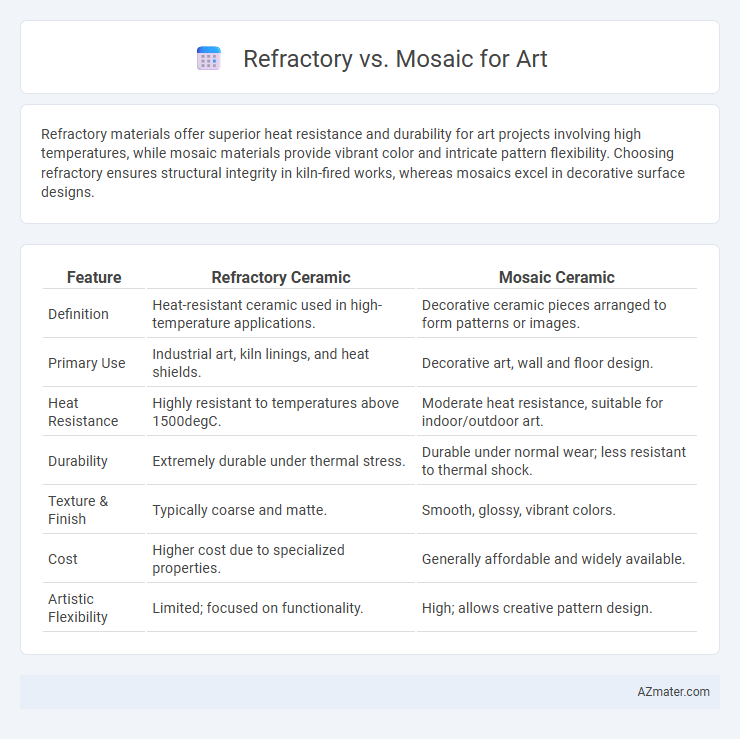
Refractory materials offer superior heat resistance and durability for art projects involving high temperatures, while mosaic materials provide vibrant color and intricate pattern flexibility. Choosing refractory ensures structural integrity in kiln-fired works, whereas mosaics excel in decorative surface designs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Refractory Ceramic | Mosaic Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Heat-resistant ceramic used in high-temperature applications. | Decorative ceramic pieces arranged to form patterns or images. |
| Primary Use | Industrial art, kiln linings, and heat shields. | Decorative art, wall and floor design. |
| Heat Resistance | Highly resistant to temperatures above 1500degC. | Moderate heat resistance, suitable for indoor/outdoor art. |
| Durability | Extremely durable under thermal stress. | Durable under normal wear; less resistant to thermal shock. |
| Texture & Finish | Typically coarse and matte. | Smooth, glossy, vibrant colors. |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialized properties. | Generally affordable and widely available. |
| Artistic Flexibility | Limited; focused on functionality. | High; allows creative pattern design. |
Introduction to Refractory and Mosaic Art
Refractory art utilizes heat-resistant materials such as fire bricks or ceramic fibers to create sculptures and installations that withstand high temperatures, often employed in kiln or forge design. Mosaic art involves assembling small pieces of colored glass, stone, or ceramic tiles (tesserae) to form intricate patterns or images, with origins dating back to ancient Mesopotamia and Rome. Both techniques emphasize durable materials but differ fundamentally in their creation processes--refractory art focusing on heat endurance and mosaics on visual composition through tessellation.
Defining Refractory Art: Meaning and Materials
Refractory art encompasses creations made from heat-resistant materials such as fireclay, silica, and special refractory bricks capable of withstanding extreme temperatures without degrading. These materials enable artists to explore high-temperature processes like kiln firing, metal casting, and glasswork, ensuring durability and stability in their pieces. Unlike mosaic art, which uses small, often fragile tesserae made from glass, stone, or ceramic, refractory art centers on materials engineered for thermal endurance and structural integrity in furnace environments.
Understanding Mosaic Art: Techniques and Styles
Mosaic art involves assembling small pieces of glass, stone, or ceramic called tesserae to create intricate patterns and images, requiring precision in color selection and placement for visual impact. Techniques vary from direct methods, where tesserae are placed directly onto a surface, to indirect methods involving temporary backing for complex designs. Styles range from classical Roman and Byzantine mosaics with detailed figurative scenes to modern abstract compositions emphasizing texture and color contrasts.
