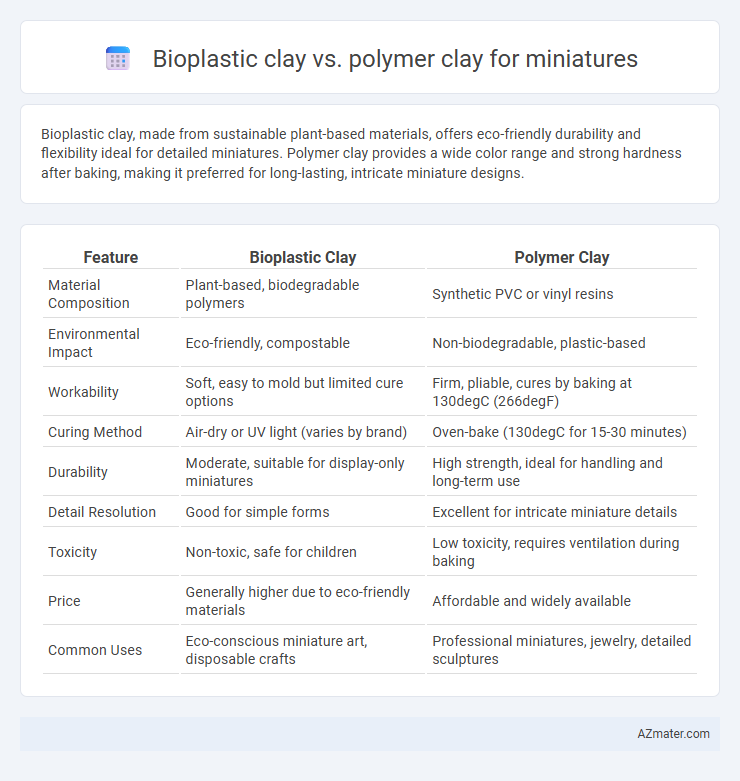
Bioplastic clay, made from sustainable plant-based materials, offers eco-friendly durability and flexibility ideal for detailed miniatures. Polymer clay provides a wide color range and strong hardness after baking, making it preferred for long-lasting, intricate miniature designs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bioplastic Clay | Polymer Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Plant-based, biodegradable polymers | Synthetic PVC or vinyl resins |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, compostable | Non-biodegradable, plastic-based |
| Workability | Soft, easy to mold but limited cure options | Firm, pliable, cures by baking at 130degC (266degF) |
| Curing Method | Air-dry or UV light (varies by brand) | Oven-bake (130degC for 15-30 minutes) |
| Durability | Moderate, suitable for display-only miniatures | High strength, ideal for handling and long-term use |
| Detail Resolution | Good for simple forms | Excellent for intricate miniature details |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic, safe for children | Low toxicity, requires ventilation during baking |
| Price | Generally higher due to eco-friendly materials | Affordable and widely available |
| Common Uses | Eco-conscious miniature art, disposable crafts | Professional miniatures, jewelry, detailed sculptures |
Introduction to Bioplastic Clay and Polymer Clay
Bioplastic clay, derived from renewable resources such as cornstarch and natural fibers, offers an eco-friendly alternative to traditional polymer clay, which is a synthetic material made primarily from polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Bioplastic clay is biodegradable and non-toxic, making it ideal for environmentally conscious miniature artists, while polymer clay provides superior durability, flexibility, and a wide range of vibrant colors suitable for detailed modeling. Selecting between bioplastic clay and polymer clay depends on factors like sustainability preferences and the desired finish and strength of miniature creations.
