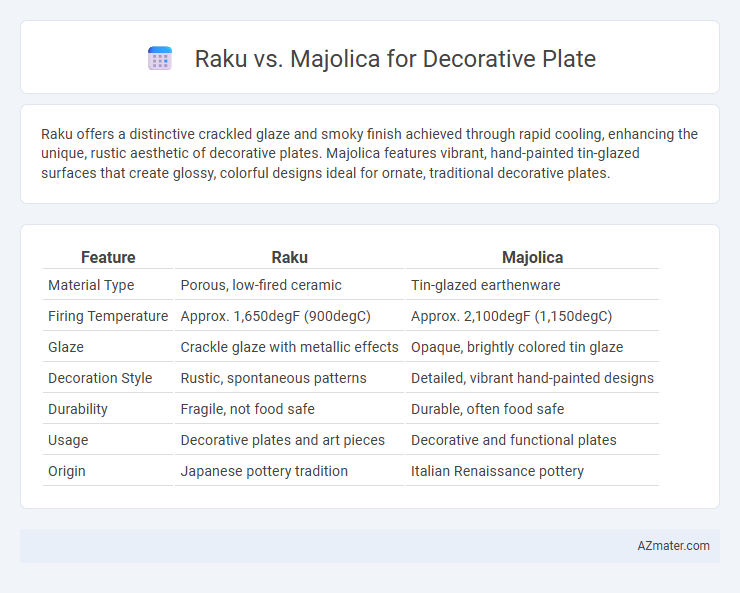
Raku offers a distinctive crackled glaze and smoky finish achieved through rapid cooling, enhancing the unique, rustic aesthetic of decorative plates. Majolica features vibrant, hand-painted tin-glazed surfaces that create glossy, colorful designs ideal for ornate, traditional decorative plates.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Raku | Majolica |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Porous, low-fired ceramic | Tin-glazed earthenware |
| Firing Temperature | Approx. 1,650degF (900degC) | Approx. 2,100degF (1,150degC) |
| Glaze | Crackle glaze with metallic effects | Opaque, brightly colored tin glaze |
| Decoration Style | Rustic, spontaneous patterns | Detailed, vibrant hand-painted designs |
| Durability | Fragile, not food safe | Durable, often food safe |
| Usage | Decorative plates and art pieces | Decorative and functional plates |
| Origin | Japanese pottery tradition | Italian Renaissance pottery |
Introduction to Raku and Majolica Decorative Plates
Raku decorative plates, originating from traditional Japanese pottery techniques, feature rapid firing and cooling processes that create unique crackled glazes and organic textures, making each piece distinct. Majolica decorative plates, rooted in Italian Renaissance ceramics, are characterized by their vibrant, tin-glazed surfaces adorned with intricate hand-painted designs that emphasize bold colors and detailed patterns. Both Raku and Majolica plates serve as artistic centerpieces, blending historical craftsmanship with decorative appeal in home interiors.
Historical Origins of Raku and Majolica Techniques
Raku pottery originated in 16th-century Japan as a hand-shaped, low-firing ceramic technique used in tea ceremonies, emphasizing spontaneity and natural glaze effects. Majolica, developed during the Italian Renaissance, features tin-glazed earthenware with vibrant polychrome designs inspired by Moorish and Spanish influences. Both techniques showcase distinct historical contexts: Raku emphasizes simplicity and wabi-sabi aesthetics, while Majolica reflects intricate, colorful decoration rooted in Mediterranean artistry.
Key Materials Used in Raku vs Majolica
Raku decorative plates are primarily crafted using porous earthenware clay, which allows for quick cooling and dramatic glaze effects during the raku firing process. In contrast, Majolica plates utilize a tin-glaze over a white earthenware body, creating a bright, opaque surface ideal for detailed, colorful painted designs. The distinct materials and glazes in Raku and Majolica influence both the aesthetic qualities and durability of the finished decorative plates.
Firing Processes: Raku vs Majolica
Raku firing involves rapidly removing ceramic pieces from a hot kiln and placing them into combustible materials, creating unique crackle patterns and smoky effects due to rapid cooling and reduction atmosphere. Majolica firing uses a slower, controlled process where pottery is first bisque-fired, then coated with a tin glaze and fired again at a lower temperature to achieve a glossy, brightly colored surface. The distinct firing methods of Raku emphasize unpredictability and texture, while Majolica focuses on color vibrancy and smooth finish.
Surface Decoration and Glazing Differences
Raku decorative plates feature a distinctive surface decoration achieved through a rapid cooling process that creates crackled textures and metallic lusters, emphasizing organic and unpredictable patterns. Majolica plates are characterized by their vibrant, opaque glaze colors applied over a white tin-glazed surface, allowing for detailed hand-painted designs with a glossy, smooth finish. The glazing on Raku results in varied, often matte effects with smoky iridescence, while Majolica's glazing is consistently bright and glossy, providing a durable, richly colored decorative surface.
Color Palette and Finish Comparison
Raku decorative plates feature an earthy, metallic color palette with unpredictable crackle patterns and a matte to semi-gloss finish, offering a rustic, organic aesthetic. Majolica plates showcase vibrant, saturated colors with glossy, smooth glazes that highlight intricate relief designs and detailed brushwork. The contrast in finish and color intensity makes Raku ideal for naturalistic, textured decor, while Majolica suits bold, ornate, and brightly colored interior accents.
Durability and Practical Use of Plates
Raku plates, known for their unique crackled glaze and artistic finish, tend to be more fragile and susceptible to chipping due to their rapid cooling technique, making them less ideal for frequent practical use. Majolica plates, crafted with tin-glazed earthenware, offer higher durability and resistance to everyday wear, making them better suited for both decorative purposes and regular use. The dense, glazed surface of Majolica provides enhanced resistance to moisture and stains, ensuring longer-lasting aesthetic appeal and functionality.
Artistic Styles and Aesthetic Appeal
Raku ceramics exhibit a distinctive smoky texture and organic cracks that highlight a rustic, unpredictable beauty, resonating with wabi-sabi aesthetics and emphasizing natural imperfection. Majolica plates feature vibrant, glossy glazes with intricate hand-painted designs, reflecting Renaissance artistic traditions and Mediterranean influences that create a lively, colorful visual impact. Their contrasting artistic styles offer unique aesthetic appeals--Raku's raw, earthy spirit versus Majolica's detailed, vivid elegance--catering to diverse decorative preferences.
Popularity and Cultural Impact
Raku pottery, known for its rapid firing process and unpredictable glaze effects, enjoys significant popularity in contemporary art circles and embodies a strong cultural connection to Japanese tea ceremonies. Majolica, with its vibrant tin-glazed surface and intricate Renaissance-inspired designs, holds enduring appeal in Western decorative arts and has influenced European ceramic traditions for centuries. Both styles continue to shape decorative plate trends by blending historical significance with unique visual aesthetics.
Choosing Between Raku and Majolica for Decorative Plates
Choosing between Raku and Majolica for decorative plates depends on the desired aesthetic and technique: Raku offers a unique, crackled texture with metallic hues achieved through rapid cooling and reduction firing, appealing to those who prefer an organic, rustic look. Majolica, characterized by its vibrant, glossy glazes and intricate hand-painted designs on a white tin-glazed surface, suits collectors seeking colorful, detailed artistry with a Mediterranean heritage. Both styles provide distinctive visual appeal, but Raku emphasizes texture and spontaneity while Majolica prioritizes vivid color and ornate patterns.
Infographic: Raku vs Majolica for Decorative Plate
 azmater.com
azmater.com