Sagger provides high-temperature resistance and protects tiles during firing, while faience, a glazed ceramic material, offers decorative appeal and waterproof qualities for tile surfaces. Tiles made with saggers ensure durability in kiln environments, whereas faience tiles excel in aesthetic design and surface finish.
Table of Comparison
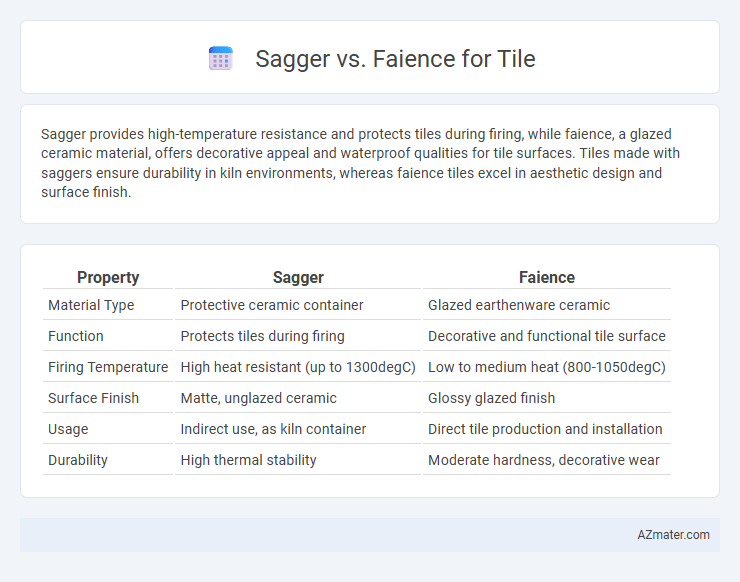
| Property | Sagger | Faience |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Protective ceramic container | Glazed earthenware ceramic |
| Function | Protects tiles during firing | Decorative and functional tile surface |
| Firing Temperature | High heat resistant (up to 1300degC) | Low to medium heat (800-1050degC) |
| Surface Finish | Matte, unglazed ceramic | Glossy glazed finish |
| Usage | Indirect use, as kiln container | Direct tile production and installation |
| Durability | High thermal stability | Moderate hardness, decorative wear |
Introduction to Sagger and Faience Tiles
Sagger tiles are specially designed ceramic containers used in kiln firing to protect delicate faience tiles from direct flame and ash, ensuring their intricate glazes remain intact. Faience tiles, renowned for their vibrant, glossy surfaces and intricate patterns, are crafted from tin-glazed earthenware, originating from the Mediterranean region. The interaction between saggers and faience tiles during the firing process highlights the importance of controlled environments in preserving the color and texture quality of historic and decorative ceramics.
Historical Development of Sagger and Faience Techniques
Sagger, originating in ancient China around the Han Dynasty, served as a protective clay casing used during kiln firing to shield ceramics from direct flame and ash, enabling higher quality finishes. Faience, developed in ancient Egypt and the Mediterranean, involves sintered-quartz glazed pottery characterized by its bright turquoise blue-green glaze achieved through a self-glazing technique. The historical development of sagger and faience reflects distinct technological advancements in ceramic firing and glazing, with saggers focusing on kiln protection and faience emphasizing decorative surface vitrification.
Material Composition: Sagger vs Faience
Sagger is typically made from refractory clay designed to withstand high kiln temperatures and protect pottery during firing, ensuring durability and heat resistance. Faience, on the other hand, consists mainly of silica-based materials combined with alkaline substances and metal oxides, which create a glazed, brightly colored surface after firing. The fundamental difference lies in Sagger's protective composition for ceramic firing, whereas Faience emphasizes aesthetic qualities through its glazed, glass-like finish.
Tile Production Processes Compared
Sagger and faience represent distinct approaches in tile production, where saggers serve as protective containers during kiln firing to shield tiles from direct flame or kiln debris, enhancing surface quality and reducing defects. Faience refers to glazed ceramic tiles characterized by a tin-based glaze that creates a glossy, opaque finish, achieved through controlled firing processes and applying specific glaze compositions. The saggar technique primarily benefits the firing stage by maintaining tile integrity, while faience emphasizes the decorative and functional finish through complex glazing and temperature management.
Durability and Longevity: Sagger Tiles vs Faience Tiles
Sagger tiles exhibit superior durability due to their dense, high-fired clay composition, which enhances resistance to cracking and wear compared to faience tiles. Faience tiles, though prized for their decorative glazed surfaces, are more susceptible to chipping and surface damage over time, reducing their longevity in high-traffic areas. For applications demanding long-lasting performance and structural integrity, sagger tiles are a more reliable choice due to their robust firing process and minimal porosity.
Aesthetic Differences and Surface Finishes
Sagger firing creates tiles with a rustic, matte finish characterized by natural ash deposits and unique color variations, enhancing earthy and antique aesthetics. Faience tiles feature a glossy, glass-like surface achieved through tin-glazing, offering vibrant colors and intricate patterns suitable for decorative or classical designs. The choice between sagger and faience significantly influences the tile's tactile texture and visual impact, with sagger providing a raw, organic look and faience delivering a smooth, lustrous appeal.
Common Applications in Modern Architecture
Sagger and faience are both used in modern architecture for their unique properties and aesthetic appeal. Sagger, a refractory ceramic container, protects tiles from direct flame during firing, ensuring durability and strength, making it ideal for industrial and exterior applications requiring high thermal resistance. Faience, a glazed non-clay ceramic, is favored in decorative tiling for interiors, offering vibrant colors and intricate designs often seen in bathroom walls, kitchens, and artistic facades.
Cost Analysis: Sagger vs Faience for Projects
Sagger firing involves using clay containers that protect tiles during kiln firing, typically increasing upfront material costs due to the need for specialized containers, but reducing breakage rates and long-term expenses. Faience tiles, often glazed and handcrafted, generally incur higher production costs due to labor intensity and material quality, impacting overall project budgets more significantly than mass-produced sagger-fired tiles. Cost analysis should balance sagger's initial container investment and durability benefits against faience's premium aesthetics and craftsmanship, optimizing project scalability and financial efficiency.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Sagger tiles utilize natural clay and organic materials, fired at lower temperatures which reduces energy consumption and environmental impact compared to traditional faience tiles that often require higher firing temperatures and glazes containing heavy metals. The production of sagger tiles tends to generate less waste and emits fewer pollutants, contributing to a more sustainable manufacturing process. Faience tiles may offer aesthetic appeal but often involve more intensive resource use and chemical treatments that increase their overall carbon footprint.
Choosing the Right Tile: Sagger or Faience?
Sagger tiles, crafted using a protective ceramic container during firing, offer enhanced durability and resistance to warping, making them ideal for high-temperature applications. Faience tiles, known for their glazed, decorative surface and vibrant colors, provide aesthetic appeal suitable for interior walls and artistic installations. Choosing between sagger and faience depends on the specific application requirements--opt for sagger tiles when durability and heat resistance are paramount, and select faience tiles to achieve decorative elegance and intricate designs.
Infographic: Sagger vs Faience for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com