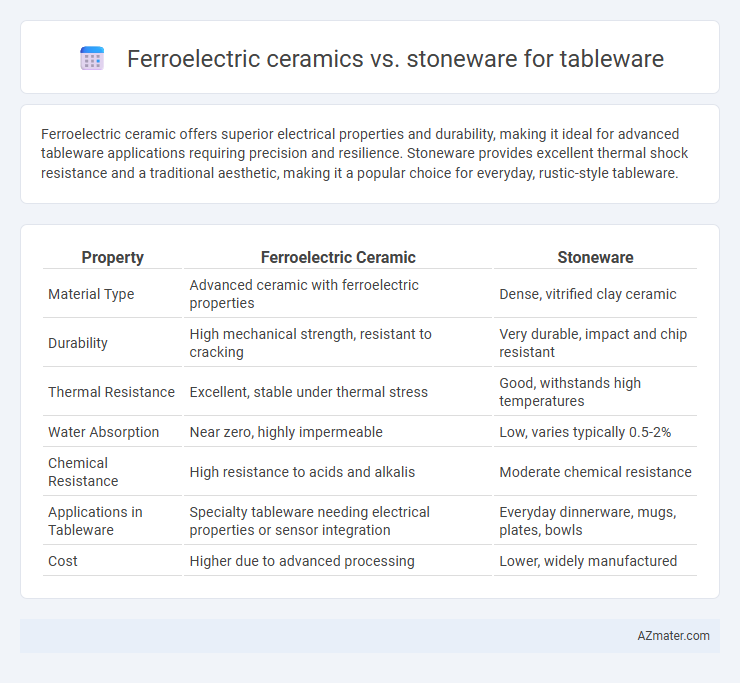
Ferroelectric ceramic offers superior electrical properties and durability, making it ideal for advanced tableware applications requiring precision and resilience. Stoneware provides excellent thermal shock resistance and a traditional aesthetic, making it a popular choice for everyday, rustic-style tableware.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ferroelectric Ceramic | Stoneware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Advanced ceramic with ferroelectric properties | Dense, vitrified clay ceramic |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, resistant to cracking | Very durable, impact and chip resistant |
| Thermal Resistance | Excellent, stable under thermal stress | Good, withstands high temperatures |
| Water Absorption | Near zero, highly impermeable | Low, varies typically 0.5-2% |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to acids and alkalis | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Applications in Tableware | Specialty tableware needing electrical properties or sensor integration | Everyday dinnerware, mugs, plates, bowls |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced processing | Lower, widely manufactured |
Introduction to Tableware Materials
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit unique dielectric properties, making them suitable for advanced tableware applications requiring thermal stability and electrical responsiveness. Stoneware, composed of dense, vitrified clay, offers durability and a non-porous surface ideal for everyday use and aesthetic appeal. The choice between ferroelectric ceramic and stoneware depends on desired functionality, heat resistance, and design preferences in tableware materials.
What is Ferroelectric Ceramic?
Ferroelectric ceramic is a type of advanced material characterized by spontaneous electric polarization that can be reversed by an external electric field, making it useful in sensors, actuators, and non-volatile memory devices. Unlike stoneware, which is a durable, non-porous fired clay ideal for everyday tableware due to its strength and heat resistance, ferroelectric ceramic offers functional properties such as piezoelectricity and high dielectric constant. The distinct electrical characteristics of ferroelectric ceramics differentiate them from traditional stoneware, which is primarily valued for its mechanical toughness and aesthetic appeal in cookware and dinnerware.
What is Stoneware?
Stoneware is a type of dense, durable ceramic fired at high temperatures between 1,100degC and 1,300degC, resulting in a non-porous, vitrified surface ideal for tableware. Unlike ferroelectric ceramics, which exhibit unique electrical properties used mainly in electronics, stoneware prioritizes strength, chip resistance, and a rustic aesthetic for everyday use. Its ability to retain heat and resist thermal shock makes stoneware a popular choice for functional and decorative kitchen items.
Material Properties: Ferroelectric Ceramic vs Stoneware
Ferroelectric ceramic exhibits high dielectric constants and strong piezoelectric properties, enabling responsiveness to electric fields and mechanical stress, which stoneware lacks. Stoneware features high durability, thermal shock resistance, and porosity suitable for everyday tableware but does not possess the electric or piezoelectric characteristics of ferroelectric ceramics. The dense, non-porous structure of ferroelectric ceramics contrasts with the porous, crystalline composition of stoneware, affecting their mechanical strength and suitability for different uses.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit superior durability due to their unique crystalline structure, offering high resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress, which extends the lifespan of tableware significantly. Stoneware, while highly durable and chip-resistant, tends to be more porous and susceptible to glaze crazing over time, potentially compromising longevity under frequent use. The enhanced durability and longevity of ferroelectric ceramic tableware make it ideal for heavy-duty and long-term applications compared to traditional stoneware.
Safety and Food Compatibility
Ferroelectric ceramics offer high chemical stability and low ion exchange, ensuring exceptional food compatibility and safety in tableware applications. Stoneware's dense, vitrified structure provides strong resistance to chipping and leaching, making it a durable, non-toxic option for everyday use. Both materials are FDA-compliant and dishwasher-safe, but ferroelectric ceramics excel in thermal shock resistance, reducing risks of crack-induced contamination.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Ferroelectric ceramic tableware offers a sleek, modern aesthetic with smooth finishes and vibrant color retention, perfect for contemporary dining settings. Stoneware provides a rustic, earthy charm with natural textures and matte glazes, appealing to those who prefer artisanal and handcrafted designs. Both materials support diverse design options, but ferroelectric ceramics excel in precision patterns and bold colors, while stoneware emphasizes organic shapes and subtle hues.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Performance
Ferroelectric ceramic exhibits exceptional heat resistance withstanding temperatures up to 1300degC, making it ideal for demanding thermal applications and rapid temperature changes without cracking. Stoneware offers robust thermal performance, typically handling up to 1200degC, but it is more prone to thermal shock compared to ferroelectric ceramics. The superior dielectric properties of ferroelectric ceramics also contribute to enhanced thermal stability and longevity in high-heat tableware environments.
Cost and Accessibility
Ferroelectric ceramic tableware typically incurs higher manufacturing costs due to advanced materials and specialized processing, limiting its accessibility primarily to luxury markets. Stoneware offers a more budget-friendly alternative, widely accessible owing to mass production and abundant raw materials. Consumers seeking cost-effective, durable tableware commonly prefer stoneware for everyday use over the technologically enhanced but pricey ferroelectric ceramic.
Choosing the Right Material for Tableware
Ferroelectric ceramics offer high dielectric properties and durability, making them suitable for advanced electronic applications rather than everyday tableware. Stoneware, composed of dense, non-porous clay fired at high temperatures, provides excellent durability, heat retention, and resistance to chipping, making it ideal for everyday use. Choosing stoneware for tableware ensures long-lasting performance, microwave and dishwasher safety, and aesthetic versatility compared to the specialized nature of ferroelectric ceramics.
Infographic: Ferroelectric ceramic vs Stoneware for Tableware
 azmater.com
azmater.com