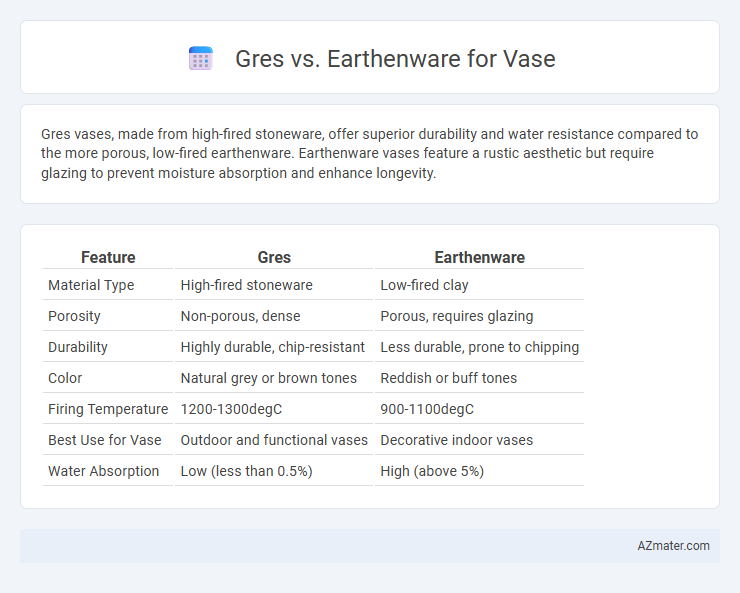
Gres vases, made from high-fired stoneware, offer superior durability and water resistance compared to the more porous, low-fired earthenware. Earthenware vases feature a rustic aesthetic but require glazing to prevent moisture absorption and enhance longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gres | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-fired stoneware | Low-fired clay |
| Porosity | Non-porous, dense | Porous, requires glazing |
| Durability | Highly durable, chip-resistant | Less durable, prone to chipping |
| Color | Natural grey or brown tones | Reddish or buff tones |
| Firing Temperature | 1200-1300degC | 900-1100degC |
| Best Use for Vase | Outdoor and functional vases | Decorative indoor vases |
| Water Absorption | Low (less than 0.5%) | High (above 5%) |
Introduction to Gres and Earthenware
Gres, known for its high density and low porosity, is a type of stoneware clay fired at high temperatures around 1200-1300degC, making it exceptionally durable and suitable for functional vases. Earthenware, fired at lower temperatures of approximately 1000-1150degC, is softer and more porous, often requiring glazing to enhance water resistance and strength. While gres offers superior toughness and resistance to chipping, earthenware allows for more vibrant glazes and intricate surface designs due to its lower firing temperature.
Material Composition and Characteristics
Gres vases are crafted from high-fired stoneware clay, resulting in a dense, durable, and non-porous material ideal for both indoor and outdoor use. Earthenware vases, made from low-fired clay, are more porous and fragile, often requiring a glaze to enhance water resistance and strength. The higher firing temperature of gres provides superior hardness and chip resistance, whereas earthenware offers a more porous and rustic aesthetic.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Gres vases exhibit superior durability and strength compared to earthenware due to their dense, vitrified composition, which makes them more resistant to chipping and cracking under impact. Earthenware, being more porous and fired at lower temperatures, tends to be more fragile and susceptible to damage from moisture absorption. Therefore, gres is ideal for long-lasting, heavy-use vases, while earthenware suits decorative purposes with lighter handling.
Aesthetic Appeal and Surface Finishes
Gres vases boast a refined, smooth surface with a subtle matte finish that highlights natural clay tones, offering a modern and minimalist aesthetic perfect for contemporary decor. Earthenware vases feature a more rustic and textured surface with varied glazing options, providing rich visual depth and vibrant colors that suit traditional or bohemian styles. Both materials allow unique surface treatments, but gres excels in sleek, uniform finishes while earthenware emphasizes artisanal charm and tactile variation.
Water Absorption and Vase Functionality
Gres vases exhibit low water absorption rates, typically below 0.5%, making them highly durable and ideal for holding water without leakage. Earthenware vases have higher porosity with water absorption ranging between 6% to 10%, requiring glazing to prevent seepage and maintain functionality. The water resistance of gres enhances vase longevity and suitability for live plants, whereas earthenware suits dry arrangements or requires additional sealing for water retention.
Suitability for Indoor and Outdoor Use
Gres vases offer superior durability and resistance to weather conditions, making them highly suitable for both indoor and outdoor use, especially in gardens or patios where exposure to moisture and temperature fluctuations is common. Earthenware vases, being more porous and less frost-resistant, are best suited for indoor environments where they remain protected from harsh weather, minimizing the risk of cracking or deterioration. For long-lasting outdoor display, gres ceramic stands out due to its dense composition and enhanced resistance to environmental stressors.
Cost and Price Considerations
Gres vases typically have a higher cost due to their durable, dense composition and resistance to chipping, making them a long-lasting investment. Earthenware vases are generally more affordable, crafted from porous clay that requires glazing, which can affect overall durability and maintenance expenses. When selecting between gres and earthenware, budget constraints and intended use should guide the decision, as gres commands premium pricing while earthenware offers cost-effective decorative options.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Gres vases exhibit high durability and resistance to stains, making them easier to maintain with simple wiping and occasional gentle cleaning, while earthenware vases are more porous and prone to absorbing moisture and stains, requiring careful handling and frequent cleaning with mild soap to prevent damage. Gres's non-porous surface reduces the risk of mold and bacterial buildup, whereas earthenware demands a thorough drying process after cleaning to avoid deterioration. Choosing gres vases reduces long-term maintenance efforts compared to the more delicate and porous composition of earthenware.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gres vases, made from high-fired stoneware, offer superior durability and lower porosity compared to earthenware, resulting in longer-lasting products that reduce waste. Earthenware requires lower firing temperatures, consuming less energy during production, which can contribute to a smaller carbon footprint despite its increased fragility. Choosing gres supports sustainability with its resistance to chipping and water absorption, minimizing the need for frequent replacements and lowering environmental impact over time.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Vase
Gres vases offer superior durability and chip resistance compared to earthenware, making them ideal for long-lasting decorative pieces. Earthenware, being more porous and less dense, is best suited for indoor use where fragility is less of a concern and aesthetic appeal is prioritized. Selecting between gres and earthenware depends on whether you value strength and longevity or traditional craftsmanship and affordability for your vase.
Infographic: Gres vs Earthenware for Vase
 azmater.com
azmater.com