Material Composition: Bioplastic vs Polymer Clay
Bioplastic clay is composed primarily of natural, biodegradable materials such as cornstarch or cellulose, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional polymer clay, which is typically made from synthetic polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and plasticizers. This difference in material composition affects durability, with polymer clay offering greater strength and flexibility required for detailed miniature work, while bioplastic clay provides a more sustainable option but may lack the same resilience. Understanding the distinct chemical structures and environmental impact of these clays is crucial for artists prioritizing either performance or sustainability in miniature modeling.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bioplastic clay, derived from renewable plant-based materials like cornstarch or cellulose, offers a biodegradable and compostable alternative to traditional polymer clay, which is primarily petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. The production of bioplastic clay typically results in a lower carbon footprint and reduced reliance on fossil fuels, enhancing sustainability in miniature crafting. However, polymer clay's durability and versatility often lead to longer-lasting creations, which can reduce waste over time despite its environmental drawbacks.
Workability and Sculpting Experience
Bioplastic clay offers superior workability with a softer, more pliable texture that allows for smooth blending and fine detail sculpting, making it ideal for intricate miniature work. Polymer clay, while firmer, provides excellent hold and structure, enabling artists to create sharp edges and durable forms but may require more effort to condition before sculpting. Both clays cure with heat, but bioplastic clay often results in a lighter, more flexible finish compared to the rigid outcome of polymer clay.
Baking and Curing Processes Compared
Bioplastic clay typically air-dries or requires low-temperature baking around 200degF (93degC) for 30 minutes, making it eco-friendly and easier to cure without specialized ovens. Polymer clay demands precise baking at higher temperatures, usually 265degF-275degF (129degC-135degC) for 15-30 minutes per 1/4 inch thickness, to avoid burning or under-curing, ensuring durability and color stability. Differences in curing processes affect final hardness, flexibility, and detailing, with polymer clay offering more consistent results but requiring controlled heat, whereas bioplastic clay suits beginners prioritizing simplicity and environmental impact.
Durability and Longevity of Miniatures
Bioplastic clay offers enhanced durability and resistance to cracking, making it a reliable choice for long-lasting miniature creations. Polymer clay, while versatile and easy to sculpt, can be more prone to brittleness over time if not properly cured and sealed. For miniatures requiring exceptional longevity, bioplastic clay's elasticity and toughness provide superior preservation against wear and environmental factors.
Color Range and Finish Quality
Bioplastic clay offers a limited color range compared to polymer clay, which provides an extensive palette with vibrant and customizable hues ideal for detailed miniature work. The finish quality of bioplastic clay tends to be matte and softer, suitable for lightweight models, whereas polymer clay cures into a hard, durable surface with options for glossy or textured finishes that enhance miniature realism. Artists favor polymer clay for its superior finishing options and rich color diversity, making it the preferred choice for professional-quality miniature creations.
Safety and Non-Toxicity Considerations
Bioplastic clay, derived from natural materials like starch and plant fibers, is often non-toxic and biodegradable, making it a safer option for children and environmentally conscious artists. Polymer clay contains polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and plasticizers, which can release fumes during baking, requiring proper ventilation to minimize health risks. Choosing bioplastic clay reduces exposure to synthetic chemicals while offering a sustainable and safe alternative for miniature crafting.
Cost and Accessibility for Artists
Bioplastic clay typically offers a more sustainable and cost-effective option for miniature artists, often priced lower due to its biodegradable components and availability in bulk. Polymer clay, while slightly more expensive, provides greater accessibility with widespread availability in various brands and colors at craft stores worldwide. Artists balancing budget and material quality tend to choose bioplastic clay for eco-friendliness and bulk savings but rely on polymer clay for precision and detailed miniature work.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Clay for Your Miniatures
Bioplastic clay offers eco-friendly and biodegradable qualities, making it ideal for environmentally conscious miniature artists focused on creating sustainable, lightweight models. Polymer clay provides superior durability, a wide color range, and excellent detail retention, making it perfect for intricate, long-lasting miniatures requiring fine sculpting and baking stability. Choosing the right clay depends on whether your priority is eco-friendliness with flexible, smooth finishes or durable, detailed creations with extensive color options and structural resilience.
Infographic: Bioplastic clay vs Polymer clay for Miniature
 azmater.com
azmater.com