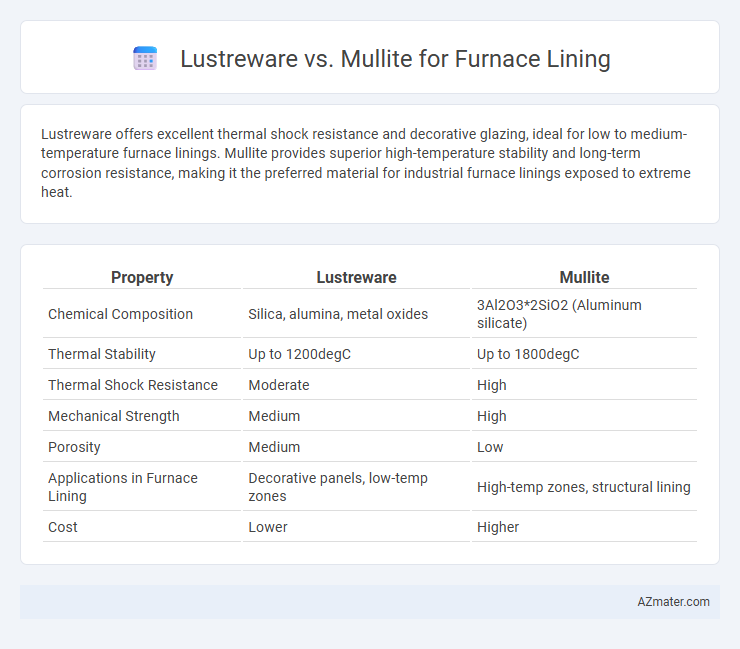
Lustreware offers excellent thermal shock resistance and decorative glazing, ideal for low to medium-temperature furnace linings. Mullite provides superior high-temperature stability and long-term corrosion resistance, making it the preferred material for industrial furnace linings exposed to extreme heat.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lustreware | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Silica, alumina, metal oxides | 3Al2O3*2SiO2 (Aluminum silicate) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1800degC |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | Medium | High |
| Porosity | Medium | Low |
| Applications in Furnace Lining | Decorative panels, low-temp zones | High-temp zones, structural lining |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Furnace lining materials such as lustreware and mullite play critical roles in high-temperature industrial applications, with mullite offering superior thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock due to its high alumina content. Lustreware, primarily ceramic with decorative glazing, provides moderate heat resistance but lacks the mechanical strength and chemical durability found in mullite linings. Choosing mullite ensures enhanced longevity and performance for furnace linings in demanding environments.
Overview of Lustreware in Industrial Applications
Lustreware, known for its reflective glaze and thermal stability, is increasingly used in furnace lining to enhance heat distribution and improve energy efficiency. Compared to mullite, lustreware offers superior surface resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion at high temperatures, making it ideal for intensive industrial environments. Its application in furnace lining helps extend service life while maintaining optimal thermal insulation properties under extreme operational conditions.
Mullite: Properties and Uses in Furnaces
Mullite is a high-temperature ceramic material widely used in furnace linings due to its exceptional thermal stability, low thermal expansion, and excellent resistance to thermal shock. Its chemical composition, primarily consisting of alumina and silica, provides superior strength and durability under extreme temperatures exceeding 1700degC, making it ideal for refractory applications. The material's resistance to slag and molten metal corrosion ensures longer service life in industrial furnaces, significantly outperforming Lustreware in functional refractory performance.
Thermal Resistance: Lustreware vs Mullite
Mullite offers superior thermal resistance with a melting point around 1840degC and excellent thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature furnace linings. Lustreware, typically a ceramic glaze with lower thermal stability, cannot withstand extreme temperatures and sudden temperature fluctuations as effectively as mullite. The high thermal conductivity and durability of mullite ensure longer furnace lifespan and enhanced performance in industrial applications.
Chemical Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Lustreware and Mullite exhibit distinct characteristics in furnace lining applications, particularly in chemical durability and corrosion resistance. Lustreware, a decorative ceramic glaze, lacks the high-temperature stability and resistance to aggressive chemical environments that Mullite provides. Mullite, an aluminosilicate ceramic, offers superior corrosion resistance and chemical durability due to its stable crystal structure and low reactivity with molten slags and alkalis in furnace atmospheres.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Lustreware exhibits higher mechanical strength compared to mullite in furnace lining applications, providing enhanced resistance to thermal shock and mechanical wear. Mullite, while offering excellent thermal stability and corrosion resistance, typically has lower flexural strength and fracture toughness than lustreware composites. Selecting lustreware can improve longevity and durability of furnace linings under heavy mechanical stress conditions.
Cost Efficiency and Lifespan
Lustreware offers a lower initial cost for furnace lining compared to Mullite, making it an economically attractive option for short-term projects or low-temperature applications. Mullite, however, provides superior thermal stability and a longer lifespan, significantly reducing maintenance and replacement expenses in high-temperature and continuous-use environments. The cost efficiency of each material ultimately depends on the furnace's operating conditions and the balance between upfront investment and long-term durability.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Lustreware furnace linings demand meticulous installation due to their delicate glaze finish, requiring skilled labor and precise temperature control to prevent cracking during setup. Maintenance involves regular inspections to preserve the decorative surface and timely repairs to address minor chips without compromising thermal integrity. In contrast, mullite linings offer easier installation with prefabricated bricks that fit securely, providing robust thermal shock resistance and reduced maintenance needs, primarily consisting of routine cleaning and replacement of worn sections to ensure prolonged durability.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Lustreware furnace linings, containing metallic oxides and lead-based compounds, pose greater environmental hazards due to potential toxic emissions and heavy metal contamination during disposal or high-temperature use. Mullite, a stable aluminosilicate ceramic, offers superior chemical inertness and thermal stability, minimizing harmful emissions and reducing environmental and occupational health risks. Its non-toxic composition and resistance to thermal shock make mullite a safer, more sustainable choice for furnace lining applications.
Choosing the Right Material: Lustreware or Mullite?
Choosing between Lustreware and Mullite for furnace lining depends on temperature resistance and thermal stability requirements. Lustreware offers excellent aesthetic appeal and moderate heat resistance, making it suitable for decorative or lower-temperature applications. Mullite provides superior thermal shock resistance, higher melting points (around 1840degC), and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial furnace linings.
Infographic: Lustreware vs Mullite for Furnace Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com