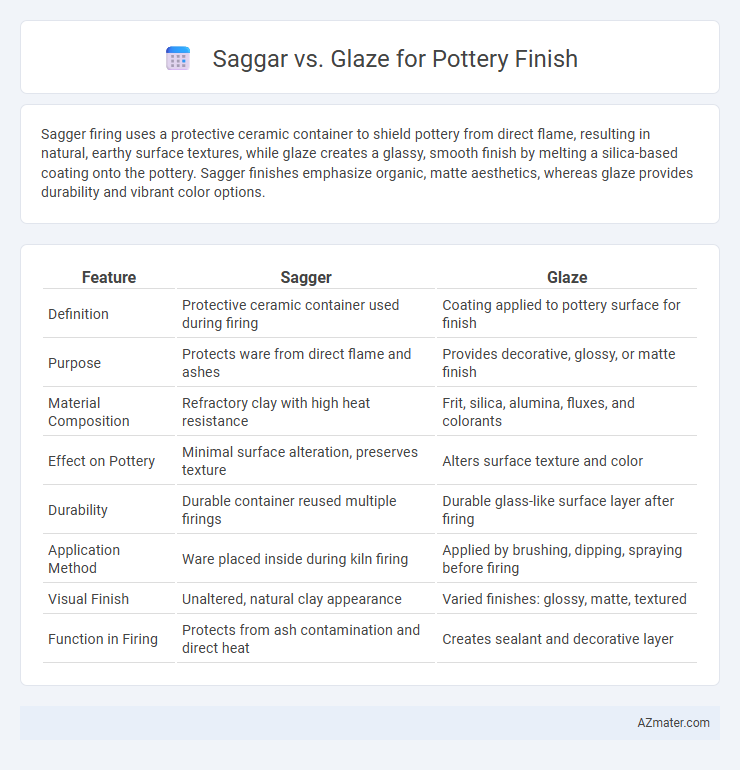
Sagger firing uses a protective ceramic container to shield pottery from direct flame, resulting in natural, earthy surface textures, while glaze creates a glassy, smooth finish by melting a silica-based coating onto the pottery. Sagger finishes emphasize organic, matte aesthetics, whereas glaze provides durability and vibrant color options.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sagger | Glaze |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Protective ceramic container used during firing | Coating applied to pottery surface for finish |
| Purpose | Protects ware from direct flame and ashes | Provides decorative, glossy, or matte finish |
| Material Composition | Refractory clay with high heat resistance | Frit, silica, alumina, fluxes, and colorants |
| Effect on Pottery | Minimal surface alteration, preserves texture | Alters surface texture and color |
| Durability | Durable container reused multiple firings | Durable glass-like surface layer after firing |
| Application Method | Ware placed inside during kiln firing | Applied by brushing, dipping, spraying before firing |
| Visual Finish | Unaltered, natural clay appearance | Varied finishes: glossy, matte, textured |
| Function in Firing | Protects from ash contamination and direct heat | Creates sealant and decorative layer |
Introduction to Pottery Finishing Techniques
Sagger and glaze are essential pottery finishing techniques that impact both the appearance and durability of ceramic pieces. A sagger is a protective container used during firing to shield pottery from direct flame and impurities, preserving the texture and color of the clay body. Glazing involves applying a glassy coating that seals the pottery surface, enhancing waterproofing and decorative effects through various colors and finishes.
What Is Sagger Firing?
Sagger firing in pottery involves enclosing ceramic pieces within a protective container called a sagger, which shields them from direct flame and contaminants during high-temperature firing in a kiln. This method allows for controlled atmospheric conditions that influence the surface texture and color of the pottery, leading to unique finishes that differ from standard glaze techniques. Sagger firing is prized for creating rustic, varied, and often unpredictable effects that enhance the artistic quality of ceramic works.
What Is Glaze Firing?
Glaze firing is a crucial pottery process where a ceramic piece coated with a glaze is heated in a kiln to vitrify the glaze, creating a smooth, glass-like surface that enhances durability and aesthetic appeal. Unlike sagger firing, which involves enclosing pottery in a protective container to influence atmospheric effects, glaze firing directly melts the glaze materials to bond with the ceramic body. This firing technique determines the texture, color, and finish quality, making it essential for achieving waterproof and decorative ceramic ware.
Key Differences Between Sagger and Glaze Finishes
Sagger and glaze finishes differ primarily in their application and appearance; a sagger finish is created by firing pottery inside a protective container called a sagger, which shields the piece from direct flame and imparts natural, smoky textures and organic color variations. In contrast, glaze involves applying a liquid glass coating that fuses to the ceramic surface during firing, producing a smooth, often glossy, watertight finish with vibrant colors or patterns. The sagger finish emphasizes unique, unpredictable effects from atmospheric interactions, while glaze provides consistent, durable surface protection and aesthetic enhancement.
Surface Effects: Sagger vs Glaze
Sagger firing creates unique surface effects by embedding pottery in combustible materials that leave organic textures, earthy tones, and unpredictable patterns on the ceramic body. Glaze produces a smooth, glass-like finish with vibrant colors and consistent textures, sealing the surface for durability and water resistance. While sagger emphasizes natural, textured aesthetics often with matte finishes, glaze offers a polished, glossy appearance that enhances both visual appeal and functionality.
Color Variations and Creative Outcomes
Saggers create unique color variations by shielding pottery from direct flame and ash, allowing for subtle, smoky effects and unpredictable patterns from natural materials like wood and leaves inside the container. Glazes provide a wide palette of vibrant, glossy finishes through chemical reactions during firing, enabling precise control over color, texture, and surface effects such as matte, glossy, or crystalline. Artists seeking organic, rustic outcomes often prefer sagger firing, while those aiming for consistent, diverse color ranges and smooth finishes rely on glazes to achieve their creative vision.
Durability and Practicality Comparison
Sagger firing creates a protective barrier around pottery that enhances durability by shielding the piece from direct flame and ash, reducing surface damage and warping. Glaze provides a glass-like coating that offers superior water resistance and a smoother finish, making it more practical for functional ware that requires non-porous surfaces. While saggers are ideal for ancient-style, rustic finishes with structural protection, glazes excel in practical applications needing both aesthetic appeal and long-term durability.
Environmental Impact of Sagger and Glaze
Sagger firing in pottery utilizes enclosed containers often made from refractory materials, reducing harmful gas emissions by trapping volatile compounds during firing, which minimizes atmospheric pollution. In contrast, glaze application frequently involves chemical compounds, some containing heavy metals that can leach into the environment during production or disposal, posing ecological risks. Choosing saggers can lower the environmental footprint by avoiding toxic glaze materials, supporting more sustainable ceramic practices.
Best Uses for Sagger and Glaze Finishes
Saggers provide a protective container for pottery during firing, ideal for achieving unique surface effects like ash deposits, reduction atmospheres, and smoke patterns that enhance texture and color variations. Glaze finishes create a smooth, glass-like coating that improves durability, waterproofing, and aesthetic appeal, with options ranging from matte to glossy and various color applications. Saggers are best used for experimental, textured finishes in reduction or smoke firing, while glazes are preferred for functional ware requiring a consistent, durable, and decorative surface.
Choosing the Right Finish for Your Pottery
Choosing between sagger and glaze finishes impacts both the aesthetic and functional qualities of pottery, with sagger firing providing varied textures and unpredictable surface effects by protecting pieces inside a container during firing. Glaze offers a smooth, glass-like coating that enhances durability, color vibrancy, and waterproof properties of the ceramic piece. Factors such as desired finish, firing temperature, and intended use should guide artisans in selecting the appropriate technique for their pottery projects.
Infographic: Sagger vs Glaze for Pottery finish
 azmater.com
azmater.com