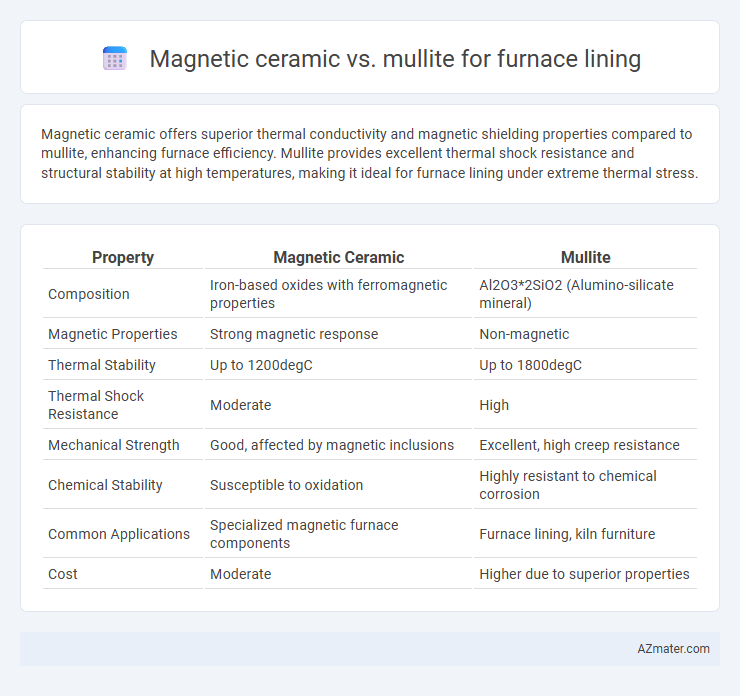
Magnetic ceramic offers superior thermal conductivity and magnetic shielding properties compared to mullite, enhancing furnace efficiency. Mullite provides excellent thermal shock resistance and structural stability at high temperatures, making it ideal for furnace lining under extreme thermal stress.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Magnetic Ceramic | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Iron-based oxides with ferromagnetic properties | Al2O3*2SiO2 (Alumino-silicate mineral) |
| Magnetic Properties | Strong magnetic response | Non-magnetic |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1800degC |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | Good, affected by magnetic inclusions | Excellent, high creep resistance |
| Chemical Stability | Susceptible to oxidation | Highly resistant to chemical corrosion |
| Common Applications | Specialized magnetic furnace components | Furnace lining, kiln furniture |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to superior properties |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Magnetic ceramics and mullite are essential furnace lining materials chosen for their thermal stability and resistance to high-temperature corrosion. Magnetic ceramics offer superior magnetic properties and thermal conductivity, making them suitable for specialized furnace components, while mullite is prized for its excellent thermal shock resistance and low thermal expansion, ensuring durability under fluctuating temperatures. Both materials play critical roles in enhancing furnace efficiency and lifespan by providing robust protection against thermal and mechanical stresses.
Overview of Magnetic Ceramic
Magnetic ceramic used in furnace linings offers superior thermal shock resistance and magnetic permeability compared to mullite, enhancing energy efficiency and operational stability in high-temperature environments. Its unique combination of ferrite materials and ceramic matrix provides improved mechanical strength and magnetic properties essential for induction heating applications. Magnetic ceramics demonstrate enhanced durability under cyclic thermal loads, making them a preferred choice in advanced furnace designs over traditional mullite linings.
Overview of Mullite
Mullite, a key refractory ceramic material, excels in furnace lining applications due to its exceptional thermal stability, low thermal expansion, and resistance to corrosion and creep at high temperatures. Its chemical composition, primarily 3Al2O3*2SiO2, ensures high melting points above 1840degC and superior mechanical strength under thermal stress. Compared to magnetic ceramics, mullite offers enhanced durability and energy efficiency in industrial furnace environments, making it a preferred choice for prolonged operational life and reduced maintenance costs.
Thermal Stability Comparison
Magnetic ceramic materials exhibit superior thermal stability in furnace linings due to their ability to withstand temperatures exceeding 1600degC without significant phase changes or structural degradation. Mullite, with a melting point around 1840degC, offers excellent thermal shock resistance and maintains structural integrity up to approximately 1400degC but is more prone to microcracking under rapid thermal cycling. The enhanced thermal stability of magnetic ceramics makes them ideal for high-temperature applications requiring prolonged exposure to extreme heat while maintaining consistent mechanical properties.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Magnetic ceramic exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to mullite, making it more resistant to cracking and mechanical stress under high-temperature furnace conditions. Mullite offers excellent thermal shock resistance and stability but has a lower fracture toughness, which can limit its durability under intense mechanical loads. For furnace lining applications requiring enhanced durability and mechanical reliability, magnetic ceramics provide a more robust solution over mullite.
Resistance to Chemical Attack
Magnetic ceramic exhibits superior resistance to chemical attack in furnace linings due to its stable iron oxide matrix, effectively withstanding acidic and basic slags often encountered in high-temperature environments. Mullite, primarily composed of alumina and silica, offers moderate chemical resistance but is more susceptible to degradation from alkali-rich slags compared to magnetic ceramics. The enhanced chemical durability of magnetic ceramic extends furnace lining life by minimizing corrosion and maintaining structural integrity under aggressive chemical exposure.
Energy Efficiency and Heat Retention
Magnetic ceramic exhibits higher thermal conductivity than mullite, enabling faster heat transfer and improved energy efficiency in furnace lining applications. Mullite offers superior heat retention due to its low thermal expansion and excellent thermal shock resistance, maintaining stable temperatures for extended periods. Choosing between magnetic ceramic and mullite depends on prioritizing either rapid heat distribution or prolonged heat preservation in furnace operations.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Magnetic ceramic offers faster installation due to its lightweight and modular design, reducing labor costs and downtime compared to the denser, more brittle mullite that requires careful handling and specialized skills. Maintenance for magnetic ceramic linings is simplified by their resistance to thermal shock and lower susceptibility to cracking, whereas mullite demands frequent inspections and repairs to address erosion and spalling under high-temperature cycles. The ease of installation and improved durability of magnetic ceramics result in longer service life and reduced maintenance intervals in furnace lining applications.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Magnetic ceramic offers superior thermal stability and lower thermal conductivity compared to mullite, resulting in reduced energy consumption and longer furnace lifespan, which improves overall cost-effectiveness. Mullite, while generally less expensive upfront, tends to require more frequent replacements due to lower thermal shock resistance, increasing maintenance costs over time. Evaluating total lifecycle costs, magnetic ceramic provides better long-term savings despite higher initial investment.
Best Applications and Recommendations
Magnetic ceramics excel in furnace linings requiring high thermal conductivity and resistance to thermal shock, making them ideal for induction furnaces and applications with rapid temperature changes. Mullite offers superior chemical stability and mechanical strength at elevated temperatures, making it the preferred choice for glass melting furnaces, kiln linings, and cement rotary kilns. For best performance, select magnetic ceramic linings in environments demanding fast heat dissipation, while opting for mullite when corrosion resistance and long service life under harsh conditions are critical.
Infographic: Magnetic ceramic vs Mullite for Furnace lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com