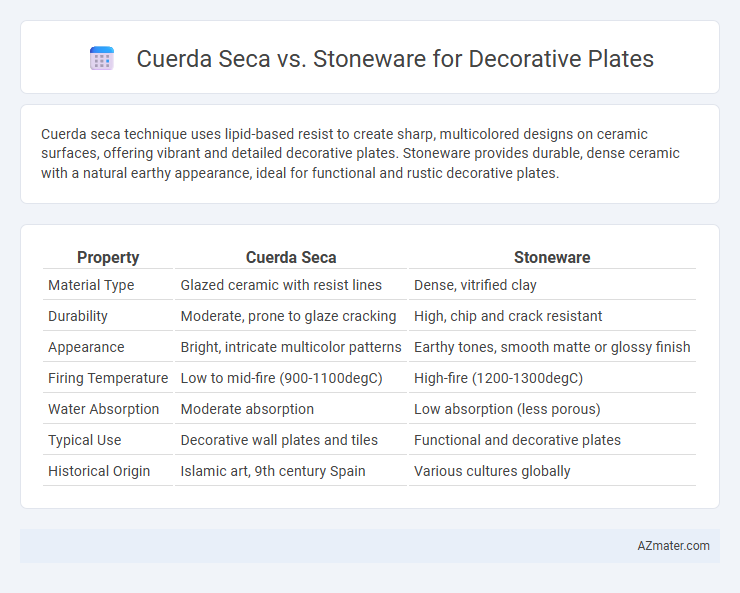
Cuerda seca technique uses lipid-based resist to create sharp, multicolored designs on ceramic surfaces, offering vibrant and detailed decorative plates. Stoneware provides durable, dense ceramic with a natural earthy appearance, ideal for functional and rustic decorative plates.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cuerda Seca | Stoneware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glazed ceramic with resist lines | Dense, vitrified clay |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to glaze cracking | High, chip and crack resistant |
| Appearance | Bright, intricate multicolor patterns | Earthy tones, smooth matte or glossy finish |
| Firing Temperature | Low to mid-fire (900-1100degC) | High-fire (1200-1300degC) |
| Water Absorption | Moderate absorption | Low absorption (less porous) |
| Typical Use | Decorative wall plates and tiles | Functional and decorative plates |
| Historical Origin | Islamic art, 9th century Spain | Various cultures globally |
Introduction to Decorative Plate Techniques
Cuerda seca and stoneware represent two distinct decorative plate techniques with unique aesthetic and functional properties. Cuerda seca involves intricate line work using colored glazes separated by a greasy resist, producing vibrant, detailed motifs ideal for artistic expression. Stoneware, fired at high temperatures, offers robust durability and a natural, earthy finish, making it suitable for both decorative and practical uses.
What is Cuerda Seca?
Cuerda seca is a traditional ceramic technique characterized by using waxy resist lines to separate colored glazes, creating intricate patterns without mixing hues during firing. Stoneware, on the other hand, refers to a dense, durable pottery fired at high temperatures, often serving as a robust base for decorative plates. Cuerda seca stands out for its vibrant, detailed imagery while stoneware emphasizes strength and longevity in tableware.
Understanding Stoneware Plates
Stoneware plates offer exceptional durability and a dense, non-porous surface ideal for decorative use, making them a preferred choice over cuerda seca techniques that rely on intricate, colorful slip lines on ceramic surfaces. The robust firing temperatures of stoneware (typically between 1,200-1,300degC) produce a sturdy, vitrified body resistant to chipping and moisture, which enhances longevity for decorative plates. Unlike cuerda seca, which emphasizes detailed patterns and color separation, stoneware focuses on functional strength combined with artistic glazing, providing versatile options for both display and practical use.
Key Materials and Processes
Cuerda seca techniques use colored glazes separated by greasy lines on earthenware, creating intricate, vibrant patterns with relatively porous surfaces. Stoneware involves high-fired clay that vitrifies to a dense, durable, and non-porous body, often with glaze applied directly to the stoneware surface for a smooth finish. The key distinction lies in cuerda seca's reliance on low-fire earthenware and detailed glaze separation versus stoneware's high-temperature vitrification process producing stronger, heavier decorative plates.
Visual and Textural Differences
Cuerda seca technique features intricate, colorful designs separated by thin black lines, creating a vibrant, mosaic-like visual effect on decorative plates, while stoneware presents a more uniform, earthy appearance with muted tones and natural glaze variations. The cuerda seca method yields a slightly raised texture where the resist lines define the patterns, offering a tactile contrast to the smooth, dense surface characteristic of fired stoneware. Stoneware's compact, vitrified body provides a firm, weighted feel, in contrast to the lighter, more visually segmented cuerda seca plates that emphasize detailed artistry.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Cuerda seca decorative plates often feature intricate, colorful designs created with a wax-resist technique, but their durability may be compromised by the glazed ceramic surface, which is prone to chipping over time. Stoneware plates, crafted from dense, non-porous clay fired at high temperatures, provide superior strength and resistance to cracking, making them ideal for long-lasting decorative use. When comparing durability and longevity, stoneware consistently outperforms cuerda seca ceramics due to its robust material composition and enhanced resistance to wear.
Design Flexibility and Artistic Expression
Cuerda seca technique offers greater design flexibility for decorative plates through its ability to separate multiple glazes with resin lines, enabling intricate patterns and vibrant color contrasts. Stoneware, with its dense, durable clay body and wider firing range, allows for varied surface textures and more subtle glaze effects, fostering unique artistic expression. Both methods support creative customization, but cuerda seca excels in detailed, colorful motifs, while stoneware emphasizes form and natural glaze variations.
Suitability for Indoor vs. Outdoor Display
Cuerda seca ceramic plates, known for their intricate glaze patterns, are typically more suited for indoor display due to their delicate surface prone to weathering and fading when exposed to outdoor elements. Stoneware, with its dense, non-porous structure and durability, offers superior resilience against moisture, temperature fluctuations, and UV rays, making it ideal for outdoor decorative plates. For collectors and decorators seeking long-lasting outdoor displays, stoneware presents a practical choice, while cuerda seca serves well in controlled indoor environments preserving artistic detail.
Cost and Accessibility
Cuerda seca decorative plates generally cost more due to the intricate hand-painting process and specialized glazes, making them less accessible for casual buyers. Stoneware plates offer greater affordability and widespread availability, benefiting from mass production techniques and durable materials. Collectors prioritizing unique artistry may invest in cuerda seca, while everyday buyers often choose cost-effective, accessible stoneware options.
Choosing the Best Technique for Your Project
Cuerda seca offers intricate, multi-colored designs ideal for highly detailed decorative plates, utilizing a resist technique that prevents glazes from mixing during firing. Stoneware provides durability and a more subdued aesthetic, with natural textures and earthy tones that suit rustic or minimalist decor styles. Selecting between cuerda seca and stoneware depends on your design complexity, color vibrancy, and the intended use of the decorative plate, ensuring optimal visual impact and longevity.
Infographic: Cuerda seca vs Stoneware for Decorative Plate
 azmater.com
azmater.com