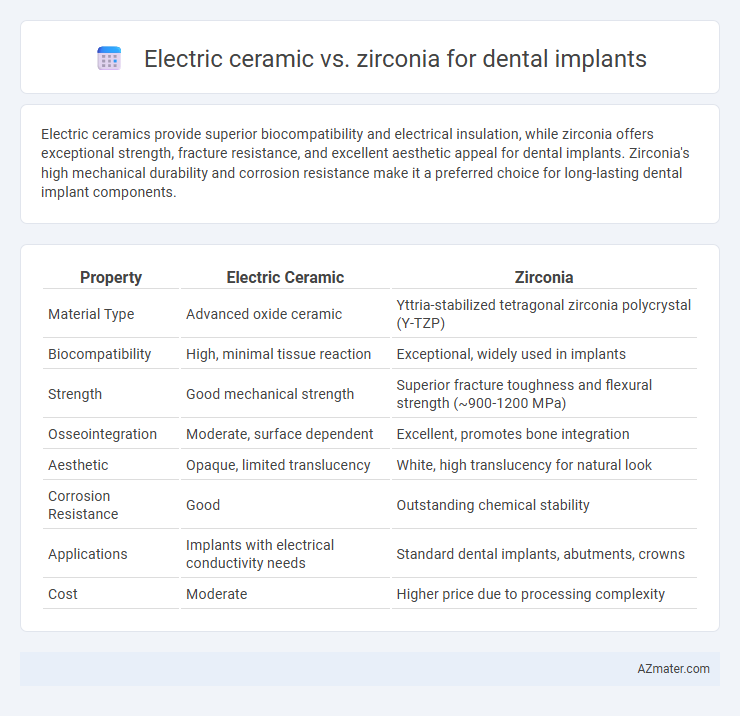
Electric ceramics provide superior biocompatibility and electrical insulation, while zirconia offers exceptional strength, fracture resistance, and excellent aesthetic appeal for dental implants. Zirconia's high mechanical durability and corrosion resistance make it a preferred choice for long-lasting dental implant components.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Electric Ceramic | Zirconia |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Advanced oxide ceramic | Yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (Y-TZP) |
| Biocompatibility | High, minimal tissue reaction | Exceptional, widely used in implants |
| Strength | Good mechanical strength | Superior fracture toughness and flexural strength (~900-1200 MPa) |
| Osseointegration | Moderate, surface dependent | Excellent, promotes bone integration |
| Aesthetic | Opaque, limited translucency | White, high translucency for natural look |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Outstanding chemical stability |
| Applications | Implants with electrical conductivity needs | Standard dental implants, abutments, crowns |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher price due to processing complexity |
Introduction to Dental Implant Materials
Dental implant materials primarily include zirconia and electric ceramic, each offering unique advantages in biocompatibility and durability. Zirconia is favored for its high fracture toughness, excellent osseointegration, and metal-free aesthetic appeal, making it a popular choice in dental restorations. Electric ceramics, although less common, provide enhanced electrical properties that can contribute to improved bone integration and antimicrobial effects in implantology.
Overview of Electric Ceramic in Dentistry
Electric ceramic in dentistry refers to advanced bioactive materials used for dental implants that exhibit excellent electrical conductivity and biocompatibility, promoting osseointegration and tissue regeneration. Compared to zirconia, electric ceramics demonstrate enhanced antibacterial properties and improved mechanical resilience under oral conditions, making them a promising alternative for durable and long-lasting dental restorations. These materials also support faster healing times and superior integration with bone, contributing to overall implant success rates.
Zirconia: Properties and Applications
Zirconia dental implants exhibit exceptional biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and high fracture toughness, making them ideal for long-term oral applications. Their bioinert surface reduces bacterial adhesion, promoting better osseointegration compared to traditional electric ceramic materials. Commonly used for single-tooth restorations and full-arch prosthetics, zirconia implants provide superior aesthetics due to their tooth-like color and translucency.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Zirconia dental implants exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to electric ceramic alternatives, with fracture toughness typically around 6-10 MPa*m^0.5, enhancing durability under masticatory forces. Electric ceramics generally present lower flexural strength, often below 500 MPa, making them less resistant to chipping or cracking in high-load areas. The higher modulus of elasticity and fracture resistance of zirconia implants contribute to improved long-term performance and reliability in dental restoration.
Biocompatibility and Tissue Response
Electric ceramic dental implants exhibit excellent biocompatibility, promoting minimal inflammatory response and supporting soft tissue integration. Zirconia implants are also highly biocompatible, with proven osteoconductive properties that enhance bone-to-implant contact and encourage stable osseointegration. Both materials demonstrate favorable tissue responses, but zirconia's superior resistance to bacterial colonization often results in improved peri-implant mucosal healing.
Aesthetics: Color and Translucency
Electric ceramic dental implants offer superior translucency and a more natural tooth color compared to zirconia, enhancing aesthetic outcomes especially in the anterior region. Zirconia, while durable and biocompatible, tends to have a more opaque appearance and may show a slightly grayish tint under certain lighting conditions. The enhanced light transmission of electric ceramic materials closely mimics natural enamel, making them a preferred choice for patients prioritizing high cosmetic standards.
Longevity and Wear Resistance
Electric ceramic dental implants offer excellent wear resistance due to their enhanced surface hardness and reduced friction coefficients, contributing to prolonged implant longevity. Zirconia implants exhibit superior biocompatibility and resistance to corrosion, which helps maintain structural integrity and durability over time. Both materials demonstrate high longevity, but zirconia's proven track record in clinical studies often positions it as the preferred choice for long-term wear resistance in dental implants.
Clinical Outcomes and Success Rates
Electric ceramic dental implants demonstrate promising biocompatibility and osseointegration, with success rates comparable to zirconia implants in early clinical studies. Zirconia implants, renowned for high fracture toughness and favorable esthetics, exhibit long-term stability with success rates often exceeding 90% in 5-year follow-ups. Clinical outcomes reveal that both materials support healthy peri-implant tissue integration, though zirconia remains the gold standard for load-bearing applications due to its mechanical strength.
Cost and Accessibility Considerations
Electric ceramic dental implants generally offer lower upfront costs compared to zirconia implants, making them more accessible for patients with budget constraints. Zirconia implants, known for their biocompatibility and durability, tend to be priced higher due to advanced materials and fabrication processes. Accessibility to electric ceramic implants is broader as more dental clinics stock these materials, while zirconia implants may require specialized providers and longer wait times.
Choosing the Right Material for Dental Implants
Zirconia offers superior biocompatibility and aesthetic appeal for dental implants due to its natural tooth-like color and high fracture toughness. Electric ceramics, while improving electrical conductivity, lack the mechanical strength and osseointegration properties critical for long-term implant success. Selecting zirconia ensures optimal integration with bone tissue and durability, making it the preferred choice for dental implant material.
Infographic: Electric ceramic vs Zirconia for Dental implant
 azmater.com
azmater.com