water absorption rates due to its expansive layered structure, leading to increased shrinkage during brick drying and firing processes. Illite clay has lower water absorption capacity, resulting in reduced shrinkage and enhanced dimensional stability in fired bricks. The choice of clay significantly affects brick durability, with Montmorillonite demanding careful moisture control to prevent cracking and Illite providing better structural integrity.
Firing Temperatures and Thermal Stability
Montmorillonite exhibits lower firing temperatures, typically around 900-1100degC, but suffers from significant shrinkage and reduced thermal stability due to its high swelling capacity. Illite, with firing temperatures ranging from 1000-1200degC, offers enhanced thermal stability and less deformation, making it more suitable for durable brick production. The higher thermal resilience of illite ensures improved mechanical strength and resistance to thermal shock in fired bricks.
Environmental Implications of Using Montmorillonite or Illite
Montmorillonite exhibits high swelling capacity and water absorption, leading to increased energy consumption during brick drying and firing processes, which impacts the carbon footprint of brick production. Illite, characterized by lower swelling and more stable structural properties, reduces cracking risk and energy needs, making it a more environmentally sustainable clay for brick manufacturing. Choosing illite-rich clay mitigates waste generation and enhances durability, contributing to lower environmental impact over the product lifecycle.
Cost and Availability for Brick Manufacturers
Montmorillonite is generally more expensive than Illite due to its higher swelling capacity and specialized applications, impacting overall brick production costs. Illite offers greater availability and abundance in many clay deposits, making it a cost-effective choice for brick manufacturers seeking consistent raw material supply. The balance between Montmorillonite's unique properties and Illite's affordability often determines the feasibility for large-scale brick production.
Case Studies in Real-World Brick Applications
Case studies reveal Montmorillonite enhances brick plasticity and water retention, improving green strength and drying resistance in real-world applications. Illite contributes to increased hardness and durability due to its stable layered structure, making bricks more resistant to weathering and mechanical stress. Comparative analyses demonstrate bricks with higher Montmorillonite content excel in molding and firing processes, while Illite-rich bricks perform better in load-bearing and outdoor environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Clay for Bricks
Montmorillonite offers superior plasticity and water absorption, making it ideal for bricks requiring high workability and strength, while Illite provides better dimensional stability and lower shrinkage during drying and firing. Selecting the right clay depends on the specific brick application; Montmorillonite suits heavy-duty structural bricks, whereas Illite is preferred for bricks with enhanced durability and resistance to cracking. Balancing plasticity and shrinkage characteristics is crucial for producing high-quality bricks tailored to construction needs.
Infographic: Montmorillonite vs Illite for Brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com