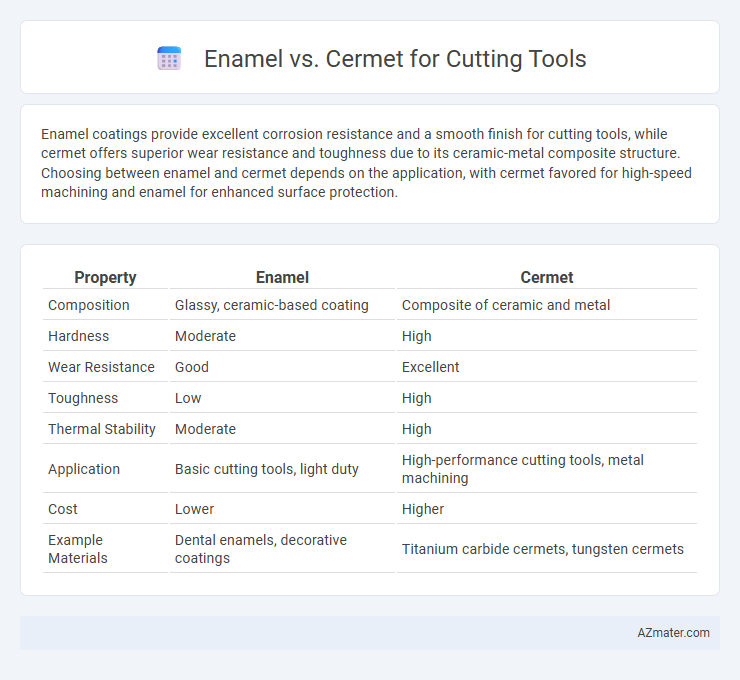
Enamel coatings provide excellent corrosion resistance and a smooth finish for cutting tools, while cermet offers superior wear resistance and toughness due to its ceramic-metal composite structure. Choosing between enamel and cermet depends on the application, with cermet favored for high-speed machining and enamel for enhanced surface protection.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Enamel | Cermet |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Glassy, ceramic-based coating | Composite of ceramic and metal |
| Hardness | Moderate | High |
| Wear Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Toughness | Low | High |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate | High |
| Application | Basic cutting tools, light duty | High-performance cutting tools, metal machining |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Example Materials | Dental enamels, decorative coatings | Titanium carbide cermets, tungsten cermets |
Introduction to Cutting Tool Materials
Cutting tool materials such as enamel and cermet are essential in machining for their durability and wear resistance. Enamel coatings provide a hard, protective layer that reduces friction and enhances tool life, while cermets combine ceramic and metallic materials to achieve high toughness and heat resistance. Selection between enamel and cermet depends on the specific application requirements, including cutting speed, material hardness, and thermal stability.
Overview of Enamel Cutting Tools
Enamel cutting tools feature a hard, glassy coating that offers excellent corrosion resistance and smooth surface finishes, making them ideal for precision machining of non-ferrous metals and plastics. Their durability is enhanced by the enamel layer, which reduces wear and improves tool life in moderate cutting conditions. These tools provide a cost-effective solution for applications requiring sharpness and resistance to chemical exposure, although they may not withstand the high temperatures and stresses encountered with tougher materials compared to cermet tools.
Overview of Cermet Cutting Tools
Cermet cutting tools combine ceramic and metallic materials, offering high wear resistance and improved toughness compared to traditional enamel-coated tools. These tools excel in high-speed machining applications, providing superior surface finish and heat resistance due to their unique microstructure. Cermet inserts are widely used in aerospace and automotive industries for precision cutting of hardened steels and superalloys.
Key Composition Differences: Enamel vs Cermet
Enamel cutting tools primarily consist of a glassy phase composed of silica and other oxides, providing a hard, wear-resistant surface ideal for precision machining. Cermet tools are composed of ceramic particles, often titanium carbide or titanium nitride, bonded with metallic materials such as nickel or cobalt, offering a balance of hardness and toughness. The key composition difference lies in enamel's vitreous, glass-based structure compared to cermet's composite ceramic-metal matrix, which influences their cutting performance and durability.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Enamel-coated cutting tools exhibit high hardness and excellent wear resistance but tend to be more brittle compared to cermet tools, which combine ceramic hardness with metallic toughness for superior fracture resistance and toughness. Cermets offer better thermal stability and higher cutting speeds due to their enhanced toughness and resistance to thermal shock, making them ideal for high-performance applications. The mechanical properties of cermets, such as improved fracture toughness and wear resistance, often surpass those of enamel coatings, resulting in longer tool life and more consistent cutting performance.
Wear Resistance and Tool Life
Cermet cutting tools exhibit superior wear resistance compared to enamel-coated tools due to their composite structure of ceramic and metallic materials, which enhances hardness and thermal stability. This increased wear resistance directly contributes to longer tool life, enabling consistent performance in high-speed machining and abrasive conditions. Enamel coatings, while providing corrosion protection, typically offer lower durability against mechanical wear, resulting in shorter tool lifespan under demanding cutting operations.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Conductivity
Enamel-coated cutting tools exhibit moderate heat resistance but lower thermal conductivity, causing heat to concentrate at the cutting edge and potentially reduce tool life. Cermet cutting tools, composed of ceramic and metallic materials, offer superior heat resistance and enhanced thermal conductivity, efficiently dissipating heat during high-speed machining. This thermal advantage reduces wear and deformation, making cermets ideal for applications requiring prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures.
Applications in Industry
Enamel-coated cutting tools excel in applications requiring corrosion resistance and smooth surface finishes, making them ideal for woodworking and light metal cutting industries. Cermet cutting tools, composed of ceramic and metallic materials, offer superior wear resistance and toughness, suited for high-speed machining of hardened steels and superalloys in automotive and aerospace manufacturing. Both materials enhance tool life and precision but are selected based on the specific cutting conditions and industrial requirements.
Cost and Availability Factors
Enamel-coated cutting tools often have lower initial costs due to simpler manufacturing processes and widespread availability in various sizes and shapes. Cermet tools, combining ceramic and metal materials, typically incur higher expenses but offer enhanced wear resistance and longer tool life, reducing overall operational costs. Availability of cermet tools can be limited compared to enamel options, impacting lead times and inventory management in manufacturing environments.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Cutting Tool
Choosing the right material for your cutting tool depends on the application requirements, with enamel coatings offering excellent corrosion resistance and smooth surface finish for light-duty cutting, while cermet provides superior hardness, wear resistance, and heat tolerance ideal for high-speed machining and heavy-duty operations. Cermet's combination of ceramic and metallic materials enhances tool life and precision in cutting hard metals, making it a preferred choice for industrial manufacturing. Opting for enamel suits less abrasive environments, whereas cermet withstands intense wear, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Infographic: Enamel vs Cermet for Cutting Tool
 azmater.com
azmater.com