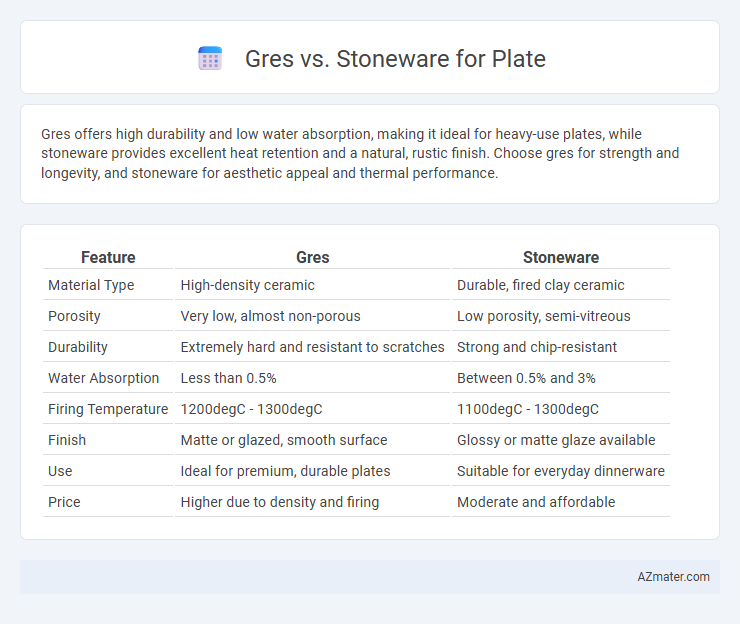
Gres offers high durability and low water absorption, making it ideal for heavy-use plates, while stoneware provides excellent heat retention and a natural, rustic finish. Choose gres for strength and longevity, and stoneware for aesthetic appeal and thermal performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gres | Stoneware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-density ceramic | Durable, fired clay ceramic |
| Porosity | Very low, almost non-porous | Low porosity, semi-vitreous |
| Durability | Extremely hard and resistant to scratches | Strong and chip-resistant |
| Water Absorption | Less than 0.5% | Between 0.5% and 3% |
| Firing Temperature | 1200degC - 1300degC | 1100degC - 1300degC |
| Finish | Matte or glazed, smooth surface | Glossy or matte glaze available |
| Use | Ideal for premium, durable plates | Suitable for everyday dinnerware |
| Price | Higher due to density and firing | Moderate and affordable |
Introduction to Gres and Stoneware Plates
Gres and stoneware plates are popular types of ceramic tableware known for their durability and aesthetic appeal. Gres, a French term for stoneware, is made from dense clay fired at high temperatures, resulting in a non-porous, chip-resistant surface ideal for everyday use. Stoneware plates, similarly fired at high heat, offer excellent strength and a natural rustic look, making them suitable for both casual dining and formal settings.
Material Composition: Gres vs Stoneware
Gres plates are made from refined stoneware clay with a higher kaolin content, resulting in a dense, hard, and non-porous material ideal for durability and resistance to chipping. Stoneware plates are composed of natural clay fired at high temperatures, creating a sturdy and vitrified body that is slightly more porous than gres but still highly durable and dishwasher safe. The key difference in material composition lies in gres's finer clay and higher density, providing a smoother, more glass-like surface compared to the more rustic texture of traditional stoneware.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Gres plates are made by firing refined clay at extremely high temperatures, typically above 1200degC, resulting in a dense, non-porous body with high durability and water resistance. Stoneware plates undergo a similar firing process but often use a combination of clay and natural minerals, fired between 1100degC and 1300degC, producing a slightly more porous and textured finish. The manufacturing process of gres emphasizes fine particle composition and vitrification for enhanced strength, while stoneware balances aesthetic appeal with robustness through varied mineral content and firing techniques.
Durability and Strength Differences
Gres plates exhibit higher durability due to their dense, vitrified composition, making them resistant to chipping and thermal shock compared to stoneware. Stoneware plates possess a slightly more porous structure but remain strong, offering good impact resistance while typically being heavier than gres. The vitrification process in gres enhances its hardness and strength, providing a longer-lasting surface ideal for frequent use in both commercial and home settings.
Aesthetic and Design Options
Gres plates offer a sleek, minimalist aesthetic with smooth finishes and earthy tones, making them ideal for modern and rustic table settings. Stoneware plates provide a broader range of design options, including textured surfaces, vibrant glazes, and hand-painted patterns, enhancing their artistic appeal. Both materials ensure durability, but stoneware's versatility in color and decoration makes it a preferred choice for visually expressive dinnerware.
Weight and Handling Considerations
Gres plates, known for their dense composition, tend to be heavier than stoneware, affecting ease of handling during daily use and storage. Stoneware offers a balance of durability and lighter weight, making it more convenient for frequent use and less strenuous to carry or stack. Weight differences influence user experience, with stoneware preferred for casual settings and gres favored for heavier-duty, long-lasting tableware.
Performance in Everyday Use
Gres plates offer exceptional durability and resistance to chipping, making them ideal for everyday use in high-traffic kitchens. Stoneware plates provide excellent heat retention and even cooking, enhancing meal presentation and temperature maintenance. Both materials deliver strong performance, but gres outperforms stoneware in toughness and longevity under frequent handling.
Safety: Food, Microwave, and Dishwasher Compatibility
Gres plates, made from dense stoneware clay, offer excellent food safety due to their non-porous surface, which resists bacteria absorption and stains. Both gres and stoneware plates typically withstand microwave use safely, but gres's higher vitrification temperature provides better thermal shock resistance. Dishwasher compatibility is strong for both materials, though gres's durability ensures longer-lasting finishes without chipping or cracking from repetitive washing cycles.
Price and Value Analysis
Stoneware plates generally offer higher durability and a more refined finish compared to gres plates, which tend to be more affordable but less resistant to chipping. Gres plates, made from vitrified clay, provide a cost-effective option with good strength but often lack the premium look and feel of stoneware. When evaluating price and value, stoneware presents a better long-term investment due to enhanced aesthetics and longevity, while gres suits budget-conscious buyers seeking practicality.
Choosing the Best Plate Material for Your Needs
Gres plates offer exceptional durability and resistance to chipping, ideal for everyday use and high-traffic settings, while stoneware provides a rustic aesthetic with excellent heat retention, perfect for both casual dining and formal presentations. Choose gres for its hardness and low porosity, ensuring long-lasting stain resistance and easy maintenance, whereas stoneware suits those seeking artisanal texture and versatility in serving hot dishes. Evaluating factors such as durability, heat retention, and design preferences will help determine the best plate material tailored to your lifestyle and dining requirements.
Infographic: Gres vs Stoneware for Plate
 azmater.com
azmater.com