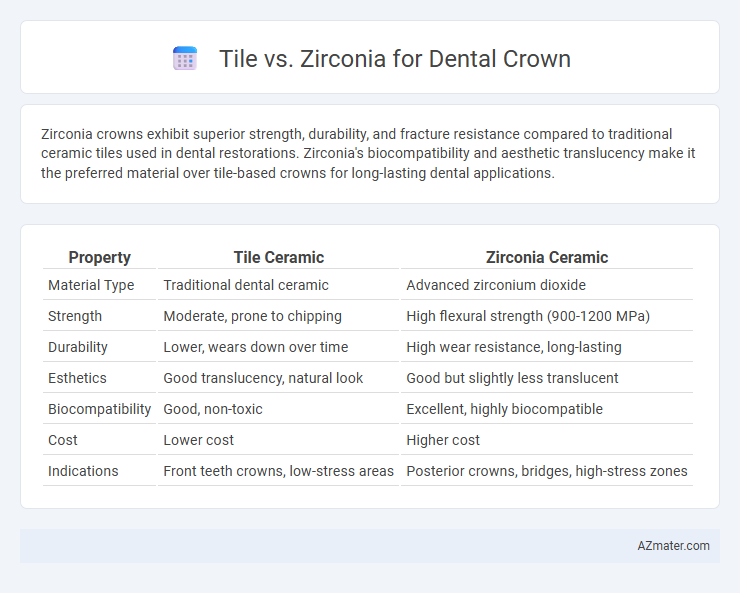
Zirconia crowns exhibit superior strength, durability, and fracture resistance compared to traditional ceramic tiles used in dental restorations. Zirconia's biocompatibility and aesthetic translucency make it the preferred material over tile-based crowns for long-lasting dental applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tile Ceramic | Zirconia Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Traditional dental ceramic | Advanced zirconium dioxide |
| Strength | Moderate, prone to chipping | High flexural strength (900-1200 MPa) |
| Durability | Lower, wears down over time | High wear resistance, long-lasting |
| Esthetics | Good translucency, natural look | Good but slightly less translucent |
| Biocompatibility | Good, non-toxic | Excellent, highly biocompatible |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Indications | Front teeth crowns, low-stress areas | Posterior crowns, bridges, high-stress zones |
Introduction to Dental Crown Materials
Dental crowns are typically made from materials such as ceramic, zirconia, and metal alloys, each offering distinct properties for durability and aesthetics. Zirconia crowns provide exceptional strength and biocompatibility, making them ideal for posterior restorations subjected to high biting forces. In contrast, traditional tile-based ceramics often emphasize superior aesthetic qualities but may lack the prolonged durability seen in zirconia crowns.
Overview of Tile-Based Dental Crowns
Tile-based dental crowns are typically made from porcelain or ceramic materials, offering excellent esthetics and biocompatibility with natural tooth structure. These crowns provide good resistance to wear and are suitable for patients with metal allergies or sensitivities. However, tile-based crowns may have lower fracture toughness compared to zirconia crowns, making them more prone to chipping under heavy occlusal forces.
What is Zirconia in Dentistry?
Zirconia in dentistry is a highly durable ceramic material used for making dental crowns, bridges, and implants due to its exceptional strength and biocompatibility. Unlike traditional tile materials, zirconia offers superior resistance to fracture and wear, making it ideal for long-lasting restorations in both anterior and posterior teeth. Its natural tooth-like color and translucency also provide excellent esthetic results while minimizing allergic reactions.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Zirconia crowns exhibit superior strength and durability compared to traditional ceramic tile crowns, making them ideal for high-stress areas like molars. With a flexural strength ranging from 900 to 1200 MPa, zirconia resists fractures and chipping better than tile materials, which typically have lower strength around 200 to 400 MPa. The enhanced toughness and long-term wear resistance of zirconia crowns contribute to their growing preference in restorative dentistry for reliable, lasting dental restorations.
Aesthetics: Appearance and Color Match
Zirconia crowns offer superior aesthetics compared to traditional tile crowns due to their translucency and natural tooth-like color, enabling a seamless blend with adjacent teeth. The high strength of zirconia allows for thinner crowns without compromising durability, resulting in a more natural appearance and better color match. Tile crowns often lack the ability to mimic the light reflection and shade variations of natural teeth, making zirconia the preferred choice for optimal aesthetic outcomes in dental restorations.
Biocompatibility and Patient Safety
Zirconia crowns exhibit superior biocompatibility compared to traditional tile-like ceramic crowns, minimizing risks of allergic reactions and gum irritation. Zirconia's dense, non-porous structure resists bacterial colonization, enhancing patient safety by reducing the likelihood of inflammation and secondary infections. This material's durability and compatibility with oral tissues make it a preferred choice for long-term dental restorations.
Longevity and Wear Resistance
Zirconia dental crowns offer superior longevity and exceptional wear resistance compared to traditional tile-based crowns, making them a preferred choice for durability. Zirconia's high flexural strength of approximately 900-1200 MPa enables it to withstand biting forces better, reducing the risk of fractures over time. Tile crowns, typically made from ceramic materials, tend to wear down faster and are more prone to chipping, limiting their lifespan in high-stress dental applications.
Cost Differences and Affordability
Tile dental crowns typically cost less than zirconia crowns due to lower material expenses and simpler manufacturing processes. Zirconia crowns offer superior durability and aesthetics but come at a higher price, often making them less affordable for budget-conscious patients. Cost differences range significantly depending on the clinic and region, with tile crowns generally priced between $300 and $700, whereas zirconia crowns can range from $800 to $2,500.
Clinical Indications and Suitability
Zirconia crowns offer superior strength and biocompatibility, making them ideal for posterior teeth restorations where high masticatory forces occur, while tile-based crowns, typically made from feldspathic porcelain or lithium disilicate, excel in aesthetic zones due to their translucency and natural tooth appearance. Clinical indications for zirconia include patients with bruxism or those requiring metal-free restorations, whereas tile crowns suit cases demanding enhanced aesthetics and minimal tooth preparation. The choice between tile and zirconia crowns depends on factors such as occlusal load, aesthetic requirements, and patient-specific conditions like allergies or sensitivity.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Dental Crown Material
Zirconia crowns offer superior strength, durability, and biocompatibility compared to traditional ceramic tiles, making them an ideal choice for long-lasting dental restorations. Ceramic tiles provide excellent aesthetics and are suitable for front teeth where appearance is the priority, but they lack the toughness required for high-stress biting areas. Selecting the right dental crown material depends on factors such as the crown's location, patient's bite force, and aesthetic preferences, with zirconia often favored for molars and tiles for visible anterior teeth.
Infographic: Tile vs Zirconia for Dental crown
 azmater.com
azmater.com