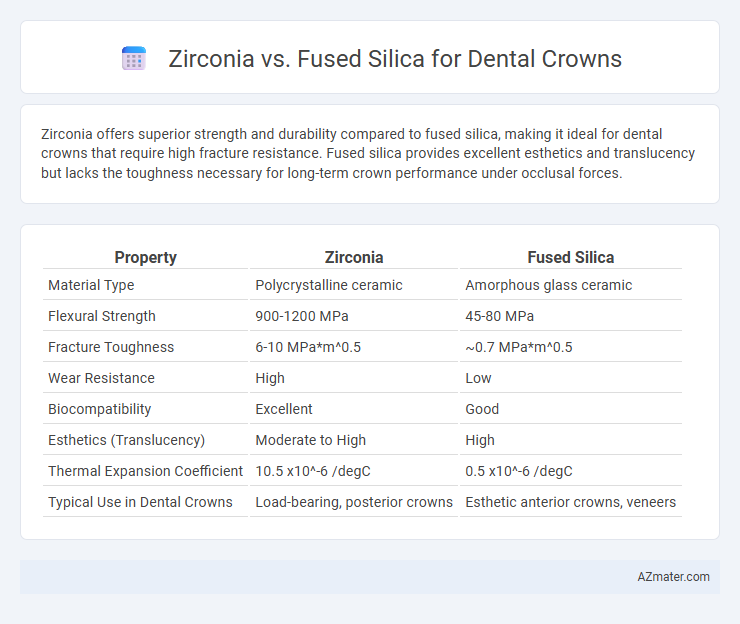
Zirconia offers superior strength and durability compared to fused silica, making it ideal for dental crowns that require high fracture resistance. Fused silica provides excellent esthetics and translucency but lacks the toughness necessary for long-term crown performance under occlusal forces.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zirconia | Fused Silica |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polycrystalline ceramic | Amorphous glass ceramic |
| Flexural Strength | 900-1200 MPa | 45-80 MPa |
| Fracture Toughness | 6-10 MPa*m^0.5 | ~0.7 MPa*m^0.5 |
| Wear Resistance | High | Low |
| Biocompatibility | Excellent | Good |
| Esthetics (Translucency) | Moderate to High | High |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 10.5 x10^-6 /degC | 0.5 x10^-6 /degC |
| Typical Use in Dental Crowns | Load-bearing, posterior crowns | Esthetic anterior crowns, veneers |
Introduction to Dental Crown Materials
Zirconia and fused silica are prominent materials used in dental crowns, distinguished by their mechanical properties and aesthetic qualities. Zirconia offers exceptional strength and fracture resistance, making it ideal for posterior crowns subject to high masticatory forces. Fused silica, known for its translucency and biocompatibility, is commonly employed in anterior restorations where aesthetic demands are critical.
Overview of Zirconia Dental Crowns
Zirconia dental crowns are highly durable, biocompatible, and offer excellent fracture resistance, making them ideal for both anterior and posterior restorations. Unlike fused silica, zirconia crowns provide superior strength and longevity, often lasting over 10 years with proper care. Their natural translucency and color stability ensure an aesthetic match to natural teeth while minimizing wear on opposing dentition.
Overview of Fused Silica Dental Crowns
Fused silica dental crowns offer exceptional biocompatibility and thermal stability, making them a reliable choice for long-term dental restorations. Their high resistance to wear and low thermal expansion minimize fracture risks and enhance patient comfort. Compared to zirconia, fused silica crowns provide superior translucency, closely mimicking natural tooth aesthetics while maintaining strength.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Zirconia dental crowns exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to fused silica crowns, with flexural strength often exceeding 900 MPa, whereas fused silica typically ranges below 100 MPa. The high fracture toughness of zirconia, approximately 9-10 MPa*m^0.5, enhances its resistance to cracking under masticatory forces, making it ideal for posterior restorations subject to heavy occlusal loads. Fused silica's lower strength and brittleness limit its use primarily to esthetic, low-stress anterior restorations where mechanical durability is less critical.
Aesthetic Properties: Zirconia vs Fused Silica
Zirconia dental crowns offer superior translucency and natural tooth-like appearance due to their advanced shading and layering techniques, making them highly aesthetic for visible teeth. Fused silica crowns provide excellent optical clarity and are highly resistant to discoloration, but tend to lack the depth and life-like translucency found in zirconia. The choice between zirconia and fused silica often depends on the balance between durability and the need for a lifelike aesthetic match in dental restorations.
Biocompatibility and Patient Safety
Zirconia demonstrates exceptional biocompatibility with minimal allergic reactions and high resistance to bacterial adhesion, making it a safe choice for dental crowns. Fused silica offers good biocompatibility but is more brittle and prone to microcracks, which may compromise long-term patient safety. Zirconia's superior mechanical strength and bioinert properties contribute to better tissue integration and reduced risk of inflammation or hypersensitivity.
Longevity and Wear Resistance
Zirconia dental crowns exhibit superior longevity and wear resistance compared to fused silica crowns due to their high fracture toughness and strength. Zirconia resists chipping and abrasion effectively, making it ideal for long-term dental restorations subjected to constant chewing forces. Fused silica, while biocompatible and aesthetically favorable, tends to have lower durability and is more prone to surface wear over time.
Ease of Fabrication and Clinical Application
Zirconia crowns offer superior ease of fabrication due to their high strength and compatibility with CAD/CAM technology, enabling precise milling and faster production times compared to fused silica. Fused silica, while providing excellent esthetics and translucency, requires more delicate handling and manual adjustments, making the fabrication process more labor-intensive. Clinically, zirconia crowns demonstrate greater durability and resistance to fracture under occlusal forces, making them suitable for posterior restorations, whereas fused silica is preferred for anterior crowns due to its superior optical properties.
Cost Comparison of Zirconia and Fused Silica Crowns
Zirconia dental crowns typically cost between $800 and $2,500 per tooth, reflecting their high durability and aesthetics, while fused silica crowns range from $500 to $1,500, offering a more affordable but less robust option. The significant price difference is driven by the superior strength and lifespan of zirconia compared to the more brittle nature of fused silica. Dental insurance often covers a portion of zirconia crowns due to their long-term benefits, whereas fused silica crowns might incur higher out-of-pocket expenses over time due to potential replacements.
Choosing the Right Material: Clinical Recommendations
Zirconia crowns are favored for their superior strength, durability, and biocompatibility, making them ideal for posterior restorations where high bite forces occur. Fused silica crowns offer excellent esthetics due to their translucency but have lower fracture toughness, thus are recommended primarily for anterior teeth with less occlusal stress. Clinical guidelines suggest selecting zirconia for long-lasting function and fused silica when optimal aesthetics are paramount, balancing mechanical requirements with patient-specific needs.
Infographic: Zirconia vs Fused silica for Dental crown
 azmater.com
azmater.com