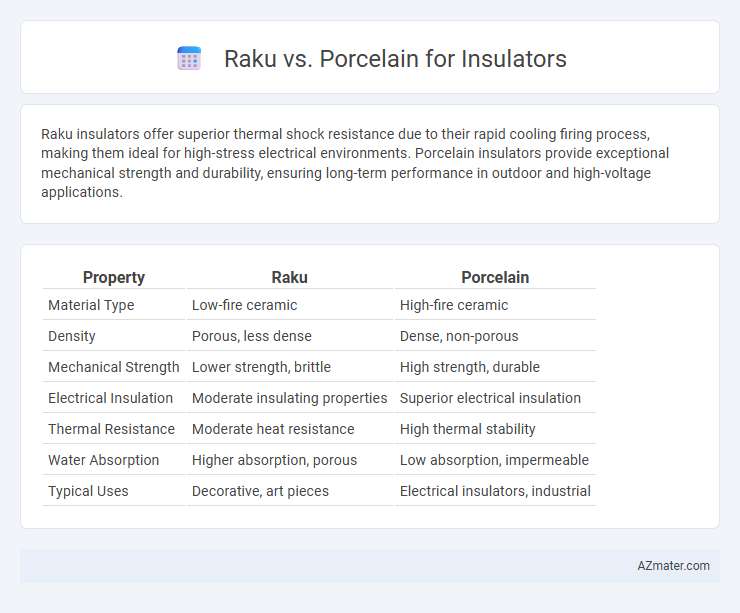
Raku insulators offer superior thermal shock resistance due to their rapid cooling firing process, making them ideal for high-stress electrical environments. Porcelain insulators provide exceptional mechanical strength and durability, ensuring long-term performance in outdoor and high-voltage applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Raku | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Low-fire ceramic | High-fire ceramic |
| Density | Porous, less dense | Dense, non-porous |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower strength, brittle | High strength, durable |
| Electrical Insulation | Moderate insulating properties | Superior electrical insulation |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate heat resistance | High thermal stability |
| Water Absorption | Higher absorption, porous | Low absorption, impermeable |
| Typical Uses | Decorative, art pieces | Electrical insulators, industrial |
Introduction to Ceramic Insulators
Ceramic insulators are essential components in electrical systems, offering high mechanical strength and excellent electrical insulation properties. Raku, a traditional Japanese pottery technique, creates porous ceramics with unique textures but lower durability and insulation compared to porcelain, which is fired at higher temperatures to produce dense, vitrified materials ideal for insulators. Porcelain's superior resistance to weather, moisture, and electrical stress makes it the preferred choice for high-voltage insulators in power transmission and distribution networks.
What is Raku?
Raku is a traditional Japanese pottery technique characterized by rapid firing and cooling processes that result in unique, crackled glaze patterns highly valued for artistic ceramic insulators. This method enhances thermal shock resistance and porosity, making Raku insulators suitable for decorative and electrical applications where aesthetics and functionality intersect. Porcelain insulators, by contrast, offer superior mechanical strength and dielectric properties, but Raku provides distinct surface textures and thermal attributes favored in specialized insulator designs.
What is Porcelain?
Porcelain is a high-strength ceramic material widely used for electrical insulators due to its excellent dielectric properties, mechanical strength, and resistance to environmental degradation. It is composed primarily of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, which are fired at high temperatures to create a dense, durable, and non-porous structure ideal for isolating electrical conductors. Porcelain insulators offer superior performance in high-voltage applications and harsh outdoor conditions, making them a reliable choice over Raku in many industrial and power distribution settings.
Material Properties: Raku vs Porcelain
Raku insulators exhibit higher thermal shock resistance due to their porous ceramic structure, allowing rapid cooling without cracking, whereas porcelain insulators provide superior mechanical strength and long-term durability under high voltage stress. Porcelain's dense, vitrified composition ensures excellent electrical insulation and resistance to environmental degradation, making it ideal for high-voltage power transmission. Raku's lightweight and artistic finish often prioritize aesthetics over performance, while porcelain emphasizes reliability and consistent insulation properties in industrial applications.
Electrical Insulating Capabilities
Raku and porcelain insulators differ significantly in electrical insulating capabilities, with porcelain exhibiting superior dielectric strength and resistance to electrical breakdown under high voltage conditions. Porcelain's dense, vitrified structure provides excellent moisture resistance and stability, making it reliable in diverse environmental conditions for high-voltage applications. In contrast, raku, being a ceramic fired at lower temperatures with a porous finish, offers lower electrical resistance and is less suitable for critical electrical insulation purposes.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Porcelain insulators exhibit superior durability thanks to their high mechanical strength, resistance to weathering, and excellent electrical insulation properties, making them ideal for long-term outdoor applications. Raku insulators, while artistically unique and thermally resistant due to their rapid cooling process, generally offer lower structural integrity and a shorter lifespan under harsh environmental conditions. Porcelain's ability to withstand significant mechanical and thermal stresses without cracking ensures a longer operational lifespan compared to the more fragile and porous nature of Raku ceramics.
Manufacturing Processes and Costs
Raku insulators are crafted through a rapid firing and cooling process that introduces unique crackle patterns, resulting in a more artistic and less uniform finish, often making them cost-effective for small-scale production but less consistent in quality. Porcelain insulators involve a complex, high-temperature firing process with precise control over material composition, ensuring durability and electrical insulation properties, which increases manufacturing costs due to longer production times and specialized equipment. The cost difference arises mainly from porcelain's industrial-scale manufacturing and superior material consistency, versus Raku's artisanal, lower-volume approach that can lead to variable performance.
Applications in Electrical Systems
Raku insulators are primarily used in decorative electrical systems due to their artful glazing and crackled textures, providing moderate dielectric strength suitable for low-voltage applications. Porcelain insulators dominate high-voltage transmission and distribution networks because of their superior mechanical strength, excellent thermal resistance, and high dielectric properties essential for reliable insulation under harsh environmental conditions. The choice between Raku and Porcelain hinges on performance requirements, with Porcelain preferred for critical electrical insulation in power grids and Raku more common in aesthetic or low-stress electrical components.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Raku pottery, known for its low firing temperature and use of natural waste materials as fuel, typically has a smaller carbon footprint compared to porcelain, which requires higher firing temperatures and more energy-intensive processes. Porcelain's raw materials, often including refined kaolin clay, demand significant mining and processing, leading to greater environmental impact and resource depletion. Sustainable manufacturing practices in raku production enhance its appeal as an eco-friendly insulator option, whereas porcelain's durability supports long-term use but involves higher initial environmental costs.
Choosing the Right Insulator: Key Considerations
Selecting the right insulator involves evaluating Raku and porcelain based on thermal resistance, durability, and electrical insulation properties. Porcelain offers superior mechanical strength and weather resistance, making it ideal for high-voltage and outdoor applications, while Raku provides better thermal shock resistance and aesthetic versatility suitable for artistic or low-stress environments. Considering environmental conditions, load requirements, and maintenance needs ensures the optimal choice between Raku and porcelain insulators for specific electrical insulation tasks.
Infographic: Raku vs Porcelain for Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com