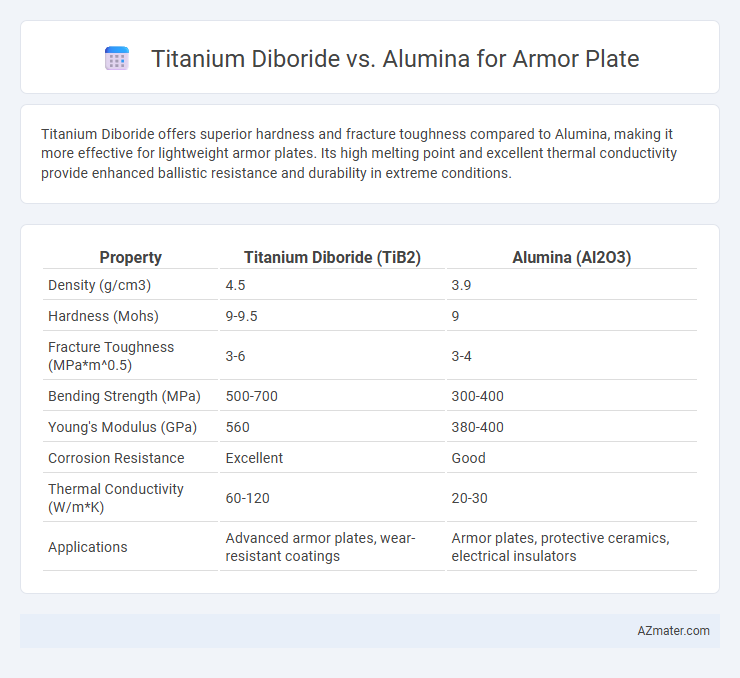
Titanium Diboride offers superior hardness and fracture toughness compared to Alumina, making it more effective for lightweight armor plates. Its high melting point and excellent thermal conductivity provide enhanced ballistic resistance and durability in extreme conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Titanium Diboride (TiB2) | Alumina (Al2O3) |
|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm3) | 4.5 | 3.9 |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 9-9.5 | 9 |
| Fracture Toughness (MPa*m^0.5) | 3-6 | 3-4 |
| Bending Strength (MPa) | 500-700 | 300-400 |
| Young's Modulus (GPa) | 560 | 380-400 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m*K) | 60-120 | 20-30 |
| Applications | Advanced armor plates, wear-resistant coatings | Armor plates, protective ceramics, electrical insulators |
Introduction to Ceramic Armor Materials
Titanium diboride (TiB2) and alumina (Al2O3) are prominent ceramic materials used in armor plating due to their exceptional hardness and high melting points. TiB2 offers superior density and fracture toughness compared to alumina, making it highly effective at dissipating impact energy and providing enhanced ballistic protection. Alumina remains widely utilized for its cost-effectiveness, high compressive strength, and excellent wear resistance, contributing to its continued application in lightweight armor systems.
Overview of Titanium Diboride and Alumina
Titanium Diboride (TiB2) is an ultra-hard ceramic material renowned for its exceptional hardness, high elastic modulus, and excellent resistance to wear and corrosion, making it ideal for advanced armor plating applications. Alumina (Al2O3), a widely used ceramic in armor systems, offers good hardness, high compressive strength, and superior thermal stability at a lower cost than TiB2. While both materials contribute to ballistic protection, TiB2's higher density and superior fracture toughness provide enhanced performance against high-velocity impacts compared to alumina.
Mechanical Properties: Strength, Hardness, and Toughness
Titanium Diboride exhibits superior hardness and compressive strength compared to Alumina, making it highly effective for armor plate applications requiring resistance to penetration and wear. Its fracture toughness surpasses that of Alumina, providing enhanced durability and resistance to cracking under impact. Despite Alumina's high hardness, Titanium Diboride's combination of greater toughness and strength offers improved performance in high-stress environments.
Ballistic Performance Comparison
Titanium Diboride (TiB2) offers superior ballistic performance compared to Alumina due to its higher hardness (approximately 3,200 HV) and greater density (~4.52 g/cm3), which enhance its ability to absorb and dissipate impact energy effectively. TiB2 exhibits exceptional fracture toughness and resistance to shear forces, resulting in improved multi-hit capability against high-velocity projectiles. Alumina, while widely used for armor, has lower hardness (around 2,000 HV) and exhibits brittle failure under extreme ballistic stress, making TiB2 a more effective material for advanced armor plate applications.
Weight and Density Considerations
Titanium diboride (TiB2) offers a significant advantage over alumina (Al2O3) in armor applications due to its lower density of approximately 4.52 g/cm3 compared to alumina's density of about 3.95-4.1 g/cm3, balancing weight and strength effectively. Despite alumina's slightly lower density, titanium diboride provides superior hardness and fracture toughness, allowing for thinner and lighter armor plates with enhanced ballistic performance. The optimized density-to-strength ratio of TiB2 results in reduced overall armor weight without compromising protective capabilities.
Cost and Availability of Materials
Titanium diboride offers superior hardness and ballistic resistance compared to alumina, but its significantly higher cost limits widespread use in armor plate applications. Alumina remains a preferred choice due to its lower material and processing costs, along with established supply chains ensuring consistent availability. Cost efficiency and material accessibility make alumina more viable for mass production of armor plates despite its relatively lower performance.
Fabrication and Processing Differences
Titanium Diboride (TiB2) armor plates exhibit superior hardness and wear resistance compared to Alumina (Al2O3), but their fabrication typically requires higher sintering temperatures exceeding 2000degC, often involving hot pressing or spark plasma sintering to achieve full densification. Alumina armor plates benefit from established, cost-effective processing methods such as pressureless sintering below 1700degC and offer easier machining post-sintering. The complexity and energy demand of TiB2 processing impact manufacturing scalability, whereas Alumina's compatibility with conventional ceramic processing techniques supports widespread production.
Thermal Stability and Environmental Resistance
Titanium Diboride exhibits superior thermal stability compared to Alumina, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 2000degC due to its high melting point of approximately 3225degC. Alumina, with a melting point around 2072degC, is less resistant to thermal shock and rapid temperature fluctuations. Titanium Diboride also demonstrates enhanced environmental resistance, offering exceptional corrosion resistance and oxidation stability in harsh environments, making it more suitable for advanced armor applications where durability under extreme conditions is critical.
Typical Applications in Armor Systems
Titanium Diboride (TiB2) offers superior hardness and high-density advantages compared to Alumina (Al2O3), making it ideal for lightweight, high-performance armor applications in military vehicles and personal protection. TiB2's enhanced ballistic resistance and fracture toughness provide better protection against high-velocity projectiles and armor-piercing rounds, while Alumina remains widely used due to its cost-effectiveness and adequate performance for general-purpose armor plates. Typical applications of TiB2 include advanced body armor, vehicle armor inserts, and aerospace armor systems where weight savings and durability are critical.
Conclusion: Material Selection Criteria
Titanium Diboride (TiB2) offers superior hardness and wear resistance compared to Alumina (Al2O3), making it more effective for high-impact armor plates in demanding environments. Alumina remains a cost-effective choice with good hardness and lightweight properties, suitable for applications where budget constraints and weight are critical factors. Material selection should balance TiB2's enhanced protective capabilities against Alumina's affordability and ease of manufacturing for optimized armor plate performance.
Infographic: Titanium Diboride vs Alumina for Armor Plate
 azmater.com
azmater.com