Historical Background: Evolution of Each Art Form
Refractory art traces its origins to ancient ceramic and pottery traditions, where heat-resistant materials enabled intricate kiln-fired creations, evolving through civilizations such as Mesopotamia and Egypt. Mosaic art, dating back to the 3rd millennium BCE in Mesopotamia and flourishing in Roman and Byzantine cultures, involves assembling small pieces of stone, glass, or tile to form detailed images, reflecting the cultural and religious narratives of those eras. Both art forms demonstrate a continuous evolution influenced by technological advancements and aesthetic preferences from antiquity to contemporary art practices.
Key Differences: Refractory vs Mosaic Art
Refractory art involves creating sculptures or functional objects using heat-resistant materials like fireclay and refractory bricks, designed to withstand high temperatures in industrial and artistic settings. Mosaic art consists of assembling small pieces of glass, stone, or tile, known as tesserae, to form intricate images or patterns on surfaces such as floors, walls, and murals. The key difference lies in refractory art's focus on thermal durability and structural integrity, while mosaic art emphasizes decorative visual composition through detailed geometric arrangements.
Applications in Contemporary and Classical Settings
Refractory materials excel in classical art for their durability in high-temperature processes like kiln-fired ceramics and glassworks, ensuring longevity and resistance to thermal shock. Mosaic art, prevalent in both contemporary and classical settings, leverages small, colored pieces of stone, glass, or ceramic to create intricate, vibrant designs that withstand weathering in architectural applications. Contemporary artists combine refractory techniques with mosaics to innovate durable, heat-resistant installations that merge traditional craftsmanship with modern aesthetics.
Artistic Processes: Creation and Installation
Refractory art involves using heat-resistant materials like firebrick or refractory cement to shape and assemble sculptures or installations that endure high temperatures, often requiring kiln firing or furnace techniques for creation and curing. Mosaic art prioritizes assembling small tesserae--glass, stone, or ceramic pieces--onto substrates with adhesives or grout, emphasizing careful placement and surface preparation during installation to achieve intricate patterns. Installation for refractory works demands heat-safe mounting and thermal insulation considerations, whereas mosaic installations focus on structural support and precise alignment for visual coherence and durability.
Durability and Maintenance Comparison
Refractory materials used in art, such as firebricks and heat-resistant mortars, offer exceptional durability and withstand extreme temperatures without degradation, making them ideal for installations exposed to high heat or weathering. Mosaics, composed of small pieces of glass, stone, or ceramic, provide a robust surface but require regular maintenance to address grout wear, potential chipping, and cleaning to preserve color vibrancy over time. The choice between refractory art and mosaics depends on the environmental conditions and maintenance capacity, with refractory materials excelling in high-heat durability and mosaics favored for intricate visual appeal despite moderate upkeep needs.
Aesthetic Appeal: Visual Impact of Each Technique
Refractory art emphasizes raw textures and industrial aesthetics through the use of heat-resistant materials, creating dynamic surfaces with a rugged, tactile visual impact. Mosaic art captivates with intricate patterns and vibrant color compositions, assembling small pieces into cohesive, detailed imagery that inspires both complexity and harmony. The stark contrast between refractory's bold, structural presence and mosaic's delicate, decorative intricacy highlights distinct aesthetic appeals tailored to different artistic expressions.
Choosing Between Refractory and Mosaic for Art Projects
Choosing between refractory and mosaic materials for art projects depends on the desired durability and visual effect; refractory materials offer excellent heat resistance ideal for kiln-fired ceramics, while mosaic tiles provide vibrant color options for decorative patterns. Refractory materials are best suited for functional art requiring structural stability under high temperatures, whereas mosaics excel in surface embellishment and intricate designs with glass or stone pieces. Assessing factors like project environment, texture, longevity, and aesthetic goals ensures the optimal choice for artistic expression and material performance.
Infographic: Refractory vs Mosaic for Art
 azmater.com
azmater.com