Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer high wear resistance and thermal stability, making them ideal for extreme lubricant applications, while boron nitride provides exceptional lubricity and chemical inertness, reducing friction in high-temperature environments. The choice between plasma-sprayed ceramics and boron nitride depends on the specific requirements for durability versus friction reduction in lubricant systems.
Table of Comparison
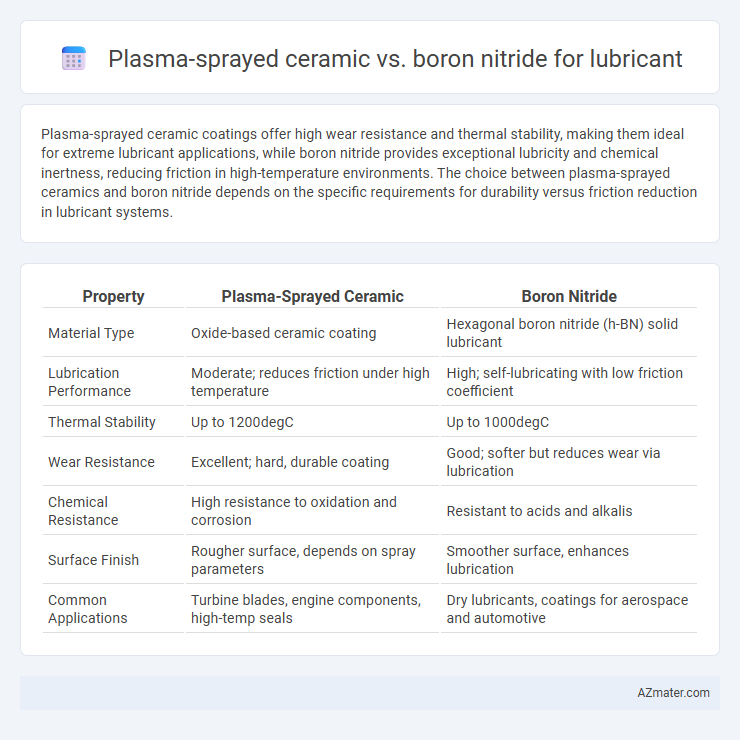
| Property | Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic | Boron Nitride |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Oxide-based ceramic coating | Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) solid lubricant |
| Lubrication Performance | Moderate; reduces friction under high temperature | High; self-lubricating with low friction coefficient |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1000degC |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent; hard, durable coating | Good; softer but reduces wear via lubrication |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to oxidation and corrosion | Resistant to acids and alkalis |
| Surface Finish | Rougher surface, depends on spray parameters | Smoother surface, enhances lubrication |
| Common Applications | Turbine blades, engine components, high-temp seals | Dry lubricants, coatings for aerospace and automotive |
Introduction to Lubricant Coatings: Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic vs Boron Nitride
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings provide high wear resistance and thermal stability, making them ideal for harsh lubricating environments requiring durable surface protection. Boron nitride, known for its excellent lubricity and chemical inertness, offers low friction and enhanced thermal conductivity, improving lubricant performance in precision applications. Comparing plasma-sprayed ceramic and boron nitride coatings reveals distinct advantages in durability versus friction reduction, crucial for selecting optimal lubricant coatings in diverse industrial settings.
Material Composition: Plasma-Sprayed Ceramics and Boron Nitride Explained
Plasma-sprayed ceramics primarily consist of aluminum oxide (Al2O3), zirconia (ZrO2), or their composites, providing exceptional hardness and high-temperature resistance ideal for lubricant coatings. Boron nitride, particularly hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), features a layered crystal structure similar to graphite, offering excellent lubricity, thermal stability, and chemical inertness. The material composition differences influence their tribological performance: plasma-sprayed ceramics deliver wear resistance and thermal barrier properties, while boron nitride enhances lubrication through low shear strength and self-lubricating characteristics.
Performance in High-Temperature Environments
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer exceptional wear resistance and thermal stability, maintaining structural integrity and lubrication properties at temperatures exceeding 1000degC. Boron nitride, particularly hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), provides excellent solid lubricity and thermal conductivity up to approximately 900degC but may degrade under extreme oxidative conditions. For high-temperature applications above 1000degC, plasma-sprayed ceramics outperform boron nitride in maintaining consistent lubrication and preventing surface degradation.
Wear and Friction Reduction Capabilities
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings exhibit superior wear resistance and significantly reduce friction by creating a hard, dense surface layer that withstands high mechanical stresses and thermal loads. Boron nitride, especially in its hexagonal form, offers excellent solid lubrication properties with low friction coefficients and self-lubricating behavior under various temperature ranges. While plasma-sprayed ceramics excel in durability and wear protection, boron nitride provides enhanced friction reduction and anti-seizure performance, making it ideal for applications requiring consistent lubrication and minimal friction.
Adhesion and Durability on Metal Substrates
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings exhibit superior adhesion to metal substrates due to their high-temperature deposition process creating strong metallurgical bonds, enhancing durability in abrasive environments. Boron nitride coatings, while offering excellent lubricity and chemical inertness, generally show lower adhesion strength on metals without additional surface treatments, potentially reducing lifespan under mechanical stress. Optimizing surface preparation and employing interlayers can improve the bonding of boron nitride but plasma-sprayed ceramics remain more robust for applications demanding long-term mechanical durability.
Chemical Stability and Corrosion Resistance
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings exhibit superior chemical stability due to their dense microstructure and resistance to oxidation, making them highly effective as lubricants in harsh chemical environments. Boron nitride, particularly hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), offers exceptional corrosion resistance and inherent lubricity, maintaining performance under high temperatures and reactive media. Both materials excel in protective lubrication, with plasma-sprayed ceramics favored for mechanical durability and boron nitride preferred for chemical inertness and self-lubricating properties.
Ease of Application and Processing Methods
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings involve high-temperature deposition requiring specialized equipment and controlled environments, making the application process complex and time-consuming compared to the simpler, low-temperature methods used for boron nitride coatings. Boron nitride can be applied via powder pressing, spray drying, or as a lubricant additive in various base fluids, offering greater versatility and ease of processing. The processing methods for boron nitride are less energy-intensive, enabling faster application and scalability for industrial lubrication systems.
Cost Efficiency and Industrial Scalability
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer high durability and thermal resistance, making them cost-efficient for heavy-duty industrial lubrication applications due to their longevity and reduced maintenance needs. Boron nitride, while providing exceptional lubricity and low friction coefficients, often incurs higher material costs and complex application processes that challenge large-scale industrial adoption. Industries seeking scalable solutions typically favor plasma-sprayed ceramics for their balance of performance, affordability, and ease of application in mass production environments.
Typical Applications and Industry Use Cases
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer superior wear resistance and high-temperature stability, making them ideal for automotive engine components, aerospace turbine blades, and industrial machinery exposed to harsh conditions. Boron nitride lubricants excel in providing low friction and excellent thermal conductivity, commonly used in electronics cooling, semiconductor manufacturing, and high-performance metal forming applications. Both materials enhance equipment longevity and performance, with ceramic coatings preferred for structural protection and boron nitride favored for dry lubrication in precision environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Lubricant Coating Solution
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring long-lasting protection. Boron nitride provides superior lubricity and thermal stability, which benefits high-temperature and low-friction environments. Selecting the right lubricant coating depends on balancing operational demands such as load capacity, temperature conditions, and desired friction levels to optimize equipment performance and durability.
Infographic: Plasma-sprayed ceramic vs Boron nitride for Lubricant
 azmater.com
azmater.com