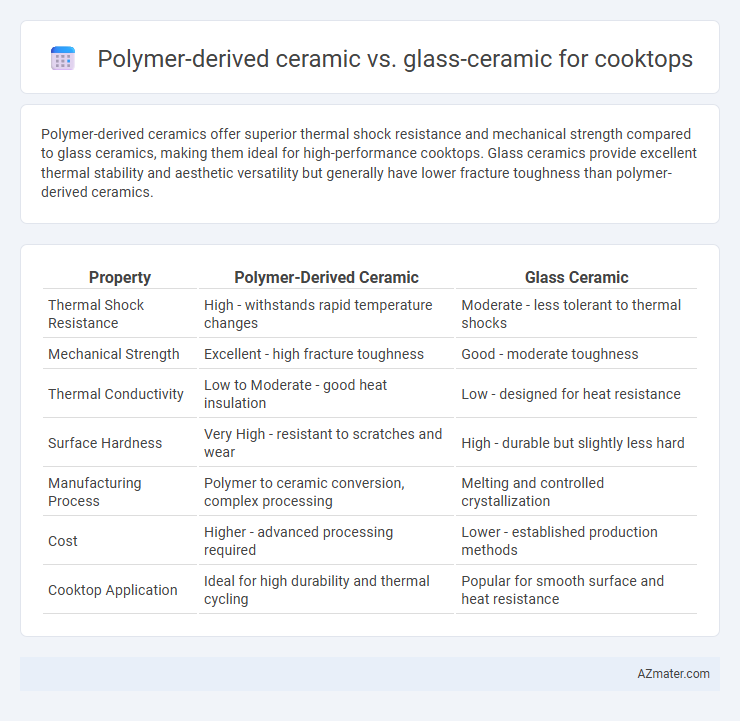
Polymer-derived ceramics offer superior thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength compared to glass ceramics, making them ideal for high-performance cooktops. Glass ceramics provide excellent thermal stability and aesthetic versatility but generally have lower fracture toughness than polymer-derived ceramics.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymer-Derived Ceramic | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Shock Resistance | High - withstands rapid temperature changes | Moderate - less tolerant to thermal shocks |
| Mechanical Strength | Excellent - high fracture toughness | Good - moderate toughness |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low to Moderate - good heat insulation | Low - designed for heat resistance |
| Surface Hardness | Very High - resistant to scratches and wear | High - durable but slightly less hard |
| Manufacturing Process | Polymer to ceramic conversion, complex processing | Melting and controlled crystallization |
| Cost | Higher - advanced processing required | Lower - established production methods |
| Cooktop Application | Ideal for high durability and thermal cycling | Popular for smooth surface and heat resistance |
Introduction to Cooktop Materials
Polymer-derived ceramics exhibit superior thermal shock resistance and higher mechanical strength compared to traditional glass ceramics, making them increasingly favored in advanced cooktop applications. Glass ceramics offer excellent heat distribution and aesthetic versatility, but their lower fracture toughness limits durability under rapid temperature changes. Selection of cooktop materials increasingly prioritizes the balance between thermal conductivity, mechanical robustness, and resistance to thermal cycling, positioning polymer-derived ceramics as a promising alternative for high-performance cooking surfaces.
Overview of Polymer-Derived Ceramics
Polymer-derived ceramics (PDCs) for cooktops feature superior thermal stability and mechanical strength compared to conventional glass ceramics, enabling better resistance to thermal shock and wear. PDCs are synthesized from liquid preceramic polymers that convert into ceramics upon pyrolysis, offering tailored microstructures and enhanced durability. These materials provide improved heat distribution and maintain structural integrity under rapid temperature changes, making them an advanced alternative for high-performance cooktop surfaces.
Overview of Glass Ceramic Materials
Glass ceramic materials for cooktops offer exceptional thermal shock resistance and durability, making them ideal for high-temperature cooking environments. Composed mainly of crystalline phases embedded within a glassy matrix, they provide excellent mechanical strength and scratch resistance compared to polymer-derived ceramics. These materials also enable efficient heat distribution and rapid cooling, ensuring safety and energy efficiency in modern kitchen appliances.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Polymer-derived ceramics exhibit superior thermal shock resistance and higher operating temperatures compared to glass ceramics, making them ideal for rapid heating and cooling cycles in cooktops. Glass ceramics offer excellent thermal conductivity and uniform heat distribution but generally have lower maximum service temperatures and reduced resistance to thermal stress. The enhanced endurance of polymer-derived ceramics under extreme thermal cycling ensures longer durability and efficiency in high-performance cooktop applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polymer-derived ceramics offer superior mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance compared to glass ceramics, making them highly durable for cooktop applications. Their inherent microstructure provides enhanced fracture toughness and resistance to cracking under rapid temperature changes. Glass ceramics, while aesthetically versatile and heat-resistant, generally exhibit lower mechanical strength and are more prone to surface damage during heavy use.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Shock
Polymer-derived ceramics exhibit superior heat resistance compared to glass ceramics, often withstanding temperatures beyond 1,200degC without deformation. Their ability to endure rapid temperature changes results in exceptional thermal shock resistance, reducing the risk of cracking during sudden heating or cooling cycles. Glass ceramics, while also heat-resistant, typically tolerate maximum temperatures around 800-1,000degC and display moderate thermal shock resistance, making polymer-derived ceramics a better choice for high-performance cooktops requiring durability under extreme heat conditions.
Chemical Stability and Stain Resistance
Polymer-derived ceramics exhibit superior chemical stability compared to glass ceramics, resisting high-temperature exposure and aggressive cleaning agents without degradation. Their enhanced stain resistance is due to a dense, non-porous microstructure that prevents absorption of oils and food residues. Glass ceramics, while thermally stable, are more prone to surface etching and staining from acidic or alkaline substances typically encountered in kitchen environments.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Polymer-derived ceramics offer superior aesthetic versatility for cooktops due to their ability to be molded into intricate shapes and customized colors, surpassing the limited design options of glass ceramics. Their matte and textured finishes provide a modern, tactile appeal that enhances kitchen decor with unique, seamless surfaces. Glass ceramics, while sleek and reflective, often restrict design creativity because of their rigid manufacturing process and standard color palettes.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polymer-derived ceramics offer lower raw material costs and simpler processing techniques compared to glass ceramics, making them more cost-effective for cooktop manufacturing. Their ability to cure at lower temperatures reduces energy consumption and shortens production cycles. Conversely, glass ceramics require high-temperature sintering and controlled crystallization, leading to higher manufacturing expenses and longer production times.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Cooktops
Polymer-derived ceramics offer superior thermal shock resistance and flexibility, making them ideal for cooktops exposed to rapid temperature changes. Glass ceramics provide excellent heat retention and a smooth, aesthetically pleasing surface but are more prone to cracking under sudden thermal stress. Selecting the right cooktop material depends on balancing durability, heat performance, and user preferences for resilience versus appearance.
Infographic: Polymer-derived ceramic vs Glass ceramic for Cooktop
 azmater.com
azmater.com