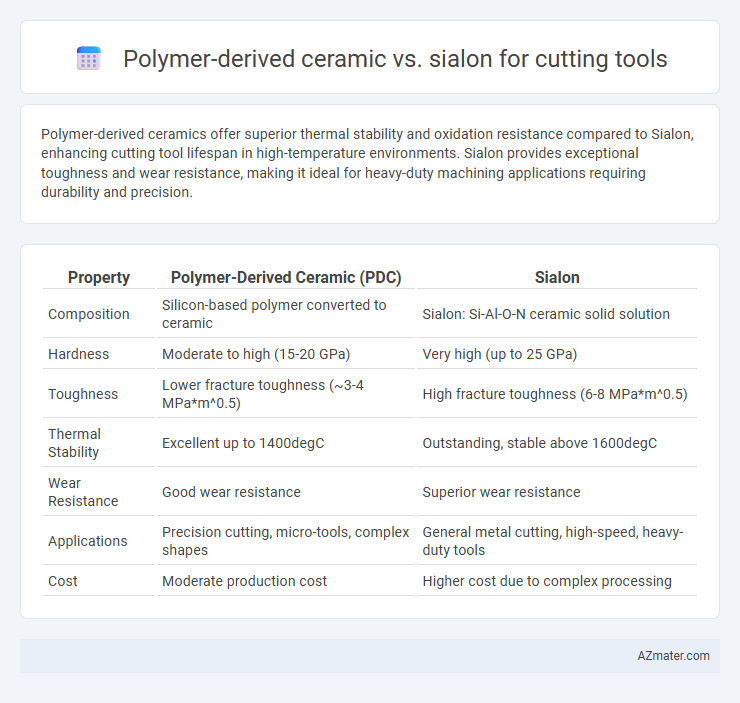
Polymer-derived ceramics offer superior thermal stability and oxidation resistance compared to Sialon, enhancing cutting tool lifespan in high-temperature environments. Sialon provides exceptional toughness and wear resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty machining applications requiring durability and precision.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymer-Derived Ceramic (PDC) | Sialon |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silicon-based polymer converted to ceramic | Sialon: Si-Al-O-N ceramic solid solution |
| Hardness | Moderate to high (15-20 GPa) | Very high (up to 25 GPa) |
| Toughness | Lower fracture toughness (~3-4 MPa*m^0.5) | High fracture toughness (6-8 MPa*m^0.5) |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent up to 1400degC | Outstanding, stable above 1600degC |
| Wear Resistance | Good wear resistance | Superior wear resistance |
| Applications | Precision cutting, micro-tools, complex shapes | General metal cutting, high-speed, heavy-duty tools |
| Cost | Moderate production cost | Higher cost due to complex processing |
Introduction to Advanced Cutting Tool Materials
Polymer-derived ceramics (PDCs) offer superior hardness and thermal stability compared to conventional cutting tool materials, making them ideal for high-performance applications requiring extreme wear resistance. Sialon ceramics, synthesized from silicon, aluminum, oxygen, and nitrogen, provide exceptional toughness and thermal shock resistance, enhancing tool life under demanding machining conditions. Both materials represent advancements in cutting tool technology by combining mechanical strength with chemical inertness to improve cutting efficiency and durability.
Overview of Polymer-Derived Ceramics (PDCs)
Polymer-derived ceramics (PDCs) are advanced inorganic materials synthesized through the pyrolysis of preceramic polymers, offering superior high-temperature stability and oxidation resistance compared to conventional ceramics. Their unique amorphous-to-crystalline microstructures enable exceptional hardness and fracture toughness, making them suitable for cutting tools exposed to extreme wear and thermal conditions. Unlike Sialon ceramics, PDCs provide tunable properties through compositional control at the molecular level, enhancing their performance in precision machining and metal cutting applications.
Understanding Sialon Ceramics
Sialon ceramics, composed primarily of silicon, aluminum, oxygen, and nitrogen, exhibit exceptional hardness, thermal stability, and wear resistance, making them ideal for cutting tool applications. Polymer-derived ceramics offer versatility in microstructure control, yet Sialon materials outperform in toughness and heat resistance due to their unique crystalline structure. Their ability to maintain strength at elevated temperatures significantly enhances tool life and machining efficiency in demanding cutting environments.
Material Properties: PDCs vs Sialon
Polymer-derived ceramics (PDCs) exhibit superior hardness and oxidation resistance compared to Sialon, making them highly effective for high-speed cutting applications. Sialon offers enhanced fracture toughness and thermal shock resistance, which is critical for maintaining tool integrity under variable machining conditions. The combination of high Young's modulus in PDCs and the exceptional wear resistance in Sialon defines the performance advantages of each material in cutting tool manufacturing.
Hardness and Wear Resistance Comparison
Polymer-derived ceramics exhibit exceptional hardness, often surpassing traditional ceramic materials, due to their homogeneous microstructure and fine grain size, which enhances their wear resistance in cutting tools. Sialon ceramics also provide high hardness and excellent wear resistance, attributed to their strong covalent bonding and toughness from silicon, aluminum, and oxygen synergy. Comparative studies reveal polymer-derived ceramics typically offer superior hardness and comparable or improved wear resistance, making them highly effective for high-performance cutting tool applications.
Thermal Stability and Chemical Inertness
Polymer-derived ceramics exhibit superior thermal stability, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1,600degC, which enhances their performance in high-speed cutting applications. Sialon ceramics, known for exceptional chemical inertness, resist oxidation and abrasive wear, providing durability in chemically aggressive machining environments. The integration of polymer-derived ceramics with Sialon properties can optimize cutting tool longevity by balancing thermal resilience and chemical resistance.
Manufacturing Processes and Cost Considerations
Polymer-derived ceramics (PDCs) offer precise microstructural control through low-temperature pyrolysis of preceramic polymers, enabling complex shapes and thin sections ideal for cutting tools, while Sialon ceramics require high-temperature sintering and hot isostatic pressing, resulting in higher energy consumption and longer manufacturing cycles. The manufacturing of PDC cutting tools benefits from reduced tooling costs and faster prototyping compared to Sialon's demanding powder processing and densification steps. Cost considerations favor PDCs in small batch production and custom applications, whereas Sialon remains competitive for large-scale, high-performance tool production due to its superior mechanical properties despite higher initial processing expenses.
Performance in Machining Difficult-to-Cut Materials
Polymer-derived ceramics exhibit superior thermal stability and oxidation resistance, making them ideal for high-speed machining of difficult-to-cut materials like titanium alloys and superalloys. Sialon cutting tools offer enhanced toughness and wear resistance, enabling sustained performance in interrupted cutting conditions and abrasive environments typical of hardened steels and cast irons. Both materials extend tool life and improve surface finish, but polymer-derived ceramics excel in extreme thermal conditions, while Sialon provides balanced mechanical strength and fracture toughness.
Environmental and Sustainability Factors
Polymer-derived ceramics (PDCs) offer significant environmental advantages over Sialon ceramics due to lower energy consumption during synthesis and the ability to tailor microstructures for extended tool life, reducing waste generation. Sialon cutting tools, while possessing excellent mechanical properties, require high-temperature processing, leading to greater carbon emissions and resource intensity. The sustainability profile of PDCs is enhanced by their potential recyclability and reduced reliance on scarce raw materials compared to Sialon-based tools, aligning better with green manufacturing goals.
Future Trends and Selection Guidelines for Cutting Tools
Polymer-derived ceramics exhibit superior thermal stability and oxidation resistance, making them ideal for high-speed cutting applications requiring enhanced durability compared to Sialon, which offers excellent toughness and fracture resistance suited for interrupted cutting operations. Future trends indicate growing integration of nanostructured polymer-derived ceramics to improve wear resistance and tool life, while Sialon compositions are being optimized for hybrid machining environments involving diverse materials. Selection guidelines emphasize matching polymer-derived ceramics with high-temperature, precision cutting, whereas Sialon is preferred for versatile, impact-heavy tasks, balancing cost-effectiveness and performance based on machining conditions.
Infographic: Polymer-derived ceramic vs Sialon for Cutting tool
 azmater.com
azmater.com