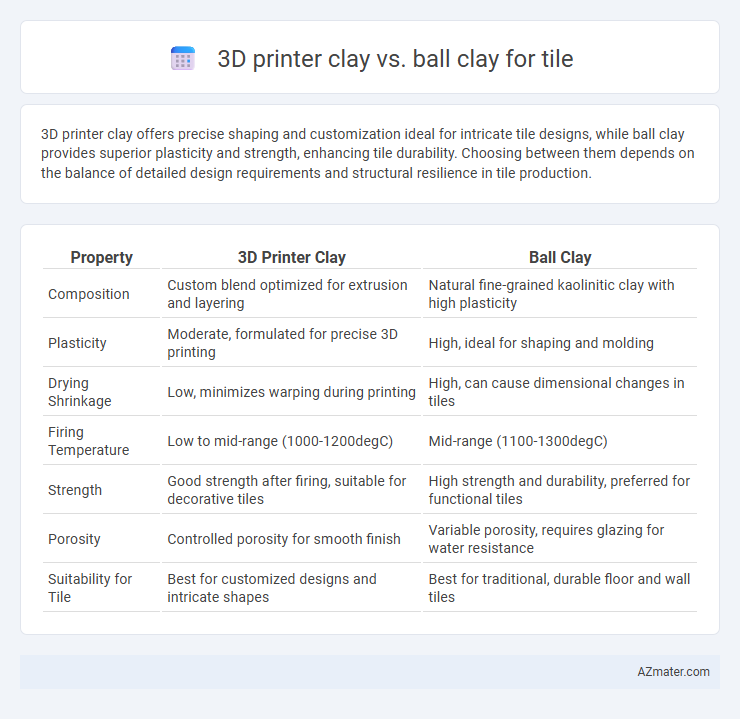
3D printer clay offers precise shaping and customization ideal for intricate tile designs, while ball clay provides superior plasticity and strength, enhancing tile durability. Choosing between them depends on the balance of detailed design requirements and structural resilience in tile production.
Table of Comparison
| Property | 3D Printer Clay | Ball Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Custom blend optimized for extrusion and layering | Natural fine-grained kaolinitic clay with high plasticity |
| Plasticity | Moderate, formulated for precise 3D printing | High, ideal for shaping and molding |
| Drying Shrinkage | Low, minimizes warping during printing | High, can cause dimensional changes in tiles |
| Firing Temperature | Low to mid-range (1000-1200degC) | Mid-range (1100-1300degC) |
| Strength | Good strength after firing, suitable for decorative tiles | High strength and durability, preferred for functional tiles |
| Porosity | Controlled porosity for smooth finish | Variable porosity, requires glazing for water resistance |
| Suitability for Tile | Best for customized designs and intricate shapes | Best for traditional, durable floor and wall tiles |
Introduction: Comparing 3D Printer Clay and Ball Clay for Tiles
3D printer clay offers precise layer-by-layer construction ideal for intricate tile designs, while ball clay is valued for its plasticity and strength in traditional tile manufacturing. Ball clay's fine particles provide excellent workability and durability, making it a staple in ceramic tile production. The selection depends on the desired tile detail, production method, and final product performance requirements.
Material Composition: 3D Printer Clay vs Ball Clay
3D printer clay typically contains a blend of synthetic polymers and fine ceramic particles designed for precise layer adhesion and extrusion properties, ensuring smooth printing and durability in tile applications. Ball clay, composed primarily of kaolinite, mica, and quartz, offers high plasticity and workability, essential for traditional tile shaping and firing processes. The key difference lies in 3D printer clay's optimized formulation for additive manufacturing versus ball clay's natural mineral composition suited for conventional ceramic production.
Workability and Molding Characteristics
3D printer clay offers superior workability with its fine particle size and consistent plasticity, allowing precise and intricate molding ideal for complex tile designs. Ball clay, known for high plasticity and strong bonding properties, provides excellent moldability but may require more water and careful drying to avoid warping in tile production. Both materials support detailed tile shaping, but 3D printer clay ensures smoother layering and finer detail control during additive manufacturing.
Firing Temperatures and Thermal Stability
3D printer clay designed for tile production typically fires at lower temperatures, around 1000degC to 1100degC, offering enhanced thermal stability and reduced shrinkage compared to ball clay, which generally requires firing between 1200degC and 1300degC. Ball clay demonstrates higher plasticity but lower thermal stability, making it prone to warping and cracking during firing. Selecting 3D printer clay ensures better dimensional accuracy and durability due to its optimized mineral composition tailored for additive manufacturing processes.
Shrinkage Rates: 3D Printer Clay vs Ball Clay
3D printer clay typically exhibits lower shrinkage rates, ranging from 5% to 8%, which helps maintain dimensional accuracy for intricate tile designs. In contrast, ball clay can have shrinkage rates between 12% and 15%, leading to more significant size reduction and potential warping during the firing process. Selecting 3D printer clay enhances precision and reduces deformation risks, making it ideal for high-detail tile production.
Surface Finish and Texture Differences
3D printer clay offers a smoother surface finish with finer detail resolution compared to ball clay, which tends to have coarser particles resulting in a more textured and slightly rougher tile surface. The fine particle size in 3D printer clay enhances the uniformity and precision of tile textures, making it ideal for intricate designs and detailed patterns. Ball clay's natural plasticity contributes to better workability but may compromise the subtlety of surface textures in tile applications.
Suitability for Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
3D printer clay designed for additive manufacturing offers higher plasticity and fine particle size, enabling precise layering and detailed tile designs compared to traditional ball clay. Ball clay, while valued for its strong bonding properties and workability in conventional ceramic processes, may pose challenges in 3D printing due to less consistency in flow and particle distribution. Optimizing clay formulations with controlled moisture content and particle size in 3D printer clay enhances dimensional accuracy and structural integrity in printed tiles.
Durability and Tile Strength Comparison
3D printer clay offers enhanced durability and tile strength due to its balanced composition and controlled particle size, resulting in fewer cracks and higher structural integrity after firing. Ball clay, while known for its plasticity and workability, often contains higher levels of impurities that can compromise tile strength and increase porosity. Comparing both materials, 3D printer clay produces tiles with superior mechanical properties and longer-lasting durability, making it more suitable for high-performance ceramic applications.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
3D printer clay offers precise application with minimal waste, making it cost-effective for small-scale, custom tile production despite its higher initial price and limited availability compared to traditional ball clay. Ball clay is widely available and significantly more affordable, ideal for large-scale tile manufacturing where material cost and bulk supply are critical factors. The choice between 3D printer clay and ball clay depends on balancing the need for precision and customization against overall production volume and material cost constraints.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Clay for Tile Production
Selecting the optimal clay for tile production depends on the specific requirements of the project; 3D printer clay offers excellent precision and customization for intricate designs, while ball clay provides superior plasticity and strength, ideal for traditional tile manufacturing. Understanding the differences in shrinkage rates, firing temperatures, and workability is crucial to achieving quality results. Ultimately, combining both clays can enhance tile durability and aesthetic appeal, balancing innovative production and structural integrity.
Infographic: 3D printer clay vs Ball clay for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com