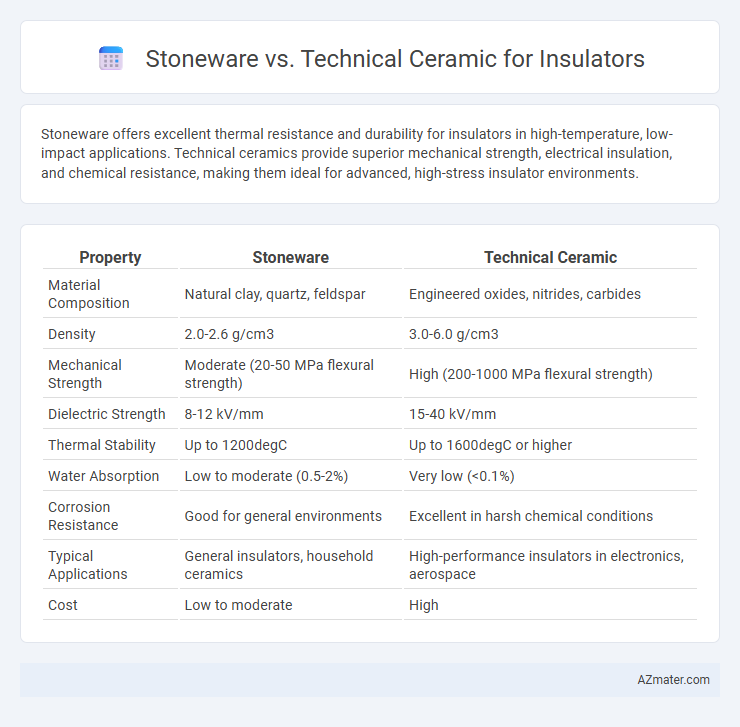
Stoneware offers excellent thermal resistance and durability for insulators in high-temperature, low-impact applications. Technical ceramics provide superior mechanical strength, electrical insulation, and chemical resistance, making them ideal for advanced, high-stress insulator environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Stoneware | Technical Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural clay, quartz, feldspar | Engineered oxides, nitrides, carbides |
| Density | 2.0-2.6 g/cm3 | 3.0-6.0 g/cm3 |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate (20-50 MPa flexural strength) | High (200-1000 MPa flexural strength) |
| Dielectric Strength | 8-12 kV/mm | 15-40 kV/mm |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1600degC or higher |
| Water Absorption | Low to moderate (0.5-2%) | Very low (<0.1%) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good for general environments | Excellent in harsh chemical conditions |
| Typical Applications | General insulators, household ceramics | High-performance insulators in electronics, aerospace |
| Cost | Low to moderate | High |
Introduction to Insulator Materials
Stoneware and technical ceramic represent two key materials used for electrical insulators, both offering excellent dielectric properties and mechanical strength. Stoneware, primarily composed of clay fired at high temperatures, provides cost-effective durability and resistance to environmental factors, making it suitable for standard voltage applications. Technical ceramics, such as alumina or silicon nitride, exhibit superior thermal stability, higher dielectric strength, and enhanced resistance to wear and corrosion, which are critical for high-performance and specialized insulator requirements.
Overview of Stoneware Insulators
Stoneware insulators are made from dense, porcelain-like clay materials fired at high temperatures to achieve excellent mechanical strength and electrical resistance, making them ideal for medium- to high-voltage power transmission. Their surface glaze provides superior weather resistance, reducing contamination and maintaining insulation properties even in harsh outdoor environments. Stoneware insulators offer cost-effective performance, durability, and robustness, distinguishing them from technical ceramics that typically provide higher precision and specialized electrical characteristics.
Overview of Technical Ceramic Insulators
Technical ceramic insulators are engineered from advanced materials such as alumina, silicon nitride, and zirconia, offering superior electrical insulation, high mechanical strength, and excellent thermal stability. These insulators perform reliably in extreme environments, including high temperatures, corrosive atmospheres, and high-voltage applications, making them ideal for modern electrical and electronic systems. Compared to traditional stoneware, technical ceramics provide enhanced durability, lower dielectric loss, and greater precision in electrical insulation performance.
Material Composition Differences
Stoneware insulators consist primarily of natural clay mixed with sand and fired at high temperatures, resulting in a dense, porous structure with moderate mechanical strength. Technical ceramics for insulators are composed of advanced engineered materials such as alumina, silicon nitride, or zirconia, offering superior electrical insulation, higher mechanical durability, and enhanced thermal stability due to their controlled microstructure and purity. The stark contrast in material composition directly impacts performance characteristics, with technical ceramics providing improved dielectric properties and resistance to environmental degradation compared to traditional stoneware.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Stoneware insulators exhibit moderate mechanical strength with good fracture resistance under typical load conditions, suitable for general-purpose electrical insulation. Technical ceramics, such as alumina and silicon nitride, demonstrate superior mechanical strength, including higher flexural and compressive strength, enabling them to withstand extreme mechanical stresses and harsh environmental conditions. The enhanced mechanical properties of technical ceramics result in improved durability and reliability for high-performance insulator applications.
Thermal and Electrical Performance
Stoneware insulators exhibit moderate thermal resistance with typical operating temperatures up to 1000degC, offering reliable electrical insulation due to their high dielectric strength and low conductivity. Technical ceramics outperform stoneware by sustaining extreme temperatures exceeding 1600degC while maintaining superior electrical insulation, characterized by exceptional dielectric constants and minimal power loss at high frequencies. The enhanced thermal shock resistance and precise microstructure of technical ceramics result in improved durability and consistent performance in high-voltage and high-temperature industrial applications.
Durability and Longevity
Stoneware insulators offer moderate durability with resistance to moisture and mechanical stress, making them suitable for standard electrical insulation needs. Technical ceramics, composed of advanced materials like alumina and silicon nitride, provide superior durability and longevity due to their exceptional hardness, thermal stability, and resistance to corrosion and wear. These properties ensure technical ceramic insulators outperform stoneware in high-demand environments, delivering extended service life and minimal maintenance.
Cost Considerations
Stoneware insulators typically offer lower initial costs due to the availability of raw materials and simpler manufacturing processes, making them economically attractive for large-scale applications. Technical ceramics, while more expensive upfront, provide superior mechanical strength, thermal stability, and durability, which can reduce long-term replacement and maintenance expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership involves balancing the higher purchase price of technical ceramics against their extended service life and enhanced performance in demanding environments.
Typical Applications in Industry
Stoneware insulators are commonly used in electrical distribution systems, offering excellent resistance to mechanical stress and weathering, making them ideal for overhead power lines and substations. Technical ceramics provide superior dielectric strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance, which makes them preferred in high-voltage applications, semiconductor manufacturing, and aerospace industries. Both materials serve critical roles in insulation, with stoneware favored for cost-effective outdoor use and technical ceramics essential for precision and high-performance environments.
Choosing the Right Insulator Material
Stoneware insulators offer durability and resistance to weathering, making them suitable for outdoor electrical applications, while technical ceramics provide superior electrical insulation, high mechanical strength, and excellent thermal stability for demanding industrial environments. Choosing the right insulator material depends on factors such as voltage level, environmental conditions, mechanical stress, and thermal requirements; technical ceramics excel in high-voltage and high-temperature scenarios, whereas stoneware is cost-effective for moderate conditions. Prioritizing properties like dielectric strength, moisture resistance, and mechanical robustness ensures optimal performance and longevity of insulators in electrical infrastructure.
Infographic: Stoneware vs Technical Ceramic for Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com