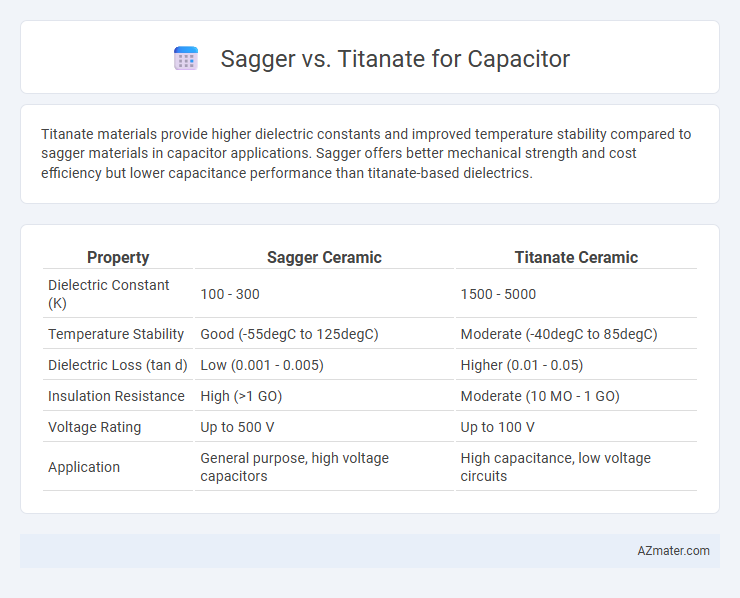
Titanate materials provide higher dielectric constants and improved temperature stability compared to sagger materials in capacitor applications. Sagger offers better mechanical strength and cost efficiency but lower capacitance performance than titanate-based dielectrics.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sagger Ceramic | Titanate Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Constant (K) | 100 - 300 | 1500 - 5000 |
| Temperature Stability | Good (-55degC to 125degC) | Moderate (-40degC to 85degC) |
| Dielectric Loss (tan d) | Low (0.001 - 0.005) | Higher (0.01 - 0.05) |
| Insulation Resistance | High (>1 GO) | Moderate (10 MO - 1 GO) |
| Voltage Rating | Up to 500 V | Up to 100 V |
| Application | General purpose, high voltage capacitors | High capacitance, low voltage circuits |
Introduction: Understanding Sagger and Titanate in Capacitors
Sagger and Titanate materials are essential components influencing capacitor performance due to their unique dielectric properties. Sagger offers high dielectric constant and temperature stability, making it suitable for applications requiring consistent capacitance over wide temperature ranges. Titanate-based capacitors exhibit excellent electrical insulation and low dielectric loss, enhancing overall efficiency and reliability in electronic circuits.
What is Sagger? Role in Capacitor Manufacturing
Sagger is a high-temperature ceramic container used in capacitor manufacturing to hold capacitor elements during firing without contamination or deformation. It provides a controlled environment to prevent oxidation and maintain the geometry of delicate ceramic layers, ensuring consistent dielectric properties. Saggers are essential for producing reliable multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) by protecting internal electrodes and dielectric materials during sintering.
Overview of Titanate: Types and Applications in Capacitors
Titanate materials, including barium titanate (BaTiO3) and strontium titanate (SrTiO3), are widely utilized in capacitor technology due to their high dielectric constants and excellent temperature stability. These perovskite-structured ceramics enhance capacitor performance by offering superior energy density and reliability in multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) and ceramic dielectric capacitors. Applications span from consumer electronics to automotive and aerospace industries, where efficient energy storage and thermal stability are critical.
Material Properties: Sagger vs Titanate Comparison
Sagger materials exhibit high thermal stability and excellent dielectric properties, making them suitable for capacitors requiring reliable performance under elevated temperatures. Titanates, specifically barium titanate, offer superior dielectric constant and high permittivity, which significantly enhances capacitance in compact capacitor designs. The choice between sagger and titanate hinges on balancing thermal resilience with dielectric efficiency to optimize capacitor functionality.
Performance Differences in Capacitor Production
Sagger materials influence capacitor performance by providing high thermal stability and preventing contamination during firing, which leads to enhanced dielectric properties and longer lifespan. Titanate-based capacitors exhibit superior electrical characteristics such as higher dielectric constant and lower dielectric loss, enabling improved capacitance and efficiency. Choosing between sagger and titanate depends on the balance between production environment control and desired capacitor electrical performance metrics.
Cost Implications: Sagger vs Titanate Solutions
Sagger capacitors typically offer lower manufacturing costs due to simpler materials and processes compared to titanate capacitors, which require more expensive raw materials and complex fabrication techniques. The higher dielectric constant of titanate materials can enhance capacitor performance but often leads to increased production expenses that impact overall cost-effectiveness. Evaluating Sagger versus Titanate solutions involves balancing cost savings with performance requirements in applications demanding specific capacitance and reliability levels.
Reliability and Durability Considerations
Sagger capacitors offer superior reliability in high-temperature environments due to their ceramic-based construction, which resists thermal degradation and mechanical stress better than titanate capacitors. Titanate capacitors, while providing higher capacitance density, often face limitations in long-term durability under frequent thermal cycling and voltage fluctuations. For critical applications requiring consistent performance over extended cycles, sagger capacitors demonstrate enhanced longevity and stability compared to titanate alternatives.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Factors
Sagger capacitors typically use ceramic materials with lower environmental footprint compared to titanate capacitors, which rely heavily on titanium dioxide, a resource-intensive mineral. The production of titanate capacitors involves higher energy consumption and generates more hazardous waste, impacting sustainability negatively. In terms of recyclability, ceramic-based saggers offer easier material recovery, making them more favorable for eco-friendly electronic manufacturing.
Industry Trends: Adoption in Modern Capacitor Manufacturing
Titanate materials demonstrate increasing adoption in modern capacitor manufacturing due to superior dielectric properties and temperature stability, enhancing device performance in automotive and energy storage sectors. Sagger compounds, though historically significant, face reduced preference as manufacturers shift toward high-K titanate ceramics offering improved capacitance and longevity. Industry trends reveal a clear shift toward titanate-based capacitors driven by demand for miniaturization and higher energy density in consumer electronics and industrial applications.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Sagger and Titanate for Capacitors
Choosing between Sagger and Titanate for capacitors depends on the specific application requirements such as dielectric constant, stability, and temperature tolerance. Sagger materials generally provide higher dielectric constants and better stability over a wide temperature range, making them ideal for high-performance capacitors in demanding electronic circuits. Titanate capacitors offer cost-effective solutions with good dielectric properties but may fall short in extreme temperature applications compared to Sagger-based ones.
Infographic: Sagger vs Titanate for Capacitor
 azmater.com
azmater